You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
When did birdwatching become cool — and why didn’t it happen in time to save me from the middle school nickname “bird boy?”
Truth is, I was fine with the light teasing I received for my teenage fixation on avifauna. It didn’t stop me from decorating the back corner of our biology classroom with clippings about Pale Male (Manhattan’s celebrity red-tail), or from earning a New York state falconry license at the age of 12, or even from watching Canada geese migrate over my high school campus while my peers ogled each other from the bleachers. Still, none of it exactly built my social capital.
That’s why lately, I’ve been delighted to see the cool kids picking up binoculars. The bird boys (and girls) won.
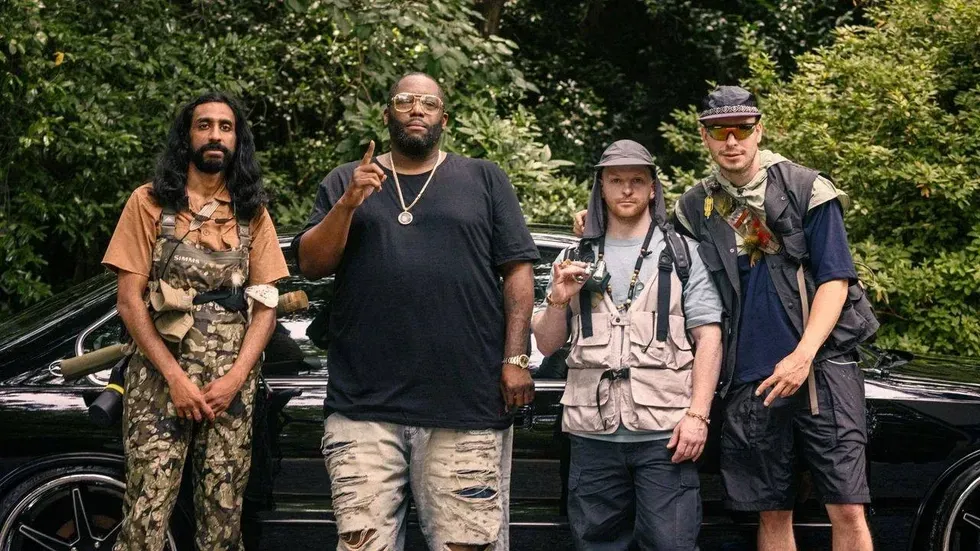

The past few years have seen increased interest in the formerly unsexy act of watching birds go about their business. Birdwatching clubs founded by young creatives are hatching in major metropolitan areas, and downtown fashion brands and high street houses alike are linking up with them for collaboration and clout. Direct-to-consumer brands are disrupting the binoculars industry. Chart-topping rappers are out spotting robins and taking field notes. It’s the beginning of a beautiful new model for tuning in to the natural world (even if it’s still pretty based in consumption).
The coolness of birding was even foreordained. All the way back in 2014, Esquire prophesied that birdwatching was about to have a moment. They were right, if a decade or so early. To take flight, birding needed to tap into a few other trends first.
The birding trend really began — like so many trends — in the throes of the coronavirus pandemic.
The lockdowns of 2020 prompted something of a renaissance for the animal kingdom, as stifling restrictions on human mobility and commerce allowed nature to briefly exhale. Wild boar roamed the streets of Haifa. Roadkill became more scarce. Without sonar, engine, or construction noise, whale song traveled our oceans unmolested.
Birds thrived, too. For example, city birds, who typically sing louder, less interesting songs than their rural relatives to compete with sound pollution, began performing softer, more intricate melodies.
Newly ordained armchair ornithologists claimed front-row seats to these small operas playing out on their fire escapes and feeders. Binocular sales went up 22% year over year. A major annual bird-spotting event that May saw unprecedented participation from the public.
Lockdowns had made birding useful. Events in the spring would make birding subversive.
The most consequential birdwatching story of the year was the fraught confrontation between a white dog walker and a Black birder in the Ramble section of Central Park on May 25, 2020. Later that day, George Floyd was killed by Minneapolis police. The two events exploded simultaneously, one representing how law enforcement makes public space unsafe for minorities, the other how ordinary white people do the same in the outdoors.
A collective called BlackAFinSTEM quickly mobilized #BlackBirdersWeek, and the next month, 17 people gathered at London’s Walthamstow Wetlands for the first outing of Flock Together, “a birdwatching collective for people of colour.” The names of certain species came under scrutiny for racist associations. Though their work is far from done, the creative efforts of activist-naturalists started dispelling the myth that nature is owned by any one community — and gave birdwatching a revolutionary appeal.
The world is also becoming more aware of what we’re doing to bird populations. In 2022, 188 countries signed a sweeping agreement pledging, among other things, to conserve nearly a third of our planet’s land and ocean by 2030. As the crowning achievement of the United Nations Biodiversity Conference in Montreal, the accord is the clearest admission yet of the extinction crisis caused by climate change and ecological destruction. Right now, some million species of plant and animal are at high risk of disappearance, a rate unseen since the extinction of the dinosaurs 65 million years ago.
Birds, the closest living relatives of those prehistoric giants, are sensitive organisms, and in North America alone, populations have dropped by more than one quarter — or three billion birds — in the last 50 years. Globally, roughly 48% of surviving bird species are experiencing population decline. If scarcity drives demand, perhaps these tragic figures are also helping lift the world’s eyes to the winged wonder in our midst.
So how do we know watching birds is finally cool?
There’s evidence in the airwaves, with Flock Together dropping EPs and mixes, using sound “as a means of bringing nature to the people,” as Fader writes. Or we can look to Doja Cat, who joined Rolling Stone staff writer Charles Holmes for an outing in Central Park on the web series Birding with Charles, struggling to reach the binocular eye cups with her formidable lashes. (The HBO series Chillin Island has a similar premise, taking musical icons like Killer Mike, Young Thug, and Rosalía into the wild.)
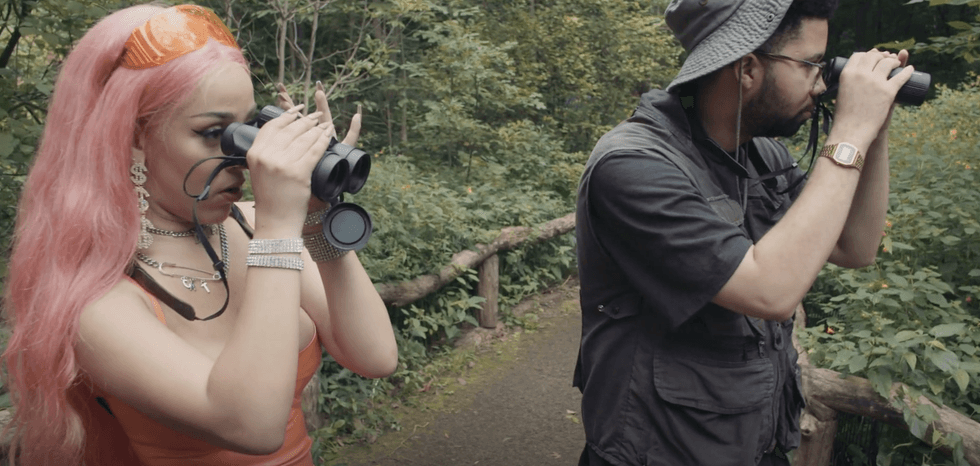

Fashion has also been touched by the avian invasion. Street style website Hypebeast posted “All the Gear You’ll Need for Birdwatching in the City,” and members of Flock Together presenting outerwear by the brand Berghaus. On Highsnobiety, the Flock Together founders modeled Gucci’s collaboration with The North Face, while Feminist Bird Club released a capsule collection featuring leopard print binocular straps with the sustainable prep-skate brand Noah.
Never missing a chance to cash in, the DTC world has brought us Nocs Provisions and its range of affordable optics, while at the more refined end of the spectrum, raptors are increasingly hot accessories in photo and video shoots. Witness Ethan Hawke holding an African hawk-eagle (furnished by my friends at Falconry Excursions) in The Rake last year. Fashion’s ongoing love affair with the outdoors plays a part too, as birders make good models for utilitarian gear. After all, we need cool clothes, too — to brave the brambles.

In my own circle, I’ve been glad to see friends turn on to birding, some even starting to cultivate native plants in their gardens to make their properties more hospitable, as recommended by experts (even if our warming planet is scrambling what native gardening means).
As for me, I’m interested in the ways this phenomenon might permeate less glamorous parts of modern life. Perhaps somewhere soon, a middle-school bird boy will finally find the courage to ask their crush on a date to see the barn swallows make their spring migration, together.
Sign up for Heatmap Daily to receive our best articles directly in your inbox:
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Representatives Jake Auchincloss and Mark Amodei want to boost “superhot” exploration.
Geothermal is about the only energy topic that Republicans and Democrats can agree on.
“Democrats like clean energy. Republicans like drilling. And everyone likes baseload power that is generated with less than 1% of the land and materials of other renewables,” Massachusetts Representative Jake Auchincloss, a Democrat, told me.
Along with Republican Representative Mark Amodei of Nevada, Auchincloss is introducing the Hot Rock Act on Friday, focusing specifically on “superhot” or “supercritical” geothermal resources, i.e. heat deposits 300 degrees Celsius or above. (Temperatures in large traditional geothermal resources are closer to 240 degrees.)
The bill — of which Heatmap got an exclusive early peek — takes a broad approach to supporting research in the sector, which is currently being explored by startups such as Quaise Energy and Mazama Energy, which in October announced a well at 331 degrees.
There’s superhot rock energy potential in around 13% of North America, modeling by the Clean Air Task Force has found — though that’s mostly around 8 miles below ground. The largest traditional geothermal facility in the U.S. is only about 2.5 miles at its deepest.
But the potential is enormous. “Just 1% of North America’s superhot rock resource has the potential to provide 7.5 terawatts of energy capacity,” CATF said. That’s compared to a little over a terawatt of current capacity.
Auchincloss and Amodei’s bill would direct the Department of Energy to establish “milestone-based research grant programs,” under which organizations that hit goals such as drilling to a specific depth, pressure, or temperature would then earn rewards. It would also instruct the DOE to create a facility “to test, experiment with, and demonstrate hot dry rock geothermal projects,” plus start a workforce training program for the geothermal industry.
Finally, it would grant a categorical exclusion from the National Environmental Policy Act for drilling to explore or confirm geothermal resources, which could turn a process that takes over a year into one that takes just a couple of months.
Geothermal policy is typically a bipartisan activity pursued by senators and House members from the Intermountain West. Auchincloss, however, is a New Englander. He told me that he was introduced to geothermal when he hosted an event in 2022 attended by executives from Quaise, which was born out of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
It turned out the company’s pilot project was in Nevada, and “I saw it was in Mark Amodei’s district. And I saw that Mark is on Natural Resources, which is the other committee of jurisdiction. And so I went up to him on the floor, and I was like, Hey there, you know, there's this company announcing this pilot,” Auchincloss told me.
In a statement, Amodei said that “Nevada has the potential to unlock this resource and lead the nation in reliable, clean energy. From powering rural communities and strengthening critical mineral production to meeting the growing demands of data centers, geothermal energy delivers dependable 24/7 power.”
Auchincloss told me that the bill “started from the simple premise of, How do we promote this technology?” They consulted climate and technology experts before reaching consensus on the milestone-based payments, workforce development, and regulatory relief components.
“I didn't have an ideological bent about the right way to do it,” Auchincloss said.
The bill has won plaudits from a range of industry groups, including the Clean Energy Buyers Association and Quaise itself, as well as environmental and policy organizations focused on technological development, like the Institute for Progress, Third Way, and the Breakthrough Institute.
“Our grassroots volunteers nationwide are eager to see more clean energy options in the United States, and many of them are excited by the promise of reliable, around-the-clock clean power from next-generation geothermal energy,” Jennifer Tyler, VP government affairs at the Citizens' Climate Lobby, said in a statement the lawmakers provided to Heatmap. “The Hot Rock Act takes a positive step toward realizing that promise by making critical investments in research, demonstration, and workforce development that can unlock superhot geothermal resources safely and responsibly.”
With even the Trump administration generally pro-geothermal, Auchincloss told me he’s optimistic about the bill’s prospects. “I expect this could command broad bipartisan support,” he said.
Plus a pre-seed round for a moon tech company from Latvia.
The nuclear headlines just keep stacking up. This week, Inertial Enterprises landed one of the largest Series A rounds I’ve ever seen, making it an instant contender in the race to commercialize fusion energy. Meanwhile, there was a smaller raise for a company aiming to squeeze more juice out of the reactors we already have.
Elsewhere over in Latvia, investors are backing an early stage bid to bring power infrastructure to the moon, while in France, yet another ultra-long-duration battery energy storage company has successfully piloted their tech.
Inertia Enterprises, yet another fusion energy startup, raised an eye-popping $450 million Series A round this week, led by Bessemer Venture Partners with participation from Alphabet’s venture arm GV, among others. Founded in 2024 and officially launched last summer, the company aims to develop a commercial fusion reactor based on the only experiment yet to achieve scientific breakeven, the point at which a fusion reaction generates more energy than it took to initiate it.
This milestone was first reached in 2022 at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s National Ignition Facility, using an approach known as inertial confinement fusion. In this method, powerful lasers fire at a small pellet of fusion fuel, compressing it until the extremely high temperature and pressure cause the atoms inside to fuse and release energy. Annie Kritcher, who leads LLNL’s inertial confinement fusion program, is one of the cofounders of Inertia, alongside Twilio co-founder Jeff Lawson and Stanford professor Mike Dunne, who formerly led a program at the lab to design a power plant based on its approach to fusion.
The Inertia team plans to commercialize LLNL’s breakthrough by developing a new fusion laser system it’s calling Thunderwall, which it says will be 50 times more powerful than any laser of its type to date. Inertia isn’t the only player trying to commercialize laser-driven fusion energy — Xcimer Energy, for example, raised a $100 million Series A in 2024 — but with its recent financing, it’s now by far the best capitalized of the bunch.
As Lawson, the CEO of the new endeavor said in the company’s press release, “Our plan is clear: build on proven science to develop the technology and supply chain required to deliver the world’s highest average power laser, the first fusion target assembly plant, and the first gigawatt, utility-scale fusion power plant to the grid.” Great, but how soon can they do it? The goal, he says, is to “make this real within the next decade.”
In more nuclear news, the startup Alva Energy launched from stealth on Thursday with $33 million in funding and a proposal to squeeze more capacity out of the existing nuclear fleet by retrofitting pressurized-water reactors. The round was led by the venture firm Playground Global.
The startup plans to boost capacity by building new steam turbines and electricity generators adjacent to existing facilities, such that plants can stay online during the upgrade. Then when a plant shuts down for scheduled maintenance, Alva will upgrade its steam generator within the nuclear containment dome. That will allow the system to make 20% to 30% more steam, to be handled by the newly built turbine-generator system.
The company estimates that these retrofits will boost each reactor’s output by 200 megawatts to 300 megawatts. Applied across the dozens of existing facilities that could be similarly upgraded, Alva says this strategy could yield roughly 10 new gigawatts of additional nuclear capacity through the 2030s — the equivalent of building about 10 new large reactors.
Biden’s Department of Energy identified this strategy, known as “uprating”, as capable of adding 2 gigawatts to 8 gigawatts of new capacity to the grid. Alva thinks it can go further. The company promises to manage the entire uprate process from ensuring regulatory compliance to the procurement and installation of new reactor components. The company says its upgrades could be deployed as quickly as gas turbines are today — a five- to six-year timeline — at a comparable cost of around $1 billion per gigawatt.
Deep Space Energy, a Latvian space tech startup, has closed a pre-seed funding round to advance its goal of becoming a commercial supplier of electricity for space missions on the moon, Mars, or even deeper into space where sunlight is scarce. The company is developing power systems that convert heat from the natural decay of radioisotopes — unstable atoms that emit radiation as they decay — into electricity.
While it’s still very early-stage, this tech’s first application will likely be backup power for defense satellites. Long term, Deep Space Energy says it “aims to focus on the moon economy” by powering rovers and other lunar installations, supporting Europe’s goal of increasing its space sovereignty by reducing its reliance on U.S. defense assets such as satellites. While radioisotope generators are already used in some space missions, the company says its system requires five times less fuel than existing designs.
Roughly $400,000 of the funding came from equity investments from the Baltic-focused VC Outlast Fund and a Lithuanian angel investor. The company also secured nearly $700,000 from public contracts and grants from the European Space Agency, the Latvian Government, and a NATO program to accelerate innovation with dual-use potential for both defense and commercial applications.
As I wrote a few weeks ago, Form Energy’s iron-air battery isn’t the only player targeting 100-plus hours of low-cost energy storage. In that piece, I highlighted Noon Energy, a startup that recently demoed its solid-oxide fuel cell system. But there’s another company aiming to compete even more directly with Form by bringing its own iron-air battery to the European market: Ore Energy. And it just completed a grid-connected pilot, something Form has yet to do.
Ore piloted its 100-hour battery at an R&D center in France run by EDF, the state-owned electric utility company. While the company didn’t disclose the battery’s size, it said the pilot demonstrated its ability to discharge energy continuously for about four days while integrating with real-world grid operations. The test was supported by the European Union’s Storage Research Infrastructure Eco-System, which aims to accelerate the development of innovative storage solutions, and builds on the startup’s earlier grid-connected installation at a climate tech testbed in the Netherlands last summer.
Founded in 2023, Ore plans to scale quickly. As Bas Kil, the company’s business development lead, told Latitude Media after its first pilot went live, “We’re not planning to do years and years of pilot-scale [projects]; we believe that our system is now ready for commercial deployment.” According to Latitude, Ore aims to reach 50 gigawatt-hours of storage per year by 2030, an ambitious goal considering its initial grid-connected battery had less than one megawatt-hour of capacity. So far, the company has raised just shy of $30 million to date, compared to Form’s $1.2 billion.
Battery storage manufacturer and virtual power plant operator Sonnen, together with the clean energy financing company Solrite, have launched a Texas-based VPP composed exclusively of home batteries. They’re offering customers a Solrite-owned 60-kilowatt-hour battery for a $20 monthly fee, in exchange for a fixed retail electricity rate of 12 cents per kilowatt-hour — a few cents lower than the market’s average — and the backup power capability inherent to the system. Over 3,000 customers have already enrolled, and the companies are expecting up to 10,000 customers to join by year’s end.
The program is targeting Texans with residential solar who previously sold their excess electricity back to the grid. But now that there’s so much cheap, utility-scale solar available in Texas, electricity retailers simply aren’t as incentivized to offer homeowners favorable rates. This has left many residents with “stranded” solar assets, turning them into what the companies call “solar orphans” in need of a new way to make money on their solar investment. Customers without rooftop solar can participate in the program as well, though they don’t get a catchy moniker.
Current conditions: New Orleans is expecting light rain with temperatures climbing near 90 degrees Fahrenheit as the city marks the 20th anniversary of Hurricane Katrina • Torrential rains could dump anywhere from 8 to 12 inches on the Mississippi Valley and the Ozarks • Japan is sweltering in temperatures as high as 104 degrees.
President Donald Trump has done what he didn’t dare attempt during his first term, repealing the finding that provided the legal basis for virtually all federal regulations to curb greenhouse gas emissions. By rescinding the 2009 “endangerment finding,” which established that planet-heating emissions harm human health and therefore qualify for restrictions under the Clean Air Act, the Trump administration hopes to unwind all rules on pollution from tailpipes, trucks, power plants, pipelines, and drilling sites all in one fell swoop. “This is about as big as it gets,” Trump said alongside Environmental Protection Agency Administrator Lee Zeldin at a White House event Thursday.
The repeal, which is sure to face legal challenges, opens up what Reuters called a new front in the legal wars over climate change. Until now, the Supreme Court had declined to hear so-called public nuisance cases brought by activists against fossil fuel companies on the grounds that the legal question of emissions was being sorted out through federal regulations. By eliminating those rules outright, litigants could once again have new standing to sue over greenhouse gas emissions. To catch up on the endangerment finding in general, Heatmap’s Robinson Meyer and Emily Pontecorvo put together a handy explainer here.
A bill winding its way through Ohio’s Republican-controlled state legislature would put new restrictions on development of wind and solar projects. The state already makes solar and wind developers jump over what Canary Media called extra hurdles that “don’t apply to fossil-fueled or nuclear power plants, including counties’ ability to ban projects.” For example, siting authorities defer to local opposition on renewable energy but “grant opponents little say over where drilling rigs and fracking waste can go.”
The new legislation would make it state policy “in all cases” for new power plants to “employ affordable, reliable, and clean energy sources.” What qualifies as “affordable, reliable, and clean”? Pretty much everything except wind and solar, potentially creating a total embargo on the energy sources at any utility scale. The legislation mirrors a generic bill promoted to states by the American Legislative Exchange Council, a right-wing policy shop.
Get Heatmap AM directly in your inbox every morning:
China’s carbon dioxide emissions fell by 1% in the last three months of 2025, amounting to a 0.3% drop for the full year. That’s according to a new analysis by Carbon Brief. The decline extends the “flat or falling” trend in China’s emissions that started in March 2024 and has now lasted nearly two years. Emissions from fossil fuels actually increased by 0.1%, but pollution from cement plunged 7%. While the grid remains heavily reliant on coal, solar output soared by 43% last year compared to 2024. Wind grew by 14% and nuclear by 8%. All of that allowed coal generation to fall by 1.9%.
At least one sector saw a spike in emissions: Chemicals, which saw emissions grow 12%. Most experts interviewed in Heatmap’s Insiders Survey said they viewed China has a climate “hero” for its emissions cuts. But an overhaul to the country’s electricity markets yielded a decline in solar growth last year that’s expected to stretch into this year.
Sign up to receive Heatmap AM in your inbox every morning:
Rivian Automotive’s shares surged nearly 15% in after-hours trading Thursday when the electric automaker announced earnings that beat Wall Street’s expectations. While it cautioned that it would continue losing money ahead of the launch of its next-generation R2 mid-size SUV, the company said it would deliver 62,000 to 67,000 vehicles in 2026, up 47% to 59% compared with 2025. Rivian CEO RJ Scaringe told CNBC that the R2 would make up the “majority of the volume” of the business by the end of next year. He told investors 2025 was a “foundational year” for the company, but that 2026 would be “an inflection point.”
Another clean energy company is now hot on the stock market. SOLV Energy, a solar and battery storage construction contractor, secured market capitalization eclipsing $6 billion in the two days since it started trading on the Nasdaq. The company, according to Latitude Media, is “the first pure-play solar and storage” company in the engineering, procurement, and construction sector of the industry to go public since 2008.
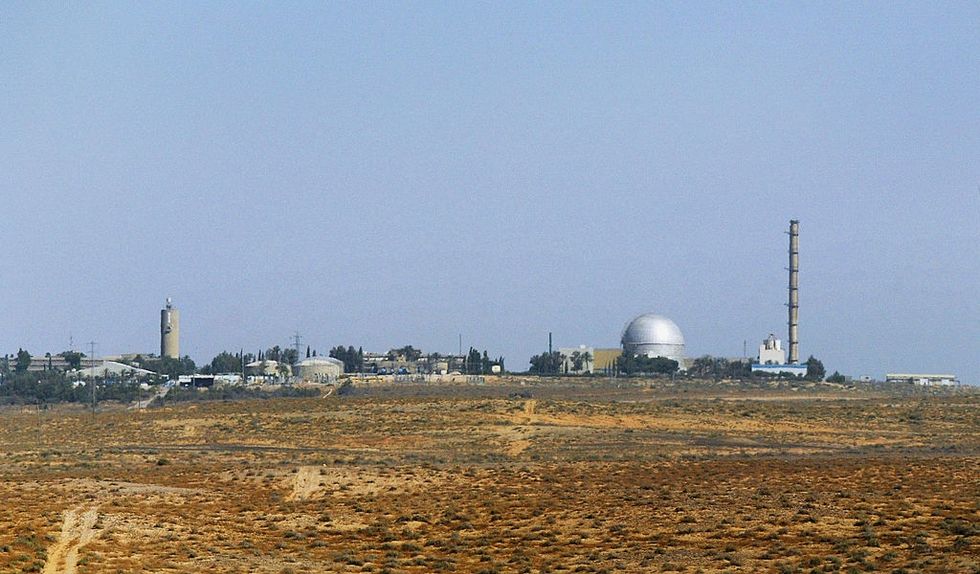

Israel has never confirmed that it has nuclear weapons, but it’s widely believed to have completed its first operating warhead in the 1960s. Rather than give up its strategic ambiguity over its arsenal, Israel instead forfeited the development of civilian nuclear energy, which would have required opening up its weapons program to the scrutiny of regulators at the United Nations’ International Atomic Energy Agency. That apparently won’t stop the U.S. from building a reactor in Israel to power a joint industrial complex. Washington plans to develop a campus with an advanced microchip factory and data centers that would be powered by a small modular reactor, NucNet reported. So-called SMRs have yet to be built at a commercial scale anywhere in the world. But the U.S. government is betting that smaller, less powerful reactors purchased in packs can bring down the cost of building nuclear plants and appeal to fearful skeptics as a novel spin on the older technology.
In reality, SMRs are based on a range of designs, some of which closely mirror traditional, large-scale reactors but for the power output, and a growing chorus of critics say the economies of scale are needed to make nuclear projects pencil out. But the true value of SMRs is for off-grid power. As I wrote last week for Heatmap, if the U.S. government wants it for some national security concern, the price doesn’t matter as much.
Of all the fusion companies racing to build the first power plant, Helion’s promise of commercial electricity before the end of the decade has raised eyebrows for its ambition. But the company has hit a milestone. On Friday morning, Helion’s Polaris prototype became the first privately developed fusion reactor to use a deuterium-tritium fuel source. The machine also set a record with plasma temperatures 150 million degrees Celsius, smashing its own previous record of 100 million degrees with an earlier iteration of Helion’s reactor.