You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
A list of terminated grants obtained by Heatmap contains a number of grants that will cost jobs and revenue in Republican-led states.

The Trump administration terminated billions in climate and clean energy grants on Wednesday, in what appears to be yet another act of retribution against Democrats over the government shutdown. White House budget director Russell Vought announced on X that “nearly $8 billion in Green New Scam funding to fuel the Left's climate agenda is being cancelled,” noting that the projects were in 16 states, all but two of which — Vermont and New Hampshire — have Democrats in their governor’s mansion. A Department of Energy release published late last night further clarified that it was terminating 321 awards supporting 223 projects, with a total closer to $7.5 billion.
But a list of the 321 canceled grants that the Department of Energy sent to Congress, obtained by Heatmap, tells a different story. While much of the funding was awarded to blue state-based companies, the intended projects would have benefitted communities elsewhere, including in Texas, Florida, and Louisiana.
The list identifies the grants by their award numbers, and includes information on the DOE office overseeing the grant, the recipient name, and state. The document does not specify the project names, the programs under which they were awarded, or the amounts awarded.
That leaves a lot of open questions about the true impact of the terminations. It’s unclear, for instance, whether the $7.5 billion price tag the Department of Energy assigned to the cancellations is an estimate of the total amount awarded or the unspent remainder still in the agency’s coffers. Five of the listed projects, worth nearly $900 million, were already announced as terminated in an earlier round of cuts back in May.
Many of the projects listed have signed contracts with the government, are already well underway, and have spent at least some of their award. For example, the Northeast Energy Efficiency Partnerships has already published copious educational materials related to its community-driven transportation plan for the Northeast, a project supported by one of the terminated grants.
The list does seem to confirm that blue state grants were the hardest hit, with 79 award cancellations in California, 41 in New York, 34 in Colorado (Secretary of Energy Chris Wright’s home state), 33 in Illinois, and 31 in Massachusetts.
But when I began looking up projects by their award number, I found that many would actually have benefitted Republican strongholds. Take, for example, Moment Energy, a Delaware-based company that was awarded $20 million by the Office of Manufacturing and Energy Supply Chains to build the first certified manufacturing facility in the United States producing battery energy storage systems from repurposed electric vehicle batteries. The plant was set to be built in Taylor, Texas, creating 50 construction jobs and 200 new permanent positions. After receiving the Energy Department’s stamp of approval, the company raised a $15 million Series A funding round in January to help finance the plant.
Also listed are a $10 million grant for Carbon Capture Inc, a California-based company, to conduct an engineering study for a direct air capture plant in Northwest Louisiana, and a $37 million grant to New York-based Urban Mining Industries to build one of its low-carbon concrete manufacturing plants in Florida. Linde, the global industrial gas company based in Connecticut, had $10 million to build hydrogen fueling stations for heavy duty trucks in La Porte, Texas, clawed back. BKV, a Colorado-based natural gas company set to study the transportation of captured CO2 by barge throughout the Gulf Coast region, also had its $2.5 million grant canceled.
In addition to hurting investments and jobs in Republican states, the Department of Energy’s cancellations also target some unlikely victims. The list names 16 grants for General Electric, including 11 for GE Vernova, the company’s manufacturing arm, which produces natural gas turbines and components for wind energy generation; many of those awards were for wind technology research projects. The agency also canceled 24 grants for the Institute for Gas Technology and the Electric Power Research Institute, the research arms of gas and electric companies’ two biggest trade groups, respectively. Several of these awards funded research projects into carbon capture and storage.
Also on the list was a more than $6.5 million grant for a controversial study to retrofit the Four Corners coal plant in New Mexico with carbon capture equipment. The plant is currently scheduled to close in 2031.
Back in May, Wright promised Congress his agency’s review of Biden-era climate funding would be over by the end of the summer. “Certainly in the next few months, by the end of this summer — hopefully before the end of this summer — we will have run through all of the four or 500 large projects that are currently in the pipeline at the DOE,” he said during a House Appropriations Committee hearing.
As reported yesterday by Bloomberg, two regional Hydrogen Hubs in California and the Pacific Northwest — projects awarded funding from the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law to develop full hydrogen production and consumption ecosystems — are on the list. That leaves the agency’s intentions for the remaining five hubs scattered throughout the Midwest, Midatlantic, Appalachia, the Great Plains, and Texas unclear. And while the list includes a few smaller grants for early-stage Direct Air Capture Hubs, it is still a mystery whether the Department of Energy plans to support the two more advanced direct air capture projects in Louisiana and Texas that were selected for $1.2 billion under the Biden administration.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
1. Marion County, Indiana — State legislators made a U-turn this week in Indiana.
2. Baldwin County, Alabama — Alabamians are fighting a solar project they say was dropped into their laps without adequate warning.
3. Orleans Parish, Louisiana — The Crescent City has closed its doors to data centers, at least until next year.
A conversation with Emily Pritzkow of Wisconsin Building Trades
This week’s conversation is with Emily Pritzkow, executive director for the Wisconsin Building Trades, which represents over 40,000 workers at 15 unions, including the International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers, the International Union of Operating Engineers, and the Wisconsin Pipe Trades Association. I wanted to speak with her about the kinds of jobs needed to build and maintain data centers and whether they have a big impact on how communities view a project. Our conversation was edited for length and clarity.
So first of all, how do data centers actually drive employment for your members?
From an infrastructure perspective, these are massive hyperscale projects. They require extensive electrical infrastructure and really sophisticated cooling systems, work that will sustain our building trades workforce for years – and beyond, because as you probably see, these facilities often expand. Within the building trades, we see the most work on these projects. Our electricians and almost every other skilled trade you can think of, they’re on site not only building facilities but maintaining them after the fact.
We also view it through the lens of requiring our skilled trades to be there for ongoing maintenance, system upgrades, and emergency repairs.
What’s the access level for these jobs?
If you have a union signatory employer and you work for them, you will need to complete an apprenticeship to get the skills you need, or it can be through the union directly. It’s folks from all ranges of life, whether they’re just graduating from high school or, well, I was recently talking to an office manager who had a 50-year-old apprentice.
These apprenticeship programs are done at our training centers. They’re funded through contributions from our journey workers and from our signatory contractors. We have programs without taxpayer dollars and use our existing workforce to bring on the next generation.
Where’s the interest in these jobs at the moment? I’m trying to understand the extent to which potential employment benefits are welcomed by communities with data center development.
This is a hot topic right now. And it’s a complicated topic and an issue that’s evolving – technology is evolving. But what we do find is engagement from the trades is a huge benefit to these projects when they come to a community because we are the community. We have operated in Wisconsin for 130 years. Our partnership with our building trades unions is often viewed by local stakeholders as the first step of building trust, frankly; they know that when we’re on a project, it’s their neighbors getting good jobs and their kids being able to perhaps train in their own backyard. And local officials know our track record. We’re accountable to stakeholders.
We are a valuable player when we are engaged and involved in these sting decisions.
When do you get engaged and to what extent?
Everyone operates differently but we often get engaged pretty early on because, obviously, our workforce is necessary to build the project. They need the manpower, they need to talk to us early on about what pipeline we have for the work. We need to talk about build-out expectations and timelines and apprenticeship recruitment, so we’re involved early on. We’ve had notable partnerships, like Microsoft in southeast Wisconsin. They’re now the single largest taxpayer in Racine County. That project is now looking to expand.
When we are involved early on, it really shows what can happen. And there are incredible stories coming out of that job site every day about what that work has meant for our union members.
To what extent are some of these communities taking in the labor piece when it comes to data centers?
I think that’s a challenging question to answer because it varies on the individual person, on what their priority is as a member of a community. What they know, what they prioritize.
Across the board, again, we’re a known entity. We are not an external player; we live in these communities and often have training centers in them. They know the value that comes from our workers and the careers we provide.
I don’t think I’ve seen anyone who says that is a bad thing. But I do think there are other factors people are weighing when they’re considering these projects and they’re incredibly personal.
How do you reckon with the personal nature of this issue, given the employment of your members is also at stake? How do you grapple with that?
Well, look, we respect, over anything else, local decision-making. That’s how this should work.
We’re not here to push through something that is not embraced by communities. We are there to answer questions and good actors and provide information about our workforce, what it can mean. But these are decisions individual communities need to make together.
What sorts of communities are welcoming these projects, from your perspective?
That’s another challenging question because I think we only have a few to go off of here.
I would say more information earlier on the better. That’s true in any case, but especially with this. For us, when we go about our day-to-day activities, that is how our most successful projects work. Good communication. Time to think things through. It is very early days, so we have some great success stories we can point to but definitely more to come.
The number of data centers opposed in Republican-voting areas has risen 330% over the past six months.
It’s probably an exaggeration to say that there are more alligators than people in Colleton County, South Carolina, but it’s close. A rural swath of the Lowcountry that went for Trump by almost 20%, the “alligator alley” is nearly 10% coastal marshes and wetlands, and is home to one of the largest undeveloped watersheds in the nation. Only 38,600 people — about the population of New York’s Kew Gardens neighborhood — call the county home.
Colleton County could soon have a new landmark, though: South Carolina’s first gigawatt data center project, proposed by Eagle Rock Partners.
That’s if it overcomes mounting local opposition, however. Although the White House has drummed up data centers as the key to beating China in the race for AI dominance, Heatmap Pro data indicate that a backlash is growing from deep within President Donald Trump’s strongholds in rural America.
According to Heatmap Pro data, there are 129 embattled data centers located in Republican-voting areas. The vast majority of these counties are rural; just six occurred in counties with more than 1,000 people per square mile. That’s compared with 93 projects opposed in Democratic areas, which are much more evenly distributed across rural and more urban areas.
Most of this opposition is fairly recent. Six months ago, only 28 data centers proposed in low-density, Trump-friendly countries faced community opposition. In the past six months, that number has jumped by 95 projects. Heatmap’s data “shows there is a split, especially if you look at where data centers have been opposed over the past six months or so,” says Charlie Clynes, a data analyst with Heatmap Pro. “Most of the data centers facing new fights are in Republican places that are relatively sparsely populated, and so you’re seeing more conflict there than in Democratic areas, especially in Democratic areas that are sparsely populated.”
All in all, the number of data centers that have faced opposition in Republican areas has risen 330% over the past six months.
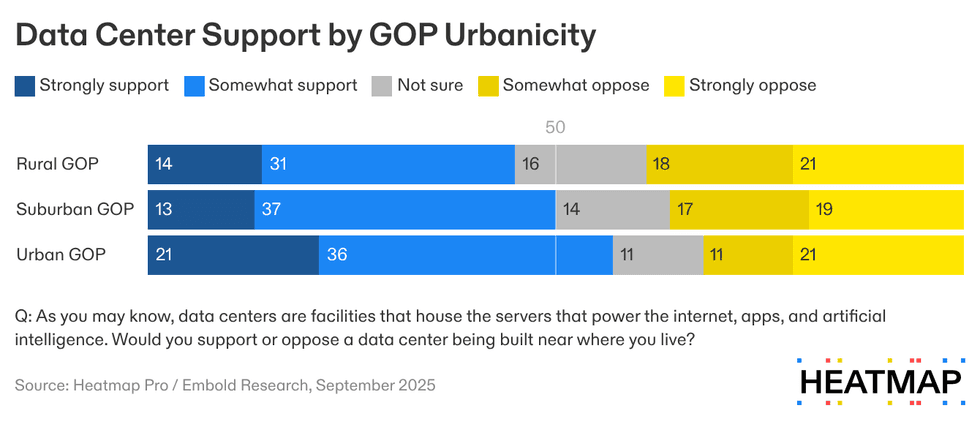
Our polling reflects the breakdown in the GOP: Rural Republicans exhibit greater resistance to hypothetical data center projects in their communities than urban Republicans: only 45% of GOP voters in rural areas support data centers being built nearby, compared with nearly 60% of urban Republicans.
Such a pattern recently played out in Livingston County, Michigan, a farming area that went 61% for President Donald Trump, and “is known for being friendly to businesses.” Like Colleton County, the Michigan county has low population density; last fall, hundreds of the residents of Howell Township attended public meetings to oppose Meta’s proposed 1,000-acre, $1 billion AI training data center in their community. Ultimately, the uprising was successful, and the developer withdrew the Livingston County project.
Across the five case studies I looked at today for The Fight — in addition to Colleton and Livingston Counties, Carson County, Texas; Tucker County, West Virginia; and Columbia County, Georgia, are three other red, rural examples of communities that opposed data centers, albeit without success — opposition tended to be rooted in concerns about water consumption, noise pollution, and environmental degradation. Returning to South Carolina for a moment: One of the two Colleton residents suing the county for its data center-friendly zoning ordinance wrote in a press release that he is doing so because “we cannot allow” a data center “to threaten our star-filled night skies, natural quiet, and enjoyment of landscapes with light, water, and noise pollution.” (In general, our polling has found that people who strongly oppose clean energy are also most likely to oppose data centers.)
Rural Republicans’ recent turn on data centers is significant. Of 222 data centers that have faced or are currently facing opposition, the majority — 55% —are located in red low-population-density areas. Developers take note: Contrary to their sleepy outside appearances, counties like South Carolina’s alligator alley clearly have teeth.