You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
On Guyana’s climate ‘morality,’ New Jersey’s energy fight, climate hybrids
Current conditions: Tropical Storm Gabrielle is gaining intensity as it tracks northward near Bermuda • Thunderstorms from Tropical Storm Mario threaten floods in the American Southwest, particularly in areas scarred by wildfire • China is bracing for Typhoon Ragasa, which could bring winds of up to 137 miles per hour.
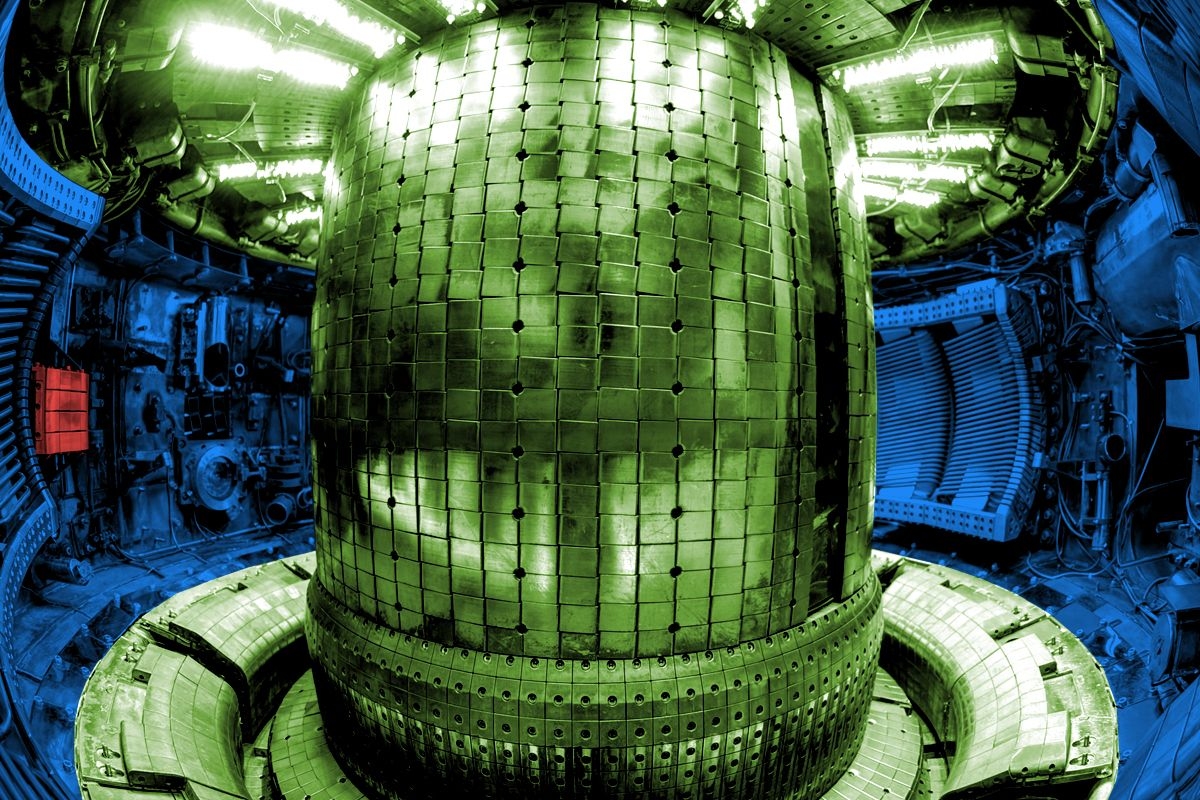
The Italian oil giant Eni announced a deal Monday morning to buy more than $1 billion worth of electricity from Commonwealth Fusion Systems’ debut power plant in Chesterfield, Virginia. It’s the Massachusetts Institute of Technology spinoff’s second major power-purchase agreement since signing its debut contract with Google in July, part of a large deal Eni described as a “strategic collaboration.” The companies did not disclose the terms of the broader contract. “It is a big vote of confidence to have Eni, who has contributed to our execution since the beginning, buy the power we intend to make in Virginia,” Bob Mumgaard, the chief executive of Commonwealth Fusion, said in a statement. “Our fusion power attracts diverse customers across the world — from hyperscalers to traditional energy leaders — because of the promise of clean, almost limitless energy.”
The U.S. is pushing hard to commercialize fusion energy. At least one company, the Microsoft-backed Helion, aims to generate its first electricity for the grid as early as 2028. But Commonwealth Fusion, which is aiming for the 2030s, has raised a third of all the private capital invested into fusion energy so far. Though fusion hopefuls have been burned before, the investment boom is a sign that, as Heatmap’s Katie Brigham wrote last year, “it is finally, possibly, almost time for fusion.”
The United Nations General Assembly has convened in New York City. With wars raging in Ukraine, Sudan, and Gaza, and Western powers such as the United Kingdom and Australia granting official recognition to the state of Palestine, climate change is likely to take a backseat outside of the New York Climate Week panels, conferences, and happy hours that take place across the city alongside the UN gathering.
The U.S. has dramatically reversed its public diplomacy on climate change since President Donald Trump returned to office. While the European Union has remained largely committed to its goals, the bloc could not find enough consensus to pass a binding climate plan ahead of the UN meeting. Instead, the 27 nations signed onto a “statement of intent,” in what the Financial Times called “a blow to hopes of EU leadership” in advance of November’s big UN climate summit, COP30, in Brazil.
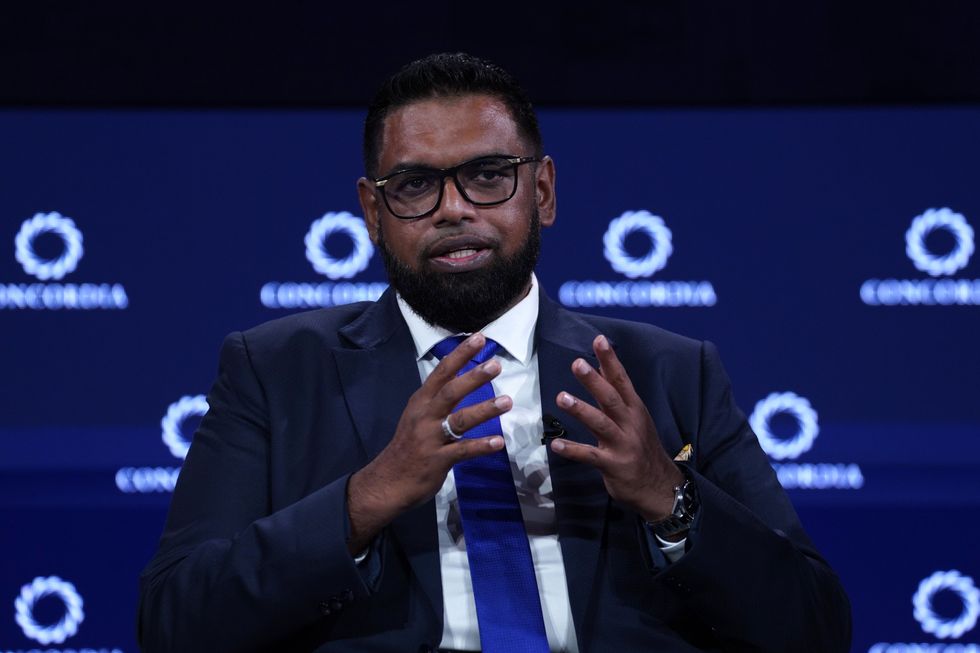

A year ago, the leader of Guyana went viral for a BBC segment in which he lambasted a British journalist for daring to lecture his tiny South American nation about climate change when his country has more carbon-absorbing forests than people, and Britain grew rich long ago felling its old-growth trees. In an interview in The New York Times series with world leaders published this past weekend ahead of the UN General Assembly, Guyana President Irfaan Ali delivers a similarly strident rebuke of critics in the rich world who oppose his country’s embrace of Exxon Mobil’s offshore drilling. “The moral question is: Who can produce what the world needs in the least environmentally damaging way? Because let’s be clear on this, too. We can’t be naïve. The world will need fossil fuel a long time into the future,” he said.
But that doesn’t mean Guyana is going all in on using fossil fuels at home. “Guyana is a new oil producer, but we are using the resource to finance our energy transition, to build resilient infrastructure, to support the region that we are in, to invest in livelihood options that will keep our forest standing, which stores many gigatons of carbon,” Ali said. “We’re investing in solar farms, hydro, natural gas, wind and biomass, all aimed at transitioning to a low-emission energy grid. We are building off-grid systems, solar farms, wind farms for the hinterland community, where the Indigenous people live.”
Republicans overhauled federal energy policy with the last budget legislation that became the One Big Beautiful Bill Act. At the moment they’re deep in negotiations over a new spending bill to forestall a government shutdown on October 1. But Congress is also already looking ahead to a possible second reconciliation bill in the fall — though that is unlikely to say much of anything about energy, according to E&E News. House Budget Committee Chair Jodey Arrington, a representative from Texas, said the first reconciliation bill “exhausted” the possibilities for energy reforms and left little “meat on the bones.” Senate Environment and Public Works Committee Chair Shelley Moore Capito, a West Virginia Republican, said energy policy would “be interesting if it develops,” but said “it’s not developing now.” Some in the clean energy world had hoped a second reconciliation bill would be a chance for moderate Republicans with a lot of wind and solar in their states to quietly reverse anti-renewables policies that made it into law in the OBBB Act. But avoiding the issue might keep more punitive policies at bay, including a Republican proposal to add new fees on electric vehicles.
Energy prices are a central theme of New Jersey’s gubernatorial race as Democrat Mikie Sherrill has repeatedly vowed to pressure the state’s regional grid operator over utility rates that surged 20% this year, and even build new nuclear reactors to meet growing demand for power. At her first televised debate Sunday night with Republican Jack Ciattarelli, Sherrill slammed the Trump administration’s cuts to renewable energy and vowed to take on utilities and the PJM Interconnection, the nation’s largest grid operator, which serves New Jersey. “Everbody at the table is at fault, and they keep dumping the costs onto the ratepayer here in New Jersey,” she said, according to a CNN transcript. “Let’s face it, some of our utility companies have made over a billion dollars in profits, and yet our ratepayers are constantly suffering.”
Ciattarelli instead blamed renewables for the high prices, a claim the data in this piece by Heatmap’s Matthew Zeitlin seriously undercuts. “Nobody wants wind farms on our Jersey Shore,” Ciattarelli asserted, and vowed to pull out of the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative, the interstate carbon-trading market in the Northeast. But his solutions didn’t sound so far off from the Democrat’s, including promises to “expand our nuclear footprint in South Jersey” and “accelerate solar on rooftops.”
Maybe call it a teal jay? Biologists at the University of Texas at Austin reported the discovery of a bird formed naturally by a green jay and a blue jay mating in the wild, marking one of the first documented examples of hybrid species created due to changing climate patterns. The two different parent species are separated by 7 million years of evolution, and their migratory ranges only recently started to overlap. “We think it’s the first observed vertebrate that’s hybridized as a result of two species both expanding their ranges due, at least in part, to climate change,” Brian Stokes, a graduate student researching ecology and evolution and first author of the study, said in a press release.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
On the real copper gap, Illinois’ atomic mojo, and offshore headwinds
Current conditions: The deadliest avalanche in modern California history killed at least eight skiers near Lake Tahoe • Strong winds are raising the wildfire risk across vast swaths of the northern Plains, from Montana to the Dakotas, and the Southwest, especially New Mexico, Texas, and Oklahoma • Nairobi is bracing for days more of rain as the Kenyan capital battles severe flooding.
Last week, the Environmental Protection Agency repealed the “endangerment finding” that undergirds all federal greenhouse gas regulations, effectively eliminating the justification for curbs on carbon dioxide from tailpipes or smokestacks. That was great news for the nation’s shrinking fleet of coal-fired power plants. Now there’s even more help on the way from the Trump administration. The agency plans to curb rules on how much hazard pollutants, including mercury, coal plants are allowed to emit, The New York Times reported Wednesday, citing leaked internal documents. Senior EPA officials are reportedly expected to announce the regulatory change during a trip to Louisville, Kentucky on Friday. While coal plant owners will no doubt welcome less restrictive regulations, the effort may not do much to keep some of the nation’s dirtiest stations running. Despite the Trump administration’s orders to keep coal generators open past retirement, as Heatmap’s Matthew Zeitlin wrote in November, the plants keep breaking down.
At the same time, the blowback to the so-called climate killshot the EPA took by rescinding the endangerment finding has just begun. Environmental groups just filed a lawsuit challenging the agency’s interpretation of the Clean Air Act to cover only the effects of regional pollution, not global emissions, according to Landmark, a newsletter tracking climate litigation.
Copper prices — as readers of this newsletter are surely well aware — are booming as demand for the metal needed for virtually every electrical application skyrockets. Just last month, Amazon inked a deal with Rio Tinto to buy America’s first new copper output for its data center buildout. But new research from a leading mineral supply chain analyst suggests the U.S. can meet 145% of its annual demand using raw copper from overseas and domestic mines and from scrap. By contrast, China — the world’s largest consumer — can source just 40% of its copper that way. What the U.S. lacks, according to Benchmark Mineral Intelligence, is the downstream processing capacity to turn raw copper into the copper cathode manufacturers need. “The U.S. is producing more copper than it uses, and is far more self-reliant than China in terms of raw materials,” Benchmark analyst Albert Mackenzie told the Financial Times. The research calls into question the Trump administration’s mineral policy, which includes stockpiling copper from jointly-owned ventures in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and domestically. “Stockpiling metal ores doesn’t help if you don’t have midstream processing,” Stephen Empedocles, chief executive of US lobbying firm Clark Street Associates, told the newspaper.
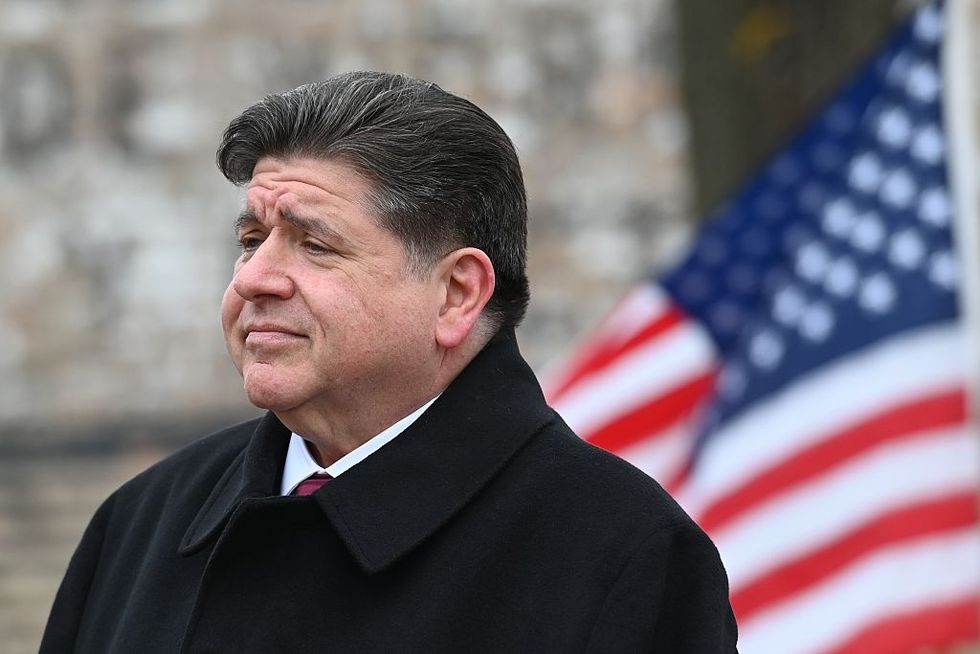

Illinois generates more of its power from nuclear energy than any other state. Yet for years the state has banned construction of new reactors. Governor JB Pritzker, a Democrat, partially lifted the prohibition in 2023, allowing for development of as-yet-nonexistent small modular reactors. With excitement about deploying large reactors with time-tested designs now building, Pritzker last month signed legislation fully repealing the ban. In his state of the state address on Wednesday, the governor listed the expansion of atomic energy among his administration’s top priorities. “Illinois is already No. 1 in clean nuclear energy production,” he said. “That is a leadership mantle that we must hold onto.” Shortly afterward, he issued an executive order directing state agencies to help speed up siting and construction of new reactors. Asked what he thought of the governor’s move, Emmet Penney, a native Chicagoan and nuclear expert at the right-leaning Foundation for American Innovation, told me the state’s nuclear lead is “an advantage that Pritzker wisely wants to maintain.” He pointed out that the policy change seems to be copying New York Governor Kathy Hochul’s playbook. “The governor’s nuclear leadership in the Land of Lincoln — first repealing the moratorium and now this Hochul-inspired executive order — signal that the nuclear renaissance is a new bipartisan commitment.”
The U.S. is even taking an interest in building nuclear reactors in the nation that, until 1946, was the nascent American empire’s largest overseas territory. The Philippines built an American-made nuclear reactor in the 1980s, but abandoned the single-reactor project on the Bataan peninsula after the Chernobyl accident and the fall of the Ferdinand Marcos dictatorship that considered the plant a key state project. For years now, there’s been a growing push in Manila to meet the country’s soaring electricity needs by restarting work on the plant or building new reactors. But Washington has largely ignored those efforts, even as the Russians, Canadians, and Koreans eyed taking on the project. Now the Trump administration is lending its hand for deploying small modular reactors. The U.S. Trade and Development Agency just announced funding to help the utility MGEN conduct a technical review of U.S. SMR designs, NucNet reported Wednesday.
Sign up to receive Heatmap AM in your inbox every morning:
Despite the American government’s crusade against the sector, Europe is going all in on offshore wind. For a glimpse of what an industry not thrust into legal turmoil by the federal government looks like, consider that just on Wednesday the homepage of the trade publication OffshoreWIND.biz featured stories about major advancements on at least three projects totaling nearly 5 gigawatts:
That’s not to say everything is — forgive me — breezy for the industry. Germany currently gives renewables priority when connecting to the grid, but a new draft law would give grid operators more discretion when it comes to offshore wind, according to a leaked document seen by Windpower Monthly.
American clean energy manufacturing is in retreat as the Trump administration’s attacks on consumer incentives have forced companies to reorient their strategies. But there is at least one company setting up its factories in the U.S. The sodium-ion battery startup Syntropic Power announced plans to build 2 gigawatts of storage projects in 2026. While the North Carolina-based company “does not reveal where it manufactures its battery systems,” Solar Power World reported, it “does say” it’s establishing manufacturing capacity in the U.S. “We’re making this move now because the U.S. market needs storage that can be deployed with confidence, supported by certification, insurance acceptance, and a secure domestic supply chain,” said Phillip Martin, Syntropic’s chief executive.
For years now, U.S. manufacturers have touted sodium-ion batteries as the next big thing, given that the minerals needed to store energy are more abundant and don’t afford China the same supply-chain advantage that lithium-ion packs do. But as my colleague Katie Brigham covered last April, it’s been difficult building a business around dethroning lithium. New entrants are trying proprietary chemistries to avoid the mistakes other companies made, as Katie wrote in October when the startup Alsym launched a new stationary battery product.
Last spring, Heron Power, the next-generation transformer manufacturer led by a former Tesla executive, raised $38 million in a Series A round. Weeks later, Spain’s entire grid collapsed from voltage fluctuations spurred by a shortage of thermal power and not enough inverters to handle the country’s vast output of solar power — the exact kind of problem Heron Power’s equipment is meant to solve. That real-life evidence, coupled with the general boom in electrical equipment, has clearly helped the sales pitch. On Wednesday, the company closed a $140 million Series B round co-led by the venture giants Andreessen Horowitz and Breakthrough Energy Ventures. “We need new, more capable solutions to keep pace with accelerating energy demand and the rapid growth of gigascale compute,” Drew Baglino, Heron’s founder and chief executive, said in a statement. “Too much of today’s electrical infrastructure is passive, clunky equipment designed decades ago. At Heron we are manifesting an alternative future, where modern power electronics enable projects to come online faster, the grid to operate more reliably, and scale affordably.”
A senior scholar at Columbia University’s Center on Global Energy Policy on what Trump has lost by dismantling Biden’s energy resilience strategy.
A fossil fuel superpower cannot sustain deep emissions reductions if doing so drives up costs for vulnerable consumers, undercuts strategic domestic industries, or threatens the survival of communities that depend on fossil fuel production. That makes America’s climate problem an economic problem.
Or at least that was the theory behind Biden-era climate policy. The agenda embedded in major legislation — including the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act and the Inflation Reduction Act — combined direct emissions-reduction tools like clean energy tax credits with a broader set of policies aimed at reshaping the U.S. economy to support long-term decarbonization. At a minimum, this mix of emissions-reducing and transformation-inducing policies promised a valuable test of political economy: whether sustained investments in both clean energy industries and in the most vulnerable households and communities could help build the economic and institutional foundations for a faster and less disruptive energy transition.
Sweeping policy reversals have cut these efforts short. Abandoning the strategy makes the U.S. economy less resilient to the decline of fossil fuels. It also risks sowing distrust among communities and firms that were poised to benefit, complicating future efforts to recommit to the economic policies needed to sustain an energy transition.
This agenda rested on the idea that sustaining decarbonization would require structural changes across the economy, not just cleaner sources of energy. First, in a country that derives substantial economic and geopolitical power from carbon-intensive industries, a durable energy transition would require the United States to become a clean energy superpower in its own right. Only then could the domestic economy plausibly gain, rather than lose, from a shift away from fossil fuels.
Second, with millions of households struggling to afford basic energy services and fossil fuels often providing relatively cheap energy, climate policy would need to ensure that clean energy deployment reduces household energy burdens rather than exacerbates them.
Third, policies would need to strengthen the economic resilience of communities that rely heavily on fossil fuel industries so the energy transition does not translate into shrinking tax bases, school closures, and lost economic opportunity in places that have powered the country for generations.
This strategy to reshape the economy for the energy transition has largely been dismantled under President Trump.
My recent research examines federal support for fossil fuel-reliant communities, assessing President Biden’s stated goal of “revitalizing the economies of coal, oil, gas, and power plant communities.” Federal spending data provides little evidence that these at-risk communities have been effectively targeted. One reason is timing: While legislation authorized unprecedented support, actual disbursements lagged far behind those commitments.
Many of the key policies — including $4 billion in manufacturing tax credits reserved for communities affected by coal closures — took years to move from statutory language to implementation guidance and final project selection. As a result, aside from certain pandemic-era programs, fossil fuel-reliant communities had received limited support by the time Trump took office last year.
Since then, the Trump administration and Congress have canceled projects intended to benefit fossil fuel-reliant regions, including carbon capture and clean hydrogen demonstrations, and discontinued programs designed to help communities access and implement federal funding.
Other elements of the strategy to reduce the country’s vulnerability to fossil fuel decline have fared even worse under the Trump administration. Programs intended to help households access and afford clean energy — most notably the $27 billion Greenhouse Gas Reduction Fund — were effectively canceled last year, including attempts to claw back previously awarded funds. More broadly, the rollback of IRA programs with an explicit equity or justice focus leaves lower-income households more exposed to the economic disruptions that can accompany an energy transition.
By contrast, subsidies and grant programs aimed at strengthening the country’s energy manufacturing base have largely survived, including tax credits supporting domestic production of batteries, solar components, and other key technologies. Even so, the investment environment has weakened. Automakers have scaled back planned U.S. battery manufacturing expansions. Clean Investment Monitor data shows annual clean energy manufacturing investments on pace to decline in 2025, after rising sharply from 2022 to 2024. Whatever one believed about the potential to build globally competitive domestic supply chains for the technologies that will power clean energy systems, those prospects have dimmed amid slowing investment and the Trump administration’s prioritization of fossil fuels.
Perhaps these outcomes were unavoidable. Building a strong domestic solar industry was always uncertain, and place-based economic development programs have a mixed track record even under favorable conditions. Still, the Biden-era approach reflected a coherent theory of climate politics that warranted a real-world test.
Over the past year, debates in climate policy circles have centered on whether clean energy progress can continue under less supportive federal policies, with plausible cases made on both sides. The fate of Biden’s broader economic strategy to sustain the energy transition, however, is less ambiguous. The underlying dependence of the United States on fossil fuels across industries, households, and many local communities remains largely unchanged.
New data from the Clean Investment Monitor shows the first year-over-year quarterly decline since the project began.
Investment in the clean economy is flagging — and the electric vehicle supply chain is taking the biggest hit.
The Clean Investment Monitor, a project by the Rhodium Group and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology’s Center for Energy and Environmental Policy Research that tracks spending on the energy transition, found that total investment in clean technology in the last three months of 2025 was $60 billion. That compares to $68 billion in the fourth quarter of 2024 and $79 billion in the third quarter of last year. While total clean investment in 2025 was $277 billion — the highest the group has ever recorded — the fourth quarter of 2025 was the first time since the Clean Investment Monitor began tracking that the numbers fell compared to the same quarter the year before.
“Since 2019, quarterly investment has surpassed the level observed in the same period of the previous year — even when quarter-on-quarter declines occurred,” the report says. “That trend ended in Q4 2025, when investment declined 11% from the level observed in Q4 2024.”
It starts downstream, with consumer purchases of clean energy technology once favored by federal tax policy: electric vehicles, heat pumps, and home electricity generation. Consumer purchases fell 36% from the third quarter to the fourth quarter, after the $7,500 federal EV credit expired on September 30.
With a consumer market for EVs being undercut, car companies responded by canceling projects and redirecting investment.
“There were a lot of big, multi-billion dollar cancellations coming from Ford specifically,” Harold Tavarez, a research analyst at Rhodium, told me. There’s been a lot of pivots from having fully electric vehicles to doing more hybrids, more internal combustion, and even extended range EVs.”
Ford alone took an almost $20 billion hit on its EV investments in 2025. The company suspended production of its all-electric F-150 Lightning late last year, despite its status as the best-selling electric pickup in the country for 2025, and announced a pivot into hybrids and extended-range EVs (which have gasoline-powered boosters onboard), including a revamped Lightning. It has also announced plans to convert some manufacturing facilities designed to produce EVs back into internal combustion plants, but it hasn’t abandoned electricity entirely. Other decommissioned EV factories will instead produce battery electric storage systems, and the company has announced a pivot to smaller, cheaper EVs.
Ford is far from alone in its EV-related pain, however. Rival Big Three automaker GM also booked $6 billion in losses for 2025, while Stellantis, the European parent company of the Chrysler, Dodge, and Jeep brands, will take as much as $26 billion in charges. EV sales fell some 46% in the fourth quarter of last year compared to the third quarter, and 36% compared to the fourth quarter of 2024, according to Cox Automotive.
Looking at the investment data holistically, the true dramatic decline was in forward-looking announcements, again heavily concentrated in the EV supply chain. The $3 billion in clean manufacturing announced in the fourth quarter of last year was an almost 50% drop from the previous quarter, “marking this quarter as the lowest period of announcements since Q4 2020,” the report says. Announcements were down about 25% for the year as a whole compared to 2024. Of the $29 billion of canceled projects Clean Investment Monitor tracked from 2018 through the end of last year, almost three quarters — some $23 billion — happened in 2025.
“Collectively, we estimate around 27,000 operational jobs in the manufacturing segment were affected by cancellations,” the report says, “two-thirds (68%) of which were tied to projects canceled in 2025.”
“One of the most frustrating parts of watching Trump wage war on all things clean energy is the apparent lack of understanding — or care — of how it impacts his stated goals,” Alex Jacquez, a former Biden economic policy official who is chief of policy and advocacy at the Groundwork Collective, told me. “The IRA built a real, competitive manufacturing base in the U.S. in a new sector for the first time in decades. Administration priorities are being hampered by blind opposition to anything Biden, IRA, or clean energy.”