You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
You’ve probably noticed — even Trump has noticed — but the reason why is as complicated as the grid itself.
You’re not imagining things: Electricity prices are surging.
Electricity rates, which have increased steadily since the pandemic, are now on a serious upward tear. Over the past 12 months, power prices have increased more than twice as fast as inflation, according to recent government data. They will likely keep rising in years to come as new data centers and factories connect to the power grid.
That surge is a major problem for the economy — and for President Trump. On the campaign trail, Trump vowed to cut Americans’ electricity bills in half within his first year in office. “Your electric bill — including cars, air conditioning, heating, everything, your total electric bill — will be 50% less. We’re going to cut it in half,” he said.
Now Trump has mysteriously stopped talking about that pledge, and on Tuesday he blamed renewables for rising electricity rates. Even Trump’s Secretary of Energy Chris Wright has acknowledged that costs are doing the opposite of what the president has promised.
Trump’s promise to cut electricity rates in half was always ridiculous. But while his administration is likely making the electricity crisis worse, the roots of our current power shock did not begin in January.
Why has electricity gotten so much more expensive over the past five years? The answer, despite what the president might say, isn’t renewables. It has far more to do with the part of the power grid you’re most familiar with: the poles and wires outside your window.
Before we begin, a warning: Electricity prices are weird.
In most of the U.S. economy, markets set prices for goods and services in response to supply and demand. But electricity prices emerge from a complicated mix of regulation, fuel costs, and wholesale auction. In general, electricity rates need to cover the costs of running the electricity system — and that turns out to be a complicated task.
You can split costs associated with the electricity system into three broad segments. The biggest and traditionally the most expensive part of the grid is generation — the power plants and the fuels needed to run them. The second category is transmission, which moves electricity across long distances and delivers it to local substations. The final category is distribution, the poles and wires that get electricity the “the last mile” to homes and businesses. (You can think of transmission as the highways for electricity and distribution as the local roads.)
In some states, especially those in the Southeast and Mountain West, monopoly electricity companies run the entire power grid — generation, transmission, and distribution. A quasi-judicial body of state officials regulates what this monopoly can do and what it can charge consumers. These monopoly utilities are supposed to make long-term decisions in partnership with these state commissions, and they must get their permission before they can raise electricity rates. But when fuel costs go up for their power plants — such as when natural gas or oil prices spike — they can often “pass through” those costs directly to consumers.
In other states, such as California or those in the Mid-Atlantic, electricity bills are split in two. The “generation” part of the bill is set through regulated electricity auctions that feature many different power plants and power companies. The market, in other words, sets generation costs. But the local power grid — the infrastructure that delivers electricity to customers — cannot be handled by a market, so it is managed by utilities that cover a particular service area. These local “transmission and distribution” utilities must get state regulators’ approval when they raise rates for their part of the bill.
The biggest driver of the power grid’s rising costs is … the power grid itself.
Historically, generation — building new power plants, and buying the fuel to run them — has driven the lion’s share of electricity rates. But since the pandemic, the cost of building the distribution system has ballooned.
Electricity costs are “now becoming a wires story and less of an electrons story,” Madalsa Singh, an economist at the University of California Santa Barbara, told me. In 2023, distribution made up nearly half of all utility spending, up from 37% in 2019, according to a recent Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory report.
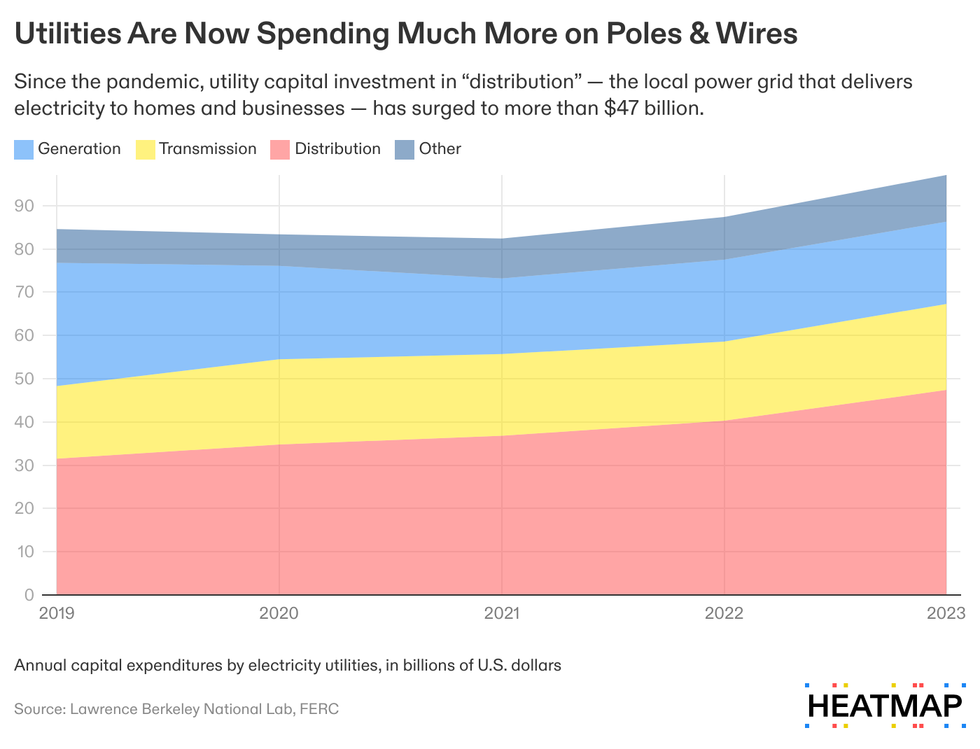
Where are these higher costs coming from? When you look under the hood, the possibly surprising answer is: the poles and wires themselves. Utilities spent roughly $6 billion more on “overhead poles, towers, and conductors” in 2023 than in 2019, according to the Lawrence Berkeley report. Spending on underground power lines — which are especially important out West to avoid sparking a wildfire — increased by about $4 billion over the same period.
Spending on transformers also surged. Transformers, which connect different circuits on the grid and keep the flow of electricity constant, are a crucial piece of transmission and distribution infrastructure. But they’ve been in critically short supply more or less since the supply chain crunch of the pandemic. Utility spending on transformers has more than doubled since 2019, according to Wood Mackenzie.
At least some of the costs are hitting because the grid is just old, Singh said. As equipment reaches the end of its life, it needs to be upgraded and hardened. But it’s not completely clear why that spike in distribution costs is happening now as opposed to in the 2010s, when the grid was almost as old and in need of repair as it was now.
Some observers have argued that for-profit utilities are “goldplating” distribution infrastructure, spending more on poles and wires because they know that customers will ultimately foot the bill for them. But when Singh studied California power companies, she found that even government-run utilities — i.e. utilities without private investors to satisfy — are now spending more on distribution than they used to, too. Distribution costs, in other words, seem to be going up for everyone.
Sprawling suburbs in some states may be driving some of those costs, she added. In California, people have pushed farther out into semi-developed or rural land in order to find cheaper housing. Because investor-owned utilities have a legal obligation to get wires and electricity to everyone in their service area, these new and more distant housing developments might be more expensive to connect to the grid than older ones.
These higher costs will usually appear on the “transmission and distribution” part of your power bill — the “wires” part, if it is broken out. What’s interesting is that as a share of total utility investment, virtually all of the cost inflation is happening on the distribution side of that ledger. While transmission costs have fluctuated year to year, they have hovered around 20% of total utility investment since 2019, according to the Lawrence Berkeley Labs report.
Higher transmission spending might eventually bring down electricity rates because it could allow utilities to access cheaper power in neighboring service areas — or connect to distant solar or wind projects. (If renewables were driving up power prices as the president claims, you might see it here, in the “transmission” part of the bill.) But Charles Hua, the founder and executive director of the think tank PowerLines, said that even now, most utilities are building out their local grids, not connecting to power projects that are farther away.
The second biggest driver of higher electricity costs is disasters — natural and otherwise.
In California, ratepayers are now partially footing the bill for higher insurance costs associated with the risk of a grid-initiated wildfire, Sam Kozel, a researcher at E9 Insight, told me. Utilities also face higher costs whenever they rebuild the grid after a wildfire because they install sensors and software in their infrastructure that might help avoid the next blaze.
Similar stories are playing out elsewhere. Although the exact hazards vary region by region, some utilities and power grids have had to pay steep costs to rebuild from disasters or prevent the likelihood of the next one occurring.
In the Southeast, for instance, severe storms and hurricanes have knocked out huge swaths of the distribution grid, requiring emergency line crews to come in and rebuild. Those one-time, storm-induced costs then get recovered through higher utility rates over time.
Why have costs gone up so much this decade? Wildfires seem to grow faster now because of climate change — but wildfires in California are also primed to burn by a century of built-up fuel in forests. The increased disaster costs may also be partially the result of the bad luck of where storms happen to hit. Relatively few hurricanes made landfall in the U.S. during the 2010s — just 13, most of which happened in the second half of the decade. Eleven hurricanes have already come ashore in the 2020s.
Because fuel costs are broadly seen as outside a utility’s control, regulators generally give utilities more leeway to pass those costs directly through to customers. So when fuel prices go up, so do rates in many cases.
The most important fuel for the American power grid is natural gas, which produces more than 40% of American electricity. In 2022, surging demand and rising European imports caused American natural gas prices to increase more than 140%. But it can take time for a rise of that magnitude to work its way to consumers, and it can take even longer for electricity prices to come back down.
Although natural gas prices returned to pre-pandemic levels by 2023, utilities paid 30% more for fuel and energy that year than they did in 2019, according to Lawrence Berkeley National Lab. That’s because higher fuel costs do not immediately get processed in power bills.
The ultimate impact of these price shocks can be profound. North Carolina’s electricity rates rose from 2017 to 2024, for instance, largely because of natural gas price hikes, according to an Environmental Defense Fund analysis.
The final contributor to higher power costs is the one that has attracted the most worry in the mainstream press: There is already more demand for electricity than there used to be.
A cascade of new data centers coming onto the grid will use up any spare electron they can get. In some regions, such as the Mid-Atlantic’s PJM power grid, these new data centers are beginning to drive up costs by increasing power prices in the capacity market, an annual auction to lock in adequate supply for moments of peak demand. Data centers added $9.4 billion in costs last year, according to an independent market monitor.
Under PJM’s rules, it will take several years for these capacity auction prices to work their way completely into consumer prices — but the process has already started. Hua told me that the power bill for his one-bedroom apartment in Washington, D.C., has risen over the past year thanks largely to these coming demand shocks. (The Mid-Atlantic grid implemented a capacity-auction price cap this year to try to limit future spikes.)
Across the country, wherever data centers have been hooked up to the grid but have not supplied or purchased their own around-the-clock power, costs will probably rise for consumers. But it will take some time for those costs to be felt.
In order to meet that demand, utilities and power providers will need to build more power plants, transmission lines, and — yes — poles and wires in the years to come. But recent Trump administration policies will make this harder. The reconciliation bill’s termination of wind and solar tax credits, its tariffs on electrical equipment, and a new swathe of anti-renewable regulations will make it much more expensive to add new power capacity to the strained grid. All those costs will eventually hit power bills, too, even if it takes a few years.
“We're just getting started in terms of price increases, and nothing the federal administration is doing ‘to assure American energy dominance’ is working in the right direction,” Kozel said. “They’re increasing all the headwinds.”
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
The FREEDOM Act aims to protect energy developments from changing political winds.
A specter is haunting permitting reform talks — the specter of regulatory uncertainty. That seemingly anodyne two-word term has become Beltway shorthand for President Donald Trump’s unrelenting campaign to rescind federal permits for offshore wind projects. The repeated failure of the administration’s anti-wind policies to hold up in court aside, the precedent the president is setting has spooked oil and gas executives, who warn that a future Democratic government could try to yank back fossil fuel projects’ permits.
A new bipartisan bill set to be introduced in the House Tuesday morning seeks to curb the executive branch’s power to claw back previously-granted permits, protecting energy projects of all kinds from whiplash every time the political winds change.
Dubbed the FREEDOM Act, the legislation — a copy of which Heatmap obtained exclusively — is the latest attempt by Congress to speed up construction of major energy and mining projects as the United States’ electricity demand rapidly eclipses new supply and Chinese export controls send the price of key critical minerals skyrocketing.
Two California Democrats, Representatives Josh Harder and Adam Gray, joined three Republicans, Representatives Mike Lawler of New York, Don Bacon of Nebraska, and Chuck Edwards of North Carolina, to sponsor the bill.
While green groups have criticized past proposals to reform federal permitting as a way to further entrench fossil fuels by allowing oil and gas to qualify for the new shortcuts, Harder pitched the bill as relief to ratepayers who “are facing soaring energy prices because we’ve made it too hard to build new energy projects.”
“The FREEDOM Act delivers the smart, pro-growth certainty that critical energy projects desperately need by cutting delays, fast-tracking approvals, and holding federal agencies accountable,” he told me in a statement. “This is a common sense solution that will mean more energy projects being brought online in the short term and lower energy costs for our families for the long run.”
The most significant clause in the 77-page proposal lands on page 59. The legislation prohibits federal agencies and officials from issuing “any order or directive terminating the construction or operation of a fully permitted project, revoke any permit or authorization for a fully permitted project, or take any other action to halt, suspend, delay, or terminate an authorized activity carried out to support a fully permitted project.”
There are, of course, exceptions. Permits could still be pulled if a project poses “a clear, immediate, and substantiated harm for which the federal order, directive, or action is required to prevent, mitigate, or repair.” But there must be “no other viable alternative.”
Such a law on the books would not have prevented the Trump administration from de-designating millions of acres of federal waters to offshore wind development, to pick just one example. But the legislation would explicitly bar Trump’s various attempts to halt individual projects with stop work orders. Even the sweeping order the Department of the Interior issued in December that tried to stop work on all offshore wind turbines currently under construction on the grounds of national security would have needed to prove that the administration exhausted all other avenues first before taking such a step.
Had the administration attempted something similar anyway, the legislation has a mechanism to compensate companies for the costs racked up by delays. The so-called De-Risking Compensation Fund, which the bill would establish at the Treasury Department, would kick in if the government revoked a permit, canceled a project, failed to meet deadlines set out in the law for timely responses to applications, or ran out the clock on a project such that it’s rendered commercially unviable.
The maximum payout is equal to the company’s capital contribution, with a $5 million minimum threshold, according to a fact-sheet summarizing the bill for other lawmakers who might consider joining as co-sponsors. “Claims cannot be denied based on project permits or energy technology type,” the document reads. A company that would have benefited from a payout, for example, would be TC Energy, the developer behind the Keystone XL oil pipeline the Biden administration canceled shortly after taking office.
Like other permitting reform legislation, the FREEDOM Act sets new rules to keep applications moving through the federal bureaucracy. Specifically, it gives courts the right to decide whether agencies that miss deadlines should have to pay for companies to hire qualified contractors to complete review work.
The FREEDOM Act also learned an important lesson from the SPEED Act, another bipartisan bill to overhaul federal permitting that passed the House in December but has since become mired in the Senate. The SPEED Act lost Democratic support — ultimately passing the House with just 11 Democratic votes — after far-right Republicans and opponents of offshore wind leveraged a special carveout to continue allowing the administration to commence its attacks on seaborne turbine projects.
The amendment was a poison pill. In the Senate, a trio of key Democrats pushing for permitting reform, Senate Energy and Natural Resources ranking member Martin Heinrich, Environment and Public Works ranking member Sheldon Whitehouse, and Hawaii senator Brian Schatz, previously told Heatmap’s Jael Holzman that their support hinged on curbing Trump’s offshore wind blitz.
Those Senate Democrats “have made it clear that they expect protections against permitting abuses as part of this deal — the FREEDOM Act looks to provide that protection,” Thomas Hochman, the director of energy and infrastructure policy at the Foundation for American Innovation, told me. A go-to policy expert on clearing permitting blockages for energy projects, Hochman and his center-right think tank have been in talks with the lawmakers who drafted the bill.
A handful of clean-energy trade groups I contacted did not get back to me before publication time. But American Clean Power, one of the industry’s dominant associations, withdrew its support for the SPEED Act after Republicans won their carveout. The FREEDOM Act would solve for that objection.
The proponents of the FREEDOM Act aim for the bill to restart the debate and potentially merge with parts of the previous legislation.
“The FREEDOM Act has all the critical elements you’d hope to see in a permitting certainty bill,” Hochman said. “It’s tech-neutral, it covers both fully permitted projects and projects still in the pipeline, and it provides for monetary compensation to help cover losses for developers who have been subject to permitting abuses.”
Maybe utilities’ “natural monopoly” isn’t so natural after all.
Debates over electricity policy usually have a common starting point: the “natural monopoly” of the transmission system, wherein the poles and wires that connect power plants to homes and businesses have exclusive franchises in a certain territory and charge regulated rates to access them.
The thinking is that without a monopoly franchise, no one would make the necessary capital expenditures to build and maintain the power lines and grid infrastructure necessary to connect the whole system, especially if they thought someone would build a new transmission line nearby. So while a government body oversees investment and prices, the utility itself is not subject to market-based competition.
But what if someone really did want to build their own wires?
“There are at least two of us who do not think that electricity is a natural monopoly,” Glen Lyons, the founder of Advocates for Consumer Regulated Electricity, told me.
The other one is Travis Fisher, an energy scholar at the Cato Institute, who corrected his friend and colleague.
“Between me, and Joseph Schumpeter, and Wayne Cruz, and Glen Lyons, there’s at least four of us. Only three of us are alive,” Fisher said, referencing the Austrian economist Schumpeter, who died in 1950, and the libertarian scholar Cruz, who was a critic of the restructuring of the electricity market in the 1990s.
Fisher and Lyons, however, are the team behind a proposal put out on Tuesday by the libertarian Cato Institute calling for “consumer-regulated electricity.” Instead of a transmission system with a monopoly franchise that independent generators can connect to and sell power to utilities in a process regulated by a combination of a public utility commission and regional transmission organization or independent system operators, CRE systems would be physically islanded electricity systems that customers would privately and voluntarily sign up for.
Crucially, CRE would not be regulated under existing federal law, and would have no connection to the existing grid, allowing for novel price structures and even physical set-ups, like running on different frequencies or even direct current, Fisher said.
They would also, Fisher and Lyons argue, help solve the dilemma haunting electricity policymakers: how to bring new load on the grid quickly without saddling existing ratepayers with the cost of paying for utility upgrades.
“If enabled, CRE utilities would generate, transmit, and sell electricity directly to customers under voluntary contracts, without interconnecting to the existing regulated grid or seeking permission from economic regulators at the state or federal level,” the Cato proposal reads.
This idea has a natural audience among political conservatives, as it’s essentially a bet that more entrepreneurship and less regulation will solve some of our biggest energy system problems. On the other hand, utilities tend to be a powerful force in conservative politics at both the state and federal levels, which is one reason why these kinds of ideas are still marginal.
But less marginal than they have been.
Consumer-regulated electricity is more than just another think tank white paper. It has also won the approval of the influential American Legislative Exchange Council, better known as ALEC, a conservative group that writes model legislation for state legislatures to adopt. Fisher proposed version of the consumer-regulated utilities plan to the network in December of last year, and ALEC approved it in January.
A few days after the group finalized the model policy to allow CRE at the state level, Arkansas Senator Tom Cotton proposed his own version in the form of the DATA Act, which would “amend the Federal Power Act to exempt consumer-regulated electric utilities from Federal regulation.”
While the CRE proposal is a big conceptual departure from about a century of electricity regulation, the actual reform is modest. Fisher and Lyons propose a structure would apply solely to “sophisticated customers … who voluntarily contract for service and can manage their own risks,” i.e. big industrial users like data centers, not your home.
While this sounds like behind the meter generation, whereby large electricity users such as, say, xAI in Memphis, simply set up their own electricity plants, CRE goes further. The idea is to capture the self-regulation benefits of building your own power within a structure that still allows for the economies of scale of a grid. Or in the words of Cato’s proposal, CRE “would enable third-party utilities to serve many customers, resulting in lower costs, higher reliability, and a smaller environmental footprint compared to self-supply options.”
Fisher and Lyons argue that CRE would also have an advantage over so-called co-location, where data centers are built adjacent to generation and share interconnection with the grid, which still requires interacting with public utility commissions and utilities. The pair have also suggested that the Department of Energy and the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission use its existing rulemaking process on data center interconnection to encourage states to pass the necessary laws to allow islanded utility systems.
While allowing totally private utility systems may be a radical — and certainly a libertarian — departure from the utility regulation system as it exists today, proposals are popping up on both the left and the right to try to reduce utility influence over the electricity system.
Tom Steyer, the hedge fund billionaire and climate investor who is running for governor of California, has said that he would “break up the utility monopolies to lower electric bills by 25%.” In a January press conference, Steyer clarified that he “wants to force utility companies to choose cheaper ways of wildfire-proofing their infrastructure and give customers other options for buying power, including making it easier to build neighborhood-level solar projects or allowing more communities to operate their own local grids,” according to CalMatters. California already has some degree of retail choice, although a more expansive version of a retail competition model infamously collapsed during the 2001 rolling blackouts.
To Fisher, while his and Lyons’ proposal is in some ways radical, it is also not a particularly big risk. If there’s truly no demand for private electricity networks, none will be built and nothing will change, even if there’s regulatory reform to allow for it.“I’m not surprised to see it get traction,” Fisher said of the plan, “just because there’s no downside, and the upside could be absolutely nothing — or it could be a breakthrough.”
On offshore wind wins, China’s ‘strong energy nation,’ and Japan’s deep-sea mining
Current conditions: Yet another snow storm is set to powder parts of the Ohio Valley and the Mid-Atlantic • Cyclone Fytia is deluging Madagascar, causing flooding that left at least three dead and 30,000 displaced in a country still reeling from the recent overthrow of its government • Scotland and England are bracing for a gusty 33-hour blizzard, during which temperatures are forecast to drop below freezing.
He’s fashioned the military’s Defense Logistics Agency into a tool to fund mineral refineries. He’s gone on a shopping spree that made Biden administration officials “jealous,” taking strategic equity stakes in more than half a dozen mining companies. Now President Donald Trump is preparing to launch a strategic stockpile for critical minerals in what Bloomberg billed as “a bid to insulate manufacturers from supply shocks as the U.S. works to slash its reliance on Chinese rare earths and other metals.” Dubbed Project Vault, the venture will be seeded with a $10 billion loan from the Export-Import Bank of the U.S. and another $1.67 billion in private capital. More than a dozen companies have committed to work on the stockpile, including General Motors, Stellantis, Boeing, Google, and GE Vernova.
The shale industry, meanwhile, showed it’s matured enough to go through some consolidation. Oklahoma City-based gas giant Devon Energy is merging with Houston-headquartered Coterra Energy in an all-stock deal that CNBC said would create “a large-cap producer with a top position in the Permian Basin. The deal would establish a combined company with an enterprise value of $58 billion, marking the largest merger in the sector since Diamondback bought Endeavor Energy Resources for $26 billion in 2024. The deal comes as low prices from the global oil glut squeeze U.S. shale drillers — and as the possibility of more oil from Venezuela threatens the sector with fresh competition.
Offshore wind is now five-for-five in its legal brawls with Trump. With Orsted’s latest victory in the Sunrise Wind case on Monday, I’ll let Heatmap’s Jael Holzman serve as the ring announcer spelling out the stakes of the legal victory: “If the government were to somehow prevail in one or more of these cases, it would potentially allow agencies to shut down any construction project underway using even the vaguest of national security claims. But as I have previously explained, that behavior is often a textbook violation of federal administrative procedure law.”
Germany is set to quadruple its installed solar capacity to 425 gigawatts by 2045, according to a forecast from a trade group representing utilities and grid operators. The projections, Renewables Now reported, mean the country needs to expand its transmission system. Installed onshore wind capacity should triple to around 175 gigawatts by that same year. Battery storage is on track to rise about 68 gigawatts, from roughly 2 gigawatts today. Demand is also set to grow. Data centers, which make up just 2 gigawatts of demand on the grid today, are forecast to balloon to nearly 37 gigawatts in the next 19 years.
Sign up to receive Heatmap AM in your inbox every morning:

In October, the Chinese Communist Party published the framework of its next Five-Year Plan, the 15th such industrial strategy. The National People’s Congress is set to formally approve the proposal next month. But on Monday, the energy analyst John Kemp called the latest five-word phrase, articulated in the form of “formal input” from the party’s Central Committee, “the most succinct statement of China’s energy policy.” Those words: “Building a strong energy nation.” The suggested edits from the committee described “accelerating the construction of a strong energy nation” as “extremely important and timely” and called its “main shortcomings” the ongoing reliance on imported oil and gas.
Unlike in the U.S., where the Trump administration is working to halt construction of renewables, the officials in Beijing boast that China’s “installed capacity of wind and solar has ranked first in the world for many consecutive years.” Like the U.S., the Central Committee pitched the plan as “an urgent requirement” for “gaining the initiative in great power competition.”
Japan is mounting a new push to implement a decade-old plan to extract rare earths from the ocean floor. A state-owned research vessel just completed a test mission to retrieve an initial sample of mineral-rich mud from a location 20,000 feet below the surface, the South China Morning Post reported. The government of Sanae Takaichi wants to start processing metal-bearing mud from the seabed for tests within a year. “It’s about economic security,” Shoichi Ishii, program director for Japan’s National Platform for Innovative Ocean Developments, told Bloomberg. “The country needs to secure a supply chain of rare earths. However expensive they may be, the industry needs them.”
With global negotiations over a licensing framework for legalizing deep sea mining in international waters has stalled, the U.S. just finalized a rule to speed up American permitting for the nascent sector, clearing the way for Washington to fulfill Trump’s pledge to go it alone if the United Nations’ International Seabed Authority didn’t act first.
A week after signing an historic trade agreement with the European Union, India has inked another deal with the U.S. That means the world’s two largest consumer markets are now wide open to Indian industry, which relies heavily on coal. New Delhi isn’t just going to scrap all those coal-fired factories and forges. But the government’s latest budget earmarks about $2.4 billion over five years to speed up deployment of carbon capture equipment across heavy industry, Carbon Herald reported. The plan focuses on steel, cement, power, refining, and chemicals.