You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
On Toyota’s recalls, America’s per-capita emissions, and Sierra Club drama

Current conditions: Drought is worsening in the U.S. Northeast, where cities such as Pittsburgh and Bangor, Maine have recorded 30% less rainfall than average • Temperatures in the Mississippi Valley are soaring into the triple digits, with cities such as Omaha, Nebraska and St. Louis breaking daily temperature records with highs of up to 20 degrees Fahrenheit above average • A heat wave in Mecca, Saudi Arabia, has sent temperatures as high as 114 degrees.
Orsted is offering investors a nearly 70% discount on the new shares issued to raise money to save its American offshore wind projects amid the Trump administration’s aggressive crackdown on the industry. The Danish energy giant won nearly unanimous approval from its shareholders earlier this month for a rights issue aimed at raising $9.4 billion. Shares in the company, which is half owned by the government in Copenhagen, closed around $32 each on Friday. But the offering of 901 million new shares came at a subscription rate of about $10.50 each. Orsted’s projects in the northeastern U.S. already “struggled” with what The Wall Street Journal listed as “supply-chain bottlenecks, higher interest rates, and trouble getting tax credits,” which culminated in the restructuring last year that saw the company “pull out of two high-profile wind projects off the coast of New Jersey.”
The offshore wind industry, as I noted in yesterday’s newsletter, is just starting to fight back. The owners of the Rhode Island offshore project Revolution Wind, which Trump halted unilaterally, filed a lawsuit claiming the administration illegally withdrew its already-finalized permits. After the administration filed a lawsuit to revoke the permits of US Wind’s big project off Maryland’s coast, the company said it intends “to vigorously defend those permits in federal court, and we are confident that the court will uphold their validity and prevent any adverse action against them.” But the multi-agency assault on offshore turbine projects has only escalated in recent months, as the timeline Heatmap’s Emily Pontecorvo produced shows. And Orsted is facing other headwinds. The company just warned investors of lower profits this year after weaker-than-forecast wind speeds reduced the output of its turbines.
Toyota issued a voluntary recall for some 591,000 Toyota and Lexus cars over a slight glitch in the display screen. The 12.3-inch screen could fail to turn on after the car started, or go black while driving. Toyota said it will begin notifying owners if affected vehicles by mid-November. The move came just days after the Japanese auto giant — which owns both its eponymous passenger car brand and the associated luxury line, Lexus — recalled 62,000 electric vehicles, including the Toyota bZ4X SUV and the Lexus RZ300e sedan and its luxury SUV, the RZ450. Subaru, in which Toyota owns a minority stake, is also recalling its electric SUV, the Solterra. With all four EVs, the issue revolved around a faulty windshield defroster that “may not remove frost, ice and/or fog from the windshield glass due to a software issue in the electrical control unit,” the company said in a press release..
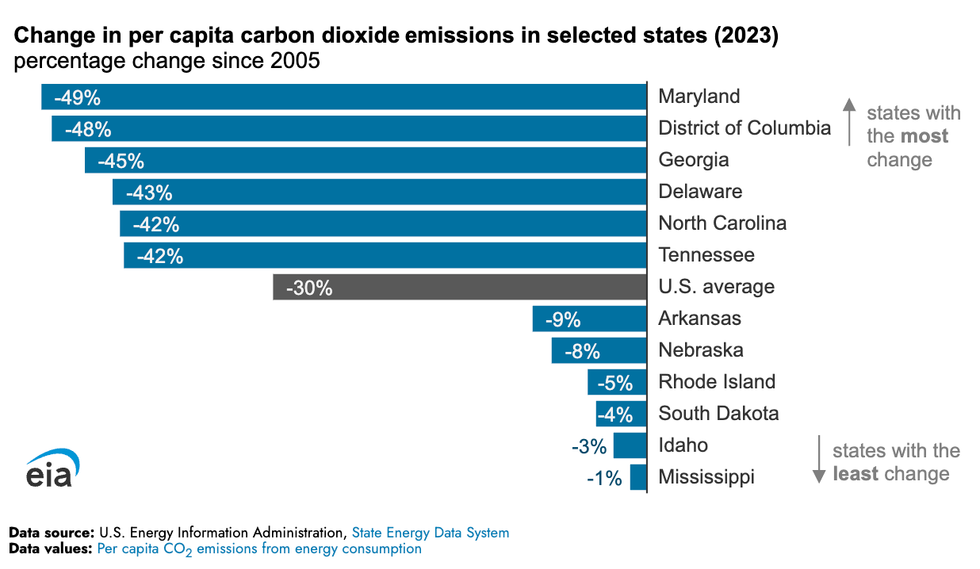
Americans who complain that the U.S. should bear less responsibility for mitigating climate change like to point out that China produces far more planet-heating emissions per year, and that India is not far behind. The cumulative nature of carbon in the atmosphere makes for an easy rebuke, since the U.S. and Western Europe are overwhelmingly responsible for the emissions of the past two centuries. But a less historically abstract response could be that Americans still have by far the highest per capita emissions of any large country. That doesn’t mean the U.S. isn’t making progress on a per capita level, though. Between 2005 and 2023, per capita emissions from primary energy consumption decreased in every U.S. state, with an average drop of 30%, even as the American population grew by 14%, according to a new analysis by the U.S. Energy Information Administration. The dip is largely thanks to the electric power sector burning less coal. Increased electricity generation from natural gas, which releases about half as much carbon per unit of energy when burned as coal, and the growth of renewables such as wind and solar have reduced the need for the dirtier fuel. But the EIA forecasts that overall U.S. emissions are set to climb by 1% as electricity demand increases.
For those keen to shrink their individual carbon output at a much faster pace than American society at large, Heatmap’s award-winning Decarbonize Your Life series walks through the benefits and drawbacks to driving less, eating less steak, installing solar panels, and renovating homes to be more energy efficient.
Following rebellions from various state chapters, the Sierra Club terminated its executive director, Ben Jealous, last month, as I reported here in this newsletter at the time. Now the group has named its new leader: Loren Blackford. The Sierra Club veteran, who served in various senior roles before taking on the interim executive director job last month, won unanimous support from the group’s board of directors on Saturday.
Jealous had previously served as a chief executive of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People and the 2018 Democratic nominee for Maryland governor before becoming the first non-white leader of the 133-year-old Sierra Club. His appointment marked a symbolic turning of the page from the group’s early chapters under its founder, John Muir, who made numerous derogatory remarks about Black and Native Americans. Jealous was accused of sexual harassment earlier this year.
Thermal battery company Fourth Power just announced $20 million in follow-on funding, building on its $19 million Series A round from 2023. While other thermal storage companies such as Rondo and Antora are targeting the decarbonization of high-temperature industrial processes such as smelting or chemical manufacturing, Fourth Power aims to manufacture long-duration energy storage systems for utilities and power producers.
“In our view, electricity is the biggest problem that needs to be solved,” Fourth Power’s CEO Arvin Ganesan told Heatmap’s Katie Brigham. “There is certainly a future application for heat, but we don’t think that’s where to start.” The company’s tech works by taking in excess renewable electricity from the grid, which is used to heat up liquid tin to 2,400 degrees Celsius, nearly half the temperature of the sun’s surface. That heat is then stored in carbon blocks and later converted back into electricity using thermophotovoltaic cells. This latest funding will accelerate the deployment of the startup’s first one megawatt hour demonstration plant.
The tropical storm that later became Hurricane María formed exactly eight years ago today and went on to lay waste to Puerto Rico’s aging electrical system. The grid remains fragile and expensive, with frequent outages and some of the highest rates in the U.S. on the hours when the power is accessible. That has spurred a boom in rooftop solar panels. Now more than 10% of the island’s electricity consumption comes from rooftop solar power. Data released by the grid operator LUMA Energy showed approximately 1.2 gigawatts of residential and commercial rooftop solar had been installed under Puerto Rico’s net-metering regulations as of June 2025. New analysis by the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis found that is equal to about 10.3% of Puerto Rico’s total power consumption — and that’s not counting any off-grid systems.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Julie Liu is converting gas customers to heat pumps, one home at a time.
For Julie Liu, electrifying a home is like putting on an Off- Off- Broadway show.
Working almost entirely alone, Liu serves as producer, stage manager, and director, bankrolling the production, hiring the crew, arranging the logistics, choreographing the action, and dazzling the audience — the homeowner or tenants — along the way. Heat pumps and induction stoves are the stars. Plumbers, HVAC technicians, and insulation specialists sub in for set decorators, sound engineers, and costume designers. Electricians play themselves.
If all goes well, after just a week or so of focused, frenzied work, the show arrives at the grand finale: the capping of the gas line.
Liu has staged this performance more than 25 times since 2023 as the implementation contractor for Electric Advantage, an incentive program in New York offered by the gas and electric utility Con Edison. The program covers 100% of the cost of replacing a building owner’s gas-powered appliances with electric versions, plus installing insulation and air sealing. Although it sounds too good to be true, there’s no catch — except that you have to be lucky enough to own a building that’s eligible for the program and agree to cut your gas connection.
ConEd, as it’s known, delivers natural gas to just over a million customers in the Bronx, Manhattan, Northern Queens, and Westchester County, and qualifies buildings for the program by first identifying sections of pipeline on the peripheries of its network that are due for replacement. Then it runs a cost-benefit analysis. If it would be cheaper to electrify all of the buildings served by a given stretch of gas main than to dig up the street and replace the pipe, the company starts going out to the homeowners and businesses along the line to gauge their interest. If the owners agree to go electric, that’s when Liu steps in.
There’s no established name for what Liu does. “It’s not a home improvement business, it’s not an energy efficiency business, it’s not an HVAC business,” she told me. “It’s about putting together a tight live production.” An apt title would be “electrification contractor” — one of the few, if not the only one of her kind operating in the New York area.
Anyone who has tried to electrify even just one appliance in their home has probably wished they could hire someone like Liu. Between finding an available and trustworthy contractor, navigating quotes and equipment choices, and managing ballooning costs, the process is often frustrating and confusing. It’s a major time commitment, not to mention a big capital investment — not a winning formula for mass adoption.
Liu doesn’t offer her services to just any homeowner, though. She only takes on jobs that come through contracts with utilities and government agencies like the New York State Energy Research and Development Authority, or NYSERDA. Having ConEd’s backing is actually one of the major benefits Liu brings to the work. It means she’s held to stringent standards of performance. Her business fronts the full cost of every Electric Advantage project, putting up tens of thousands of dollars for parts and labor, and only gets paid back by the utility after she demonstrates she’s met every requirement. Engineers check her design choices on the front end and the installations on the back end. A missing anti-tip bracket on a stove once almost cost her an entire $100,000 job, she told me.
Liu is the first to admit that all of this is a huge headache and a tough business model. She also fundamentally believes in this being utility-backed work. When a homeowner pursues a project on their own, the oversight is only as strong as their own ability to vet contractors and manage the job — which, with limited time, information, and leverage in the market, is likely not nearly as strong as Liu’s.
“My conviction is, for the middle class to thrive, we need to have a lot of things that are expensive to do and complex to do to become utilities,” Liu said. “That’s my hypothesis since I was 22.”
In the climate world, a lot of advocates and experts also believe that a utility-run program like Electric Advantage is the key to unlocking an all-electric future, although for slightly different reasons. When random individual homeowners decide to electrify, a shrinking number of remaining gas customers have to pay to maintain the entire pipeline system. If utilities instead strategically prune the gas system while helping customers go electric, the theory goes, it can reduce costs for remaining gas customers while also creating sustained demand for heat pump retrofits. This would help build the workforce necessary to perform them and create economies of scale.
The problem is, ConEd has 4,400 miles of gas mains. In just over two years of running Electric Advantage, the utility has retired about half of one mile. If the program, or similar ones at other New York utilities, were ever to scale from converting about a dozen buildings a year to taking on the whole state, it would need a lot more Julie Lius. ConEd has a small network of contractors who take on projects with more limited scopes, but Liu is the only one doing whole-home decarbonization.
“It’s high capex deployment of complex work in the field, and you have to have people who go into people’s homes and not piss them off,” said Liu. “That’s a very unique business.”
Liu is not exactly a known figure in the world of building electrification. She’s not on social media or otherwise broadcasting her accomplishments or policy views. You won’t find her headlining clean energy panels or on the boards of nonprofits. But Liu has been quietly leading building electrification in the New York area for nearly a decade. Her early belief in heat pumps and determination to bring them to the New York market helped lay the foundation for future programs in the state.
Long before all of this, Liu was a Taiwanese immigrant growing up in Hacienda Heights, Los Angeles. Her family moved to California from Taipei in 1983, just before she entered seventh grade. Liu told me she “did all the good, dutiful-daughter things.” Her family owned a small furniture manufacturing business, and she went to college at Carnegie Mellon for business and industrial design with the intention of helping her dad produce “more inspiring furniture than colonial reproductions.”
Then her education at Carnegie Mellon took her in a different direction. The programs were built around “productivity, process orientation, efficiency, build it cheaper, faster — it’s all about, can you get things done?” She developed an appreciation for utilities, in a broad sense — for how much of the economy was built around “serving more and more people at scale, and serving them better things.”
When she graduated in the mid-1990s, Liu broke the news to her parents that she wanted to get into telecommunications — the hot field at the time. She initially thought she wanted to work at the Federal Communications Commission, but some early mentors warned her that she wasn’t suited for government work and connected her with a job at DirectTV. “You’re too eager to get things done, you’ll be banging your head against the wall,” she recalled being told at the time. “Go to the private sector.”
She went on to spend the next 15-odd years working in satellite television in New York, with a brief interlude starting a software-as-a-service company with an ex-boyfriend that was a little too ahead of its time, according to Liu. She was successful in the industry, but she wasn’t very happy, she told me. She felt like she was “growing couch potatoes.”
By 2014, after a few zigs and zags — business school, a stint at an online real estate startup in Luxembourg — Liu found herself back in New York, unemployed, and spending a lot of her time trying to fix up the rat-infested Brooklyn brownstone she owned. The building had an oil-burning heating system that was draining her bank account. She wanted to install minisplit heat pumps, which were everywhere back in Taiwan, but at the time nobody was really doing that in New York.
In early 2016, still unemployed and living off savings and tenant rent, Liu reached out to the New York State Energy Research and Development Authority, or NYSERDA, to ask about incentives for minisplits, and got connected to a consulting firm called the Levy Partnership that was putting together a proposal for the agency’s first-ever heat pump pilot project. The company told her that brownstones were too difficult and expensive, though, and that it was planning to propose doing the pilot in just a couple of mobile homes on Long Island.
Liu was peeved. Statistically that wouldn’t have even constituted a demonstration, she told me. “That’s not even an alpha in the world of where I came from, satellite communications.” She made a bet with the firm. It was a Thursday. If she could get a bunch of her neighbors to sign letters of interest in the pilot by Monday, she told the company, then “you’re gonna copy and paste that trailer park proposal and say there’s gonna be one for brownstones.”
Needless to say, she got the letters. But Liu didn’t just get the Levy Partnership to expand its proposal or to include her brownstone in the pilot. She convinced it to hire her to help implement the projects. She had looked up the census data on home heating and saw that about half the boilers in the New York City area used expensive heating oil. “I was like, there’s the money,” she told me. She saw that people could lower their bills by switching to heat pumps, while also getting access to better cooling in the summertime. “The business opportunity was just like when I got into satellite, right? It was a transition,” she said.
A week after she and the firm co-submitted their proposal to NYSERDA, Liu incorporated her new company under the name Centsible House. (Her business now goes by the name Carta Electric Homes.) NYSERDA awarded the team the funding a few months later, and by March 2017 they were executing agreements with homeowners to participate. The pilot ran for two years and installed heat pumps in 20 homes throughout Brooklyn, Queens, the Bronx, and Long Island, including Liu’s brownstone. Learnings from those projects informed the development of New York’s statewide Clean Heat program, a partnership between utilities and the state that launched in 2020, offering rebates for heat pumps. Liu was “patient zero,” she told me.
After that, NYSERDA as well as ConEd and another local utility, National Grid, hired Liu for other demonstration projects and heat pump programs. She racked up more than a dozen trainings and certifications from the Building Performance Institute, the Environmental Protection Agency, and various equipment manufacturers, developing expertise in building envelopes, heat pumps, refrigerant systems, and health and safety.
In this piecemeal way, Liu created the job of the electrification contractor from the ground up. By the time ConEd was preparing to launch the Electric Advantage program, Liu had the only contracting business in the area that was essentially purpose-built to take it on.
On a recent Thursday morning in Croton, New York, a suburb of New York City, the show was behind schedule. Liu and I pulled up to a two-family house at the top of a hill to oversee what was supposed to be the “grand finale” day of an Electric Advantage-funded retrofit.
In this case, workers had already put in a new electrical panel, minisplit heat pumps, and a heat pump clothes dryer. Now, electricians would rewire the kitchens with 220-volt outlets for new induction stoves, while a father and son duo of plumbers would put heat pump water heaters in the basement, and a weatherization team would spray insulation around the perimeter of the basement roof and attic floor.
While still sitting in the driveway, Liu called PC Richard, the appliance store, to check on the stove delivery, but the sales rep on the other end was confused — she didn’t have anything scheduled. Liu kept her cool and worked it out, setting a new delivery date for the following day. She turned to me, with sympathy, to let me know this meant I wouldn’t get the denouement she had promised — the cutting and capping of the gas line. She made sure the plumbers could come back on Friday to finish the job.
The planning for this project began many months before, with a knock on the door from a man named Mark Brescia, who manages Electric Advantage for ConEd. Brescia does all the initial outreach, making house calls, phone calls, and sending emails, trying to sell homeowners on the idea. Part of the challenge is that in most cases, unless 100% of the buildings served by a given gas main agree to participate, the company can’t move forward because it won’t be able to retire the pipe. The majority of successful Electric Advantage projects to date have replaced gas mains that were serving a single building.
The company doesn’t sell the program to customers by talking about climate change or emissions. Instead, Brescia explains that the money that would have been spent digging up a gas pipeline could instead be used to buy them brand new appliances. “Customers are excited about the opportunity to make their everyday living more comfortable,” Brescia told me when I asked what the biggest selling point tended to be. They also “no longer worry about having to spend money to replace equipment when it fails.” If the building owner is interested, the next step is for them to schedule a visit from Liu, who does a site evaluation and budgets the job.
Survey data collected by ConEd shows that the most common reason customers decline to participate is a preference for gas cooking. The second is fear of higher electric bills. ConEd makes no guarantees to customers that their overall bills will go down if they participate, but by pairing the new appliances with air sealing and insulation, it tries to ensure the homes will run as efficiently as possible. Liu does her best to provide customer education, walking them through how to operate their heat pumps correctly — running the devices consistently, rather than turning them up and down or on and off, which uses more energy. Customers can also opt in to a special ConEd electricity rate that can save heat pump customers money if they run their systems this way.
“Many customers are still learning about the superior performance and convenience these technologies offer,” Brescia said. But there are also other bottlenecks to expanding the Electric Advantage program. Under New York law, if customers want to keep their gas service, ConEd must oblige them. So unless and until legislators change this “duty to serve,” the program will be hamstrung by customers who turn it down.
The program also currently only targets replacement of leak-prone “radial” mains — pipes that connect to the wider gas distribution system on just one end — as these can be removed without affecting system safety or reliability. The path to expanding it beyond these is uncertain because, as currently structured, that would start to put an untenable burden on customers.
Whether the money goes to a new gas main or a home electrification project, it comes from ConEd’s gas ratepayers through their bills. Whenever ConEd identifies a new batch of mains that meet the program’s specifications, it must submit a benefit-cost analysis to state regulators for approval to pursue the projects before it can begin reaching out to homeowners. In the most recent batch submitted to regulators, for example, replacing the 26 mains identified would have cost nearly $8 million, while the estimated cost of electrifying the buildings served was around $6 million, plus another $1 million in electric system upgrades. The latter is obviously a better deal for customers, even if, as an incentive, ConEd earns back part of the difference as a bonus — also paid for by customers.
Since gas customers pay for the program, it doesn’t totally solve the problem of a shrinking number of customers covering these major investments, even if they are spending less than they otherwise would. And once the most cost-effective projects get taken care of, the expense of electrification will be harder to justify.
Growing the program also depends on having more contractors like Liu to implement it, Brescia told me. Liu has a proven track record of coordinating multiple trades, upholding standards, and educating customers. “Delivering an exceptional customer experience is essential to building trust and driving widespread adoption of electric appliances,” he said.
Throughout the day that I spent with her, Liu vacillated over the question of whether she should or even could expand her business. Working alone enables her to keep costs down, she told me. “I cannot afford to hire additional people,” she said, “because every extra bit of cash flow I end up generating as a profit gets fed to more jobs” — that is, more electrification projects. She also doesn’t want to take on a bunch of high interest debt in order to front more capital to take on more projects.
At other points, she talked about scaling as both important and inevitable. She believes in whole-home electrification — both as a climate solution and as a way to change people’s lives for the better — and wants to see other entrepreneurs like her, especially women, be able to pursue this as a career. She already gets more job leads than she’s able to pursue. She’s starting to think about other fundraising options, such as finding private investors.
Liu also recently started working with a Columbia University masters student to develop software that would help manage and automate all of the “mind-numbing, insane amounts of reporting, submissions, and invoicing” she has to do. Although she already does all of the administrative work digitally, the process has only gotten more arduous as the various programs and companies she works with frequently change what and how she has to report back, whether due to shifting policies or just a round of McKinsey-ification. This is part of what prevents her from being able to take on more work, since all the bureaucratic overhead makes it harder for her to fully close a job and get paid.
Although it’s still very early in the process, her hope is that this kind of software solution could also make it easier for others to get into the field.
“I actually really think this is a very suitable career for every eight-year-old little girl who wants a Barbie’s dream house,” she told me. “If every woman can run a $10 million electrification business, it’d be great. I think we’ll get a lot more done.”
Current conditions: Everywhere from the Midwest to New York City are bracing for snow today • The death toll from flooding in Southeast Asia has eclipsed 1,000 • Temperatures of 95 degrees Fahrenheit in French Guiana, the westernmost border of the European Union, have broken December records.
Data centers’ projected electricity demand has grown so much in the last seven months that BloombergNEF increased its forecast by nearly 40%. In a new analysis published Monday, the consultancy estimated that power demand from U.S. data centers will surge to 106 gigawatts by 2035. That’s 36% higher than BloombergNEF’s outlook published in April, “illustrating just how quickly the sector is expanding,” the consultancy wrote.
The finding illustrates the key challenge facing the grid as data centers complete construction far faster than new gas turbines, nuclear reactors, or even solar panels can be built and patched onto the grid. That reality has put new value on the ability of data centers to power down when the grid is overtaxed, a process Heatmap’s Matthew Zeitlin described as “one weird trick for getting more data centers on the grid.” It also shows why data centers are becoming so politically contentious that the “backlash,” as our colleague Jael Holzman put it, “is swallowing American politics.”
Back in August, I told you about how the Federal Emergency Management Agency suspended staffers who signed onto a letter criticizing President Donald Trump’s plans to gut the agency. Now the Trump administration has reinstated 14 employees placed on administrative leave after their signatures on a letter addressed to Congress were considered “misconduct.” In notices sent to the workers last week, which The New York Times reviewed, FEMA said the “misconduct investigation has been closed, and as a result you are being removed from administrative leave.” The notices did not disclose the probe’s findings, and FEMA’s parent agency, the Department of Homeland Security, didn’t respond to the newspaper’s questions.
The move comes as Illinois Governor JB Pritzker accuses Trump of politicizing disaster relief. The billionaire Democrat, who is widely discussed as a potential presidential candidate in 2028, said the White House rejected two separate requests for $130 million to help households affected by storms in late July and mid-August. E&E News called the denial “unusual” since “the damage documented by the administration was at such a high level that it would routinely lead to a presidential approval for disaster aid.”
The National Renewable Energy Laboratory is dead. Long live the National Laboratory of the Rockies. The lab’s focus on clean energy wasn’t unique. Nuclear power, for example, benefits from receiving the primary focus at sites such as the Idaho, Argonne, and Oak Ridge national laboratories. But the Department of Energy said Monday that the rebranding was part of an effort to broaden NREL’s scope. “The energy crisis we face today is unlike the crisis that gave rise to NREL,” Assistant Secretary of Energy Audrey Robertson, a key deputy of Secretary of Energy Chris Wright (whose unique professional history with Wright I wrote about last week), said in a statement. “We are no longer picking and choosing energy sources. Our highest priority is to invest in the scientific capabilities that will restore American manufacturing, drive down costs, and help this country meet its soaring energy demand. The National Lab of the Rockies will play a vital role in those efforts.”
In its press release, the Energy Department said NREL was formed amid the 1973 oil crisis and that the new name “reflects the Trump Administration’s broader vision for the lab’s applied energy research, which historically emphasized alternative and renewable sources of generation, and honors the natural splendor of the lab’s surroundings in Golden, Colorado.”
Sign up to receive Heatmap AM in your inbox every morning:

In March, the Trump administration approved a $5 billion loan aimed to help restart the French oil giant TotalEnergies’ controversial liquified natural gas project in Mozambique. Though the project initially had international support, the southeast African nation has faced ongoing challenges from extreme weather and an Islamist insurgency, which mounted a deadly terrorist attack that caused work on the project to shut down in 2021. Troops from Rwanda have since come in to secure the area.
On Monday, however, the British government decided to pull its $1.15 billion loan, the Financial Times reported. Initially approved in 2020, the public financing faced fierce pushback from environmental and human rights groups. The Netherlands also announced Monday that it would stop backing the project.
Direct air capture is going big in Japan. On Tuesday morning, the U.S. carbon removal startup Heirloom announced investments from the Development Bank of Japan and Chiyoda Corporation, building on $150 million in Series B funding the company closed last year. That financing round also included investments from Japan Airlines, the industrial giant Mitsubishi Corporation, and the trading behemoth Mitsui & Co. The move comes as Japan’s greenhouse gas-trading system is poised to shift from voluntary participation to mandatory compliance next year, becoming Asia’s second-largest carbon market.
Heirloom had planned to build a giant DAC facility in Shreveport, Louisiana, as Heatmap’s Katie Brigham reported last year. But as our colleague Emily Pontecorvo wrote in October, the Trump administration looks poised to slash federal funding to support construction of DAC plants, making the fate of the Shreveport project unclear.
In the race to develop next-generation technology to harvest water straight out of the air, AirJoule Technologies has a promising lead. The GE Vernova-backed startup is already publicly traded and has deals with major industrial giants such as appliance maker Carrier. Now the company has inked a deal with a hyperscaler to sell water to cool data centers and use waste heat from the servers to power production of that same water. In a press release, the data center company, Nexus Data Centers, said AirJoule’s “waste-heat-to-water approach provides a superior solution by utilizing thermal energy we are already generating to produce high purity water for electricity production and cooling systems.”
Editor’s note: This article has been updated to correct the relationship of the new investments in Heirloom to its previous funding round.
A new working paper from a trio of eminent economists tallies the effects of warming — particularly extreme weather — on Americans’ budgets.
Attempts to quantify the costs of climate change often end up as philosophical exercises in forecasting and quantifying the future. Such projects involve (at least) two difficult tasks: establishing what is the current climate “pathway” we’re on, which means projecting hard-to-predict phenomena such as future policy actions and potential climate system feedbacks; and then deciding how to value the wellbeing of those people who will be born in the decades — or centuries — to come versus those who are alive today.
But what about the climate impacts we’re paying for right now? That’s the question explored in a working paper by former Treasury Department officials Kimberley Clausing, an economist at the University of California, Los Angeles, and Catherine Wolfram, an economist at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, along with Wolfram’s MIT colleague Christopher Knittel.
“We wanted to do the accounting exercise and put it all together,” Wolfram told me. Their method: Simply add up the existing harms of climate change, and boom, there’s your answer.
This approach stands in contrast to the more well-worn modeling and forecasting projects that make up much of the climate harms literature. “Projections about the future are important to make future-oriented policy,” Clausing told me. “But one of the things that’s kind of surprising and interesting to us that I don’t think has been fairly accounted for is how much climate change is already affecting household budgets.”
The paper is meant to intervene in current debates in climate and progressive policy circles over affordability — namely whether policy to address climate change should be put on the back (induction?) burner in light of concerns about how restrictions on fossil fuels or mandates for renewable energy can increase consumer costs, especially utility bills.
“What really motivated the paper, to be honest, is that we noticed that a lot of observers have made statements about climate policy action where they’re like, We’d love to do this, that, or the other thing, but it’s hard to do because the action would fall more heavily on the poor.”
The paper began its life in the fall as part of the semi-annual Brookings Papers on Economic Activity conference before being released this week as a working paper by the National Bureau of Economic Research this week.
Their research has not yet been peer reviewed, but the authors found that even using what they describe as a “narrow accounting” method — looking only at climate impacts from heat and extreme weather on household budgets and mortality — there were “sizable costs to U.S. households from recent climate change patterns.” Those started at $400 per year and went as high as $900 depending on how extreme weather were attributed to climate change, adding up to an aggregate cost of about $50 billion to $110 billion nationwide.
The direct effects of high temperatures may be easier to forecast, but the most extensive damage of climate change, in the United States, at least, runs downstream from high temperatures: storms, floods, and especially wildfires. Clausing and the authors attribute this to the fact that the United States has already made huge investments in adapting to heat in the form of air conditioning. Adaptations for natural disasters — flood walls, moving homes and businesses out of flood plains, universal indoor air purification, building codes for fire prevention — are farther behind.
Looking specifically at cost increases due to health effects from climate change, wildfires are the primary cost center.
“Wildfires have two impacts,” Wolfram told me. “One is the destruction that they cause — we see that in property insurance. The other thing, and that is probably the most surprising to us, is how bad the wildfire smoke has become.”
Those same wildfires, of course, feed into spiraling insurance costs, especially in the West.
Insurance costs top the list of household costs the authors attribute to climate change more broadly, making up more than half of the total. Citing research on homeowners insurance by University of Pennsylvania and University of Wisconsin researchers Benjamin Keys and Philip Mulder, the authors found that “average nominal premiums rose by 33% between 2020 and 2023, with disaster-prone areas experiencing particularly steep increases.”
One frequent argument against climate mitigation policies is that they cost the poor disproportionately; for example, a tax on gasoline has a bigger proportional effect on low-income drivers because a greater portion of their income is spent on fueling their car. But “if you don’t do anything, that has a disproportionate burden on the poor,” Clausing told me. That’s because the costs of dealing with climate change — higher insurance premiums, higher health insurance premiums, higher electric bills for more air conditioning — weigh more heavily on people with lower incomes, she and her co-authors found.
“Poor people may have a harder time and be more likely to be displaced by disasters,” Clausing told me.
The paper’s authors emphasized that their results show the need for climate adaptation as well as emissions-reducing policy, but also that forward-looking adaptation can’t happen if there’s insufficient information. Insufficient information appears to be exactly what some people want. Disputes over climate information have a well known political valence, with federal agencies under the current administration reducing their efforts to collect and publish climate data.
But the private sector has its own reasons not to be completely fulsome with climate-related risk data.
The New York Times reported this weekend, for instance, that the online real estate marketplace Zillow has removed climate risk scores from “more than one million home sale listings,” following complaints from real estate agents.“They’re doing people a disservice,” Clausing told me when I asked her about Zillow’s action.
“Of course, if my home’s on a floodplain, I’m not happy that this information is available to everyone on Zillow,” Clausing said. But the alternative is, “if my home’s in a floodplain, just pretending that that’s the same as if it were in a very safe place.” Which is fine, but it won’t stop your insurance bill from rising.