You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
Over a dozen methane satellites are now circling the Earth — and more are on the way.
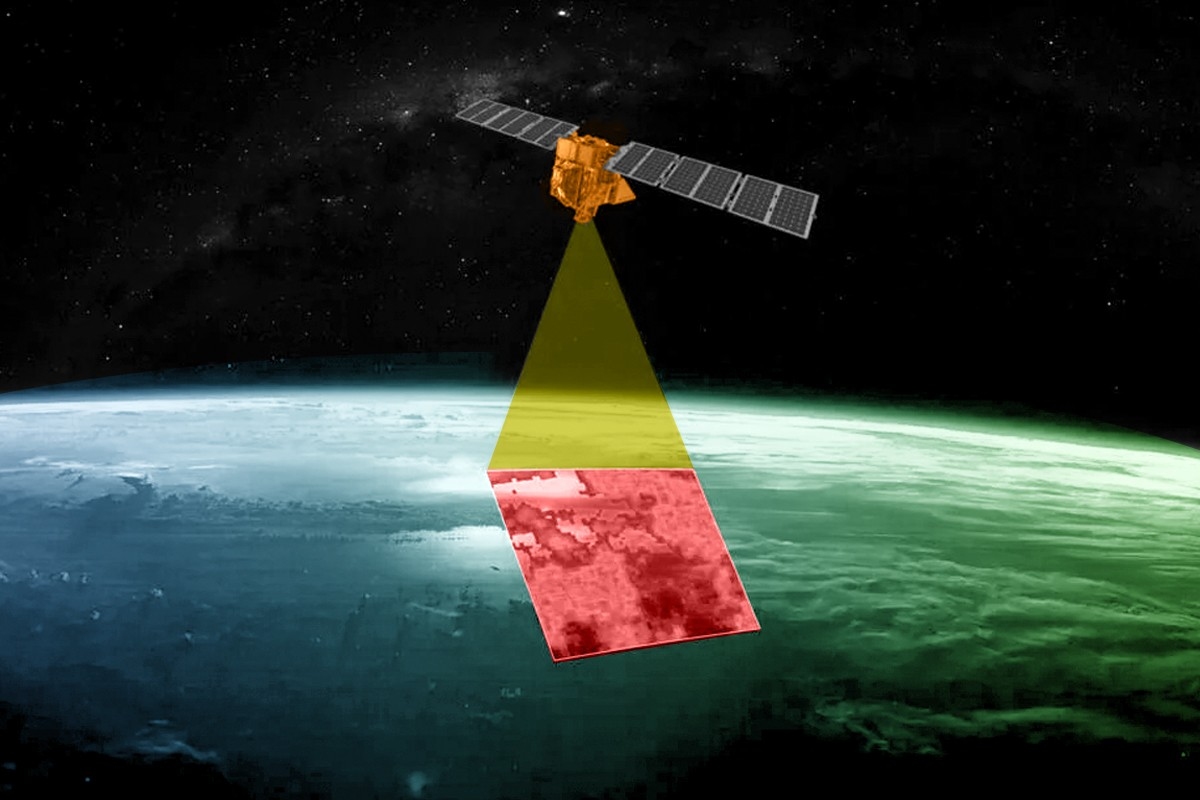

On Monday afternoon, a satellite the size of a washing machine hitched a ride on a SpaceX rocket and was launched into orbit. MethaneSAT, as the new satellite is called, is the latest to join more than a dozen other instruments currently circling the Earth monitoring emissions of the ultra-powerful greenhouse gas methane. But it won’t be the last. Over the next several months, at least two additional methane-detecting satellites from the U.S. and Japan are scheduled to join the fleet.
There’s a joke among scientists that there are so many methane-detecting satellites in space that they are reducing global warming — not just by providing essential data about emissions, but by blocking radiation from the sun.
So why do we keep launching more?
Despite the small army of probes in orbit, and an increasingly large fleet of methane-detecting planes and drones closer to the ground, our ability to identify where methane is leaking into the atmosphere is still far too limited. Like carbon dioxide, sources of methane around the world are numerous and diffuse. They can be natural, like wetlands and oceans, or man-made, like decomposing manure on farms, rotting waste in landfills, and leaks from oil and gas operations.
There are big, unanswered questions about methane, about which sources are driving the most emissions, and consequently, about tackling climate change, that scientists say MethaneSAT will help solve. But even then, some say we’ll need to launch even more instruments into space to really get to the bottom of it all.
Measuring methane from space only began in 2009 with the launch of the Greenhouse Gases Observing Satellite, or GOSAT, by Japan’s Aerospace Exploration Agency. Previously, most of the world’s methane detectors were on the ground in North America. GOSAT enabled scientists to develop a more geographically diverse understanding of major sources of methane to the atmosphere.
Soon after, the Environmental Defense Fund, which led the development of MethaneSAT, began campaigning for better data on methane emissions. Through its own, on-the-ground measurements, the group discovered that the Environmental Protection Agency’s estimates of leaks from U.S. oil and gas operations were totally off. EDF took this as a call to action. Because methane has such a strong warming effect, but also breaks down after about a decade in the atmosphere, curbing methane emissions can slow warming in the near-term.
“Some call it the low hanging fruit,” Steven Hamburg, the chief scientist at EDF leading the MethaneSAT project, said during a press conference on Friday. “I like to call it the fruit lying on the ground. We can really reduce those emissions and we can do it rapidly and see the benefits.”
But in order to do that, we need a much better picture than what GOSAT or other satellites like it can provide.
In the years since GOSAT launched, the field of methane monitoring has exploded. Today, there are two broad categories of methane instruments in space. Area flux mappers, like GOSAT, take global snapshots. They can show where methane concentrations are generally higher, and even identify exceptionally large leaks — so-called “ultra-emitters.” But the vast majority of leaks, big and small, are invisible to these instruments. Each pixel in a GOSAT image is 10 kilometers wide. Most of the time, there’s no way to zoom into the picture and see which facilities are responsible.
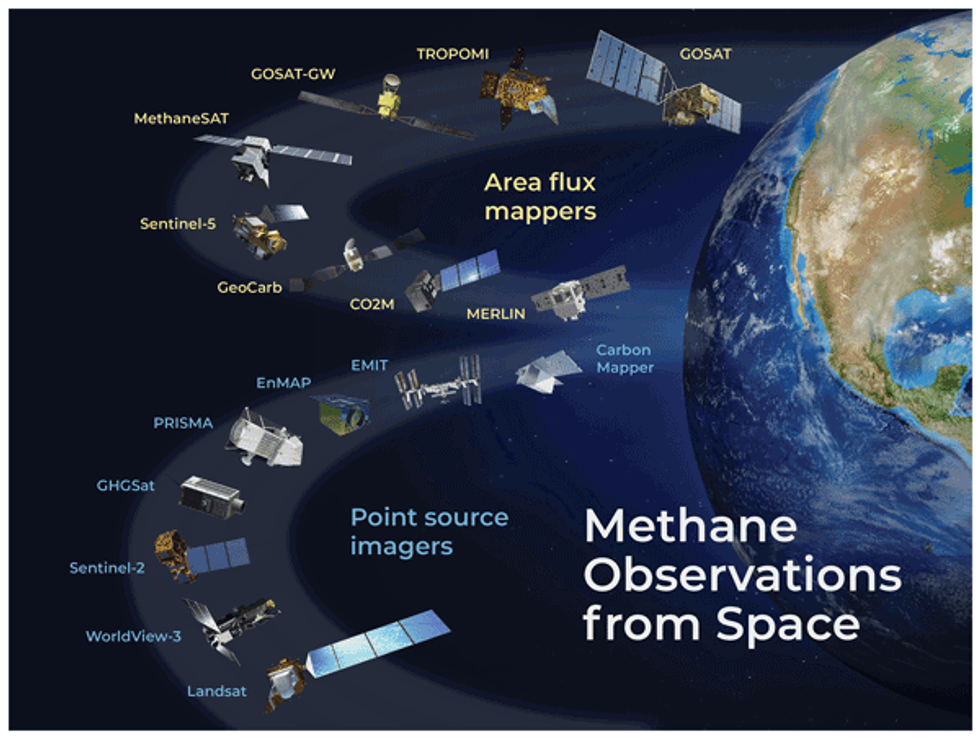
Point source imagers, on the other hand, take much smaller photos that have much finer resolution, with pixel sizes down to just a few meters wide. That means they provide geographically limited data — they have to be programmed to aim their lenses at very specific targets. But within each image is much more actionable data.
For example, GHGSat, a private company based in Canada, operates a constellation of 12 point-source satellites, each one about the size of a microwave oven. Oil and gas companies and government agencies pay GHGSat to help them identify facilities that are leaking. Jean-Francois Gauthier, the director of business development at GHGSat, told me that each image taken by one of their satellites is 12 kilometers wide, but the resolution for each pixel is 25 meters. A snapshot of the Permian Basin, a major oil and gas producing region in Texas, might contain hundreds of oil and gas wells, owned by a multitude of companies, but GHGSat can tell them apart and assign responsibility.
“We’ll see five, 10, 15, 20 different sites emitting at the same time and you can differentiate between them,” said Gauthier. “You can see them very distinctly on the map and be able to say, alright, that’s an unlit flare, and you can tell which company it is, too.” Similarly, GHGSat can look at a sprawling petrochemical complex and identify the exact tank or pipe that has sprung a leak.
But between this extremely wide-angle lens, and the many finely-tuned instruments pointing at specific targets, there’s a gap. “It might seem like there’s a lot of instruments in space, but we don’t have the kind of coverage that we need yet, believe it or not,” Andrew Thorpe, a research technologist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory told me. He has been working with the nonprofit Carbon Mapper on a new constellation of point source imagers, the first of which is supposed to launch later this year.
The reason why we don’t have enough coverage has to do with the size of the existing images, their resolution, and the amount of time it takes to get them. One of the challenges, Thorpe said, is that it’s very hard to get a continuous picture of any given leak. Oil and gas equipment can spring leaks at random. They can leak continuously or intermittently. If you’re just getting a snapshot every few weeks, you may not be able to tell how long a leak lasted, or you might miss a short but significant plume. Meanwhile, oil and gas fields are also changing on a weekly basis, Joost de Gouw, an atmospheric chemist at the University of Colorado, Boulder, told me. New wells are being drilled in new places — places those point-source imagers may not be looking at.
“There’s a lot of potential to miss emissions because we’re not looking,” he said. “If you combine that with clouds — clouds can obscure a lot of our observations — there are still going to be a lot of times when we’re not actually seeing the methane emissions.”
De Gouw hopes MethaneSAT will help resolve one of the big debates about methane leaks. Between the millions of sites that release small amounts of methane all the time, and the handful of sites that exhale massive plumes infrequently, which is worse? What fraction of the total do those bigger emitters represent?
Paul Palmer, a professor at the University of Edinburgh who studies the Earth’s atmospheric composition, is hopeful that it will help pull together a more comprehensive picture of what’s driving changes in the atmosphere. Around the turn of the century, methane levels pretty much leveled off, he said. But then, around 2007, they started to grow again, and have since accelerated. Scientists have reached different conclusions about why.
“There’s lots of controversy about what the big drivers are,” Palmer told me. Some think it’s related to oil and gas production increasing. Others — and he’s in this camp — think it’s related to warming wetlands. “Anything that helps us would be great.”
MethaneSAT sits somewhere between the global mappers and point source imagers. It will take larger images than GHGSat, each one 200 kilometers wide, which means it will be able to cover more ground in a single day. Those images will also contain finer detail about leaks than GOSAT, but they won’t necessarily be able to identify exactly which facilities the smaller leaks are coming from. Also, unlike with GHGSat, MethaneSAT’s data will be freely available to the public.
EDF, which raised $88 million for the project and spent nearly a decade working on it, says that one of MethaneSAT’s main strengths will be to provide much more accurate basin-level emissions estimates. That means it will enable researchers to track the emissions of the entire Permian Basin over time, and compare it with other oil and gas fields in the U.S. and abroad. Many countries and companies are making pledges to reduce their emissions, and MethaneSAT will provide data on a relevant scale that can help track progress, Maryann Sargent, a senior project scientist at Harvard University who has been working with EDF on MethaneSAT, told me.
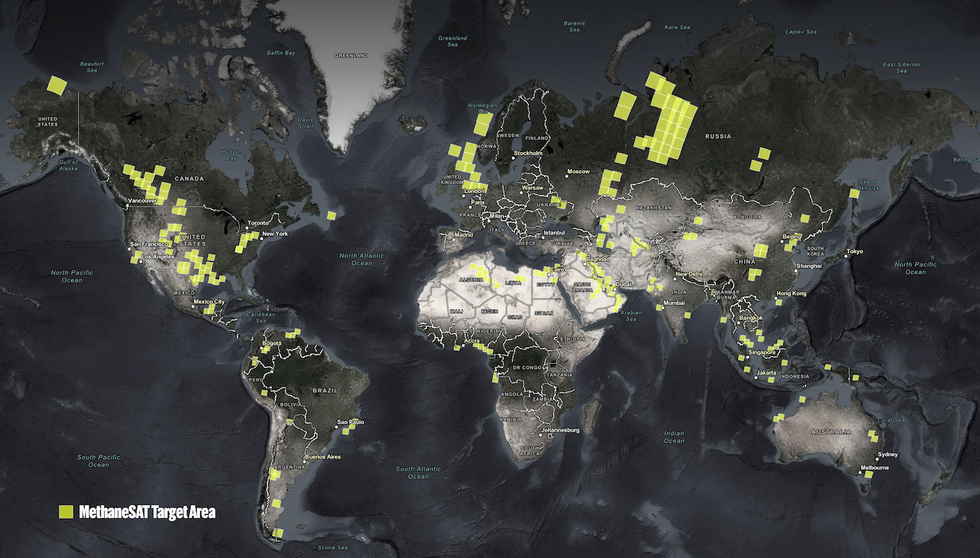
It could also help the Environmental Protection Agency understand whether its new methane regulations are working. It could help with the development of new standards for natural gas being imported into Europe. At the very least, it will help oil and gas buyers differentiate between products associated with higher or lower methane intensities. It will also enable fossil fuel companies who measure their own methane emissions to compare their performance to regional averages.
MethaneSAT won’t be able to look at every source of methane emissions around the world. The project is limited by how much data it can send back to Earth, so it has to be strategic. Sargent said they are limiting data collection to 30 targets per day, and in the near term, those will mostly be oil and gas producing regions. They aim to map emissions from 80% of global oil and gas production in the first year. The outcome could be revolutionary.
“We can look at the entire sector with high precision and track those emissions, quantify them and track them over time. That’s a first for empirical data for any sector, for any greenhouse gas, full stop,” Hamburg told reporters on Friday.
But this still won’t be enough, said Thorpe of NASA. He wants to see the next generation of instruments start to look more closely at natural sources of emissions, like wetlands. “These types of emissions are really, really important and very poorly understood,” he said. “So I think there’s a heck of a lot of potential to work towards the sectors that have been really hard to do with current technologies.”
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
After a disappointing referendum in Maine, campaigners in New York are taking their arguments straight to lawmakers.
As electricity affordability has become the issue on every politician’s lips, a coalition of New York state lawmakers and organizations in the Hudson Valley have proposed a solution: Buy the utility and operate it publicly.
Assemblymember Sarahana Shrestha, whose district covers the mid-Hudson Valley, introduced a bill early last year to buy out the Hudson Valley’s investor-owned utility, Central Hudson Gas and Electric, and run it as a state entity. That bill hung around for a while before Shrestha reintroduced it to committee in January. It now has more than a dozen co-sponsors, a sign that the idea is gaining traction in Albany.
With politicians across the country in a frenzy to quell voters’ growing anxieties over their power bills, public power advocates are seizing the moment to make a renewed case that investor-owned utilities are to blame for rising prices. A victory for public power in the Hudson Valley would be the movement’s biggest win in decades — and could serve as a blueprint for other locales.
Shrestha’s proposal, while ambitious, draws on a long history of public power campaigns in the United States, stretching from the late 1800s to the New Deal 1930s to the present. Most recently, a 2023 referendum in Maine would have seen the state take over its two largest utilities; organizers argued the move would improve service and lower rates. But as Emily Pontecorvo covered for Heatmap, Maine voters rejected the referendum by a nearly 40-point margin. Public power advocates chalked up the loss to Maine’s investor-owned utilities outspending the proposition’s supporters by more than 30 to 1.
The current Hudson Valley campaign has a lot in common with Maine’s. In both, utilities rolled out faulty billing systems that overcharged customers, fueling resentment. Both targeted utilities owned by foreign corporations (Central Hudson is owned by Fortis, a Canadian company; Central Maine Power is owned by a subsidiary of Iberdrola, a Spanish company, while Versant, another utility in the state, is a subsidiary of Enmax, a Canadian corporation). And both took place amid rate hikes.
Shrestha has spent the past year working her district, holding town halls to sell the bill to her constituents. At each one she presents the same schpiel: “I gave people a little brief story of each of the different notable fights, from Long Island Power Authority to Massena to Maine to Rochester,” she told me, “because I also want people to understand that our fight is not happening in isolation.”
Public power advocates in the Hudson Valley are certainly applying lessons from the Maine defeat to their own campaign. For one, the venue is paramount. This time, public power campaigners are gearing up for a fight in the statehouse rather than the ballot box.
Unlike a ballot proposition, state legislation typically doesn’t attract millions of dollars in television and radio advertising from deep-pocketed utilities. Sandeep Vaheesan, a legal scholar and public power expert, told me that passing a law may be a more feasible route to victory for public power.
“Legislative fights are more winnable because referenda end up being messaging wars,” Vaheesan told Heatmap. “And more often than not, the side that has money can win that war.”
The message itself is also key. One lesson Maine organizers walked away with is that affordability is a winning strategy — an insight that has only gotten more robust over the past several months.
The Climate & Community Institute, a progressive climate think tank, released a report in November reflecting on the Maine referendum that put numbers to the campaigners’ intuition. “While climate change was an issue for many in our polling,” the report states, “it often took a backseat to problems Mainers continue to experience, like rising costs and power shutoff risks.” The group also pointed me to a survey it did in the fall of 2023 — years before data centers and energy demand became top-tier political issues — in which 69% of voters said they were worried about climate change, but 85% said they were worried about energy costs.
So how could public power lower costs for ratepayers?
“If you take shareholders out of the picture — if you replace private debt with cheaper public debt — you can lower rates pretty quickly and bring energy bills down,” Vaheesan argued.
The proposed Hudson Valley Power Authority wouldn’t have a profit motive; its return on equity, currently 9.5% for Central Hudson, would be reduced to zero. As a public entity, HVPA could also access capital at much lower interest rates than a private company and would be exempt from state and federal taxes.
Investor-owned utilities also inflate customers’ bills with unnecessary capital spending, Shrestha told me.
“The only way they can drive up their profits is by expanding their capital infrastructure, which is a very rare and unique characteristic of this industry,” she said, noting that a company like Walmart can’t make a profit by overspending. “So we’re stuck with a grid that is unnecessarily bloated and cumbersome and not at all efficient.”
A feasibility report commissioned by HVPA supporters and released in December estimates that ratepayers would see their bills go down by 2% in the first year after the public takeover — and result in 14% lower bills by 2055. A competing report, issued by opponents of the legislation, claimed the delivery portion of charges could increase by 36% under HVPA due to the cost of buying out Central Hudson, though advocates criticized the report for failing to publish any data.
Hudson Valley public power supporters can take another lesson from Maine to counter a combative utility. The two Maine utilities estimated the cost for the state to acquire them would be billions of dollars more than what public power advocates estimated — though in a televised debate, an anti-referendum representative refused to defend the stated numbers until the moderator instructed her to do so.
Lucy Hochschartner, the deputy campaign manager for Pine Tree Power (Maine’s proposed state-run utility), said she often assuaged voters’ concerns over the acquisition price by comparing it to buying a house.
“Right now we pay a really high rent to [Central Maine Power],” Hochschartner told us. “We pay them more than a billion dollars in revenue a year through our electric grid. And instead we could have moved to a low-cost mortgage.”
With a public acquisition, the cost of buying the electrical and gas systems would be funded through revenue bonds, paid off through customers’ bills over time. However a spokesperson for Central Hudson, Joe Jenkins, said the company would launch a legal battle rather than agree to sell its assets to New York State.
“Fortis has made no inclination that the company is for sale,” Jenkins told me. “So to take over a company by means of eminent domain, I believe that our parents would want to see this through a court.”
While a legal battle could be costly, public power advocates say the cost of inaction is also high. Winston Yau, an energy and industrial policy manager at the Climate & Community Institute, told me that publicly run utilities are better equipped to lead the transition to carbon-free power and adapt to a warming and more turbulent climate.
“Climate disasters and extreme weather events and heat waves are a major and increasing cause of rising utility bills,” Yau said. “In the coming decades, a significant amount of new investment will be needed.”
It’s an idea with bipartisan appeal, but AOC’s former policy adviser argues that the scale of the data center problem is too big for that.
Last night, between the trumpeting of fossil fuels and the lengthy honors awarded to both veterans and hockey players, President Trump devoted a portion of his State of the Union address to announcing a “ratepayer protection pledge,” under which big tech companies pay for their own power plants for data centers — a show of how central energy prices are becoming to today’s affordability debate.
Electricity in the United States is rapidly becoming expensive and unreliable. Vast swaths of the United States are at elevated risk of outages. January’s winter storms wiped out power for millions of Americans from Louisiana to Brooklyn. In 2025, utilities requested a record $31 billion in rate increases from captive customers. Gas and electricity prices are the two highest drivers of inflation.
The main driver of these new stressors on the grid: the expected $6.7 trillion to be deployed in data centers by 2030.
Policymakers at all levels of governments are coalescing on a strategy for dealing with rising data center demand that mirrors Trump’s ratepayer protection pledge: “bring your own generation,” or BYOG. Bipartisan bills introduced in Washington by Senators Chris Van Hollen, and Josh Hawley and Richard Blumenthal; and by Representatives Rob Menendez and Greg Casar, among others, would require hyperscalers like Meta, OpenAI, and Microsoft to pay for their own power plants and grid upgrades in order to plug in. Michigan, Oregon, Florida, Washington, Georgia, Illinois, and Delaware are all at various stages of enacting BYOG legislation for data centers.
BYOG would create something like a regulatory sandbox for data centers, insulating utilities and ratepayers from the risks of data center demand. But while efforts at consumer protection are important, these policies do not grapple with the scale of data center deployment.
A sandbox won’t withstand a tidal wave. Over the next five years, the equivalent of 17 to 32 New York Cities’ worth of electricity demand is expected to be added to the grid, more than half of which will come from data centers. This incredibly wide estimate means that generators risk overbuilding.
Amidst all this uncertainty, BYOG does not address who pays for new capacity in the event the AI bubble bursts and energy infrastructure is left stranded. Neither does BYOG address the drastically mismatched lifetimes of the chips powering AI (one to three years) and power plants (25 to 30 years). The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission expects 22 New York Cities’ worth of generation to be added to the grid by 2028. Who pays for all of this generation in a decade if even 5% of projected data center demand disappears?
AI is a promising technology, but that does not prevent it from being overvalued. Policymakers must consider the risks when data centers eventually disconnect from the grid, not just when they interconnect. This means ensuring that ratepayers and taxpayers are not left footing the bill for stranded energy infrastructure if data centers disconnect prematurely.
Rather than cordoning off data centers from the rest of the electricity market, policymakers should take a stronger hand in planning these deployments for social and economic benefit. Colocating datacenters with energy-intensive industries and requiring long-term commitments from hyperscalers are more efficient solutions that would also make new data centers more politically palatable.
Public sentiment has turned overwhelmingly against data center development. These vast facilities create relatively few jobs beyond their construction, but colocated with the manufacture of energy-intensive products like aluminum, steel, or fertilizer, suddenly they’re supporting employment. Colocation will also help diversify economic growth. Data center investment was responsible for a whopping 92% of GDP growth in the first half of 2025, creating a potentially dangerous dependency on continued expansion.
There are also simple legal guardrails that can provide a first line of defense against stranded costs. One is requiring long-term power purchase agreements between hyperscalers and generators. Thirteen bipartisan governors and the Trump administration recently urged the country’s largest grid operator, PJM Interconnection, to require 15-year generation contracts for hyperscalers. Notably, Van Hollen’s bill would only require states to “consider” the extension of “minimum utility contract lengths,” while the Hawley/Blumenthal and Menendez/Casar bills make no mention of contract length or stranded costs.
Hyperscalers can also curtail usage during peak demand, a policy that has seen bipartisan support in Texas. A now-famous study from Duke University last year found that if data centers were to curtail 1% of their usage during peak hours, they could avoid installing 126 gigawatts of new generation — that’s 21 New York Cities’ worth. Lawmakers have since taken to the idea. Several states are considering mandating so-called “demand response” programs, and Representatives Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez and Kathy Castor inserted a federal study on demand response into the appropriations bill Trump signed in January.
Regardless of how it’s done, ratepayers should not pay full freight for the tidal wave of infrastructure coming online, and most utility balance sheets should not be exposed to that risk. BYOG’s flaws have more to do with what it leaves out — namely that the planning of significant parts of our economy and electric system is left to tech companies, and little thought is given to the long-term ramifications of overbuilding. Rather than deal reactively with the nasty politics of a bailout, policymakers should make muscular interventions now to reduce risks for ratepayers and taxpayers.
Energy markets are not free markets. For the past century they have been heavily regulated at the state, regional, and federal level. Any discomfort with planning (or “statutory tools”) must be set aside if policymakers are going to efficiently manage the growth of data centers.
On Cybertruck deaths, Texas wind waste, and American aluminum
Current conditions: Yet more snow is dusting New York City with at least an inch fallen already, though that’s set to turn into rain later in the morning • Authorities in Saudi Arabia issued a red alert over a major sandstorm blasting broad swaths of the desert nation • Heavy snow blanketed Romania, halting transportation and taking down power lines.

In his State of the Union address Tuesday night, President Donald Trump unveiled what he called the new “ratepayer protection pledge.” Under the effort, the White House will tell “major tech companies that they have the obligation to provide for their own power needs.” By mandating the bring-your-own-generation approach, the Trump administration is endorsing a push that’s been ongoing for months. The North American Electric Reliability Corporation, the U.S. grid watchdog, called for data centers to build their own generators. An industry-backed proposal in the nation’s largest power grid would do something similar. “This is a unique strategy,” Trump said. “We have an old grid that could never handle the [amount] of electricity that’s needed.” With tech companies constructing new power plants, Trump said, towns should welcome data center projects that could end up lowering electricity rates by inviting more power onto the local grid.
The political blowback to data centers is gaining strength. It is, as my colleague Jael Holzman wrote recently, “swallowing American politics.” On the right, Senator Josh Hawley, the populist Republican from Missouri, introduced legislation this month to restrict data center construction. On the left, Senator Bernie Sanders, the democratic socialist from Vermont, reiterated his proposal this week to halt all data center projects. In the center, Pennsylvania Governor Josh Shapiro, a Democrat with unusually strong support among his state’s GOP voters, recently outlined plans for a more “selective” approach to data centers, as I reported in this newsletter.
Trump isn’t the only Republican pushing back against the data center blowback. On Tuesday, Mississippi Governor Tate Reeves delivered an impassioned defense of his state’s data center buildout. “I understand individuals who would rather not have any industrial project in their backyard. We all choose where to live, whether it’s urban, suburban, agrarian, or industrial. I do not understand the impulse to prevent our country from advancing technologically — except as civilizational suicide,” Reeves wrote in a post on X. “I don’t want to go gently. I love this country, and want her to rise. That’s why Mississippi has become the home of the world’s most impressive supercomputers. We are committed to America and American power. We know that being the hub of the world’s most awesome technology will inevitably bring prosperity and authority to our state. There is nobody better than Mississippians to wield it.”
Replying to Sanders’ proposal, Reeves said he’s “tempted to sit back and let other states fritter away the generational chance to build. To laugh at their short-sightedness. But the best path for all of us would be to see America dominate.”
Sign up to receive Heatmap AM in your inbox every morning:
The subcompact Ford Pinto gained infamy in the 1970s for its tendency to explode when the gas tank ruptured in a crash. The Ford Motor Company sold just under 3.2 million Pintos. By the official death toll, 27 people died as a result of fires from the vehicles exploding. Tesla has sold more than 34,000 Cybertrucks; already, five people have died in fire fatalities.
That, according to a calculation by the automotive blog Fuel Arc, means the Tesla Cybertruck has 14.52 deaths per 100,000 units, compared to the Ford Pinto’s 0.85 deaths. “The Cybertruck is far more dangerous (by volume) than the historic poster child for corporate greed and grossly antagonistic design,” Fuel Arc’s Kay Leadfoot wrote. “I look forward to the Cybertruck being governmentally crash-tested by the NHTSA, which it has not been thus far. Until then, I can’t recommend sitting in one.” That is, however, based on the lower death toll figure for the Pinto. Back in 1977, Mother Jones published a blockbuster cover story under the headline “Pinto Madness” claiming that the number of deaths could be as high as 900.
Texas accused the recycling company Global Fiberglass Solutions of illegally dumping thousands of wind turbine blades near the central town of Sweetgrass. The company allegedly hired several subcontractors to break down, transport and recycle the blades, but failed to properly dispose of the waste and instead created what Windpower Monthly called a “stockpile” of more than 3,000 blades across two sites in the town. Attorney General Ken Paxton, a Republican candidate for U.S. Senate, seized on a Trumpian critique of the energy source, saying the dumps damage “beautiful Texas land and threaten surrounding communities.”
Off the Atlantic Coast, meanwhile, Orsted is at a transitional moment for two of its offshore wind projects. The Danish developer just brought the vessel Wind Scylla to port after completing the installation of turbines at its Revolution Wind project in New England. The boat is headed to New York next to start installing the first wind turbine at Sunrise Wind, according to OffshoreWIND.biz.
Last month, I told you that Century Aluminum inked a deal with Emirates Global Aluminum to build the first smelter in the U.S. in half a century in Oklahoma. On Tuesday, the U.S. Aluminum Company, a local firm in the state, joined the project, signing an agreement to “explore the development of an aluminum fabrication plant near the new smelter.” If completed, the project — already dubbed Oklahoma Primary Aluminum — would roughly double U.S. primary production of the metal.
The Biden administration had placed what Heatmap’s Matthew Zeitlin called “a big bet on aluminum” back in 2024. By spring of last year, our colleague Katie Brigham was chronicling the confusion over how Trump’s tariffs on aluminum would work. With the recent Supreme Court ruling upending Trump’s trade policies, that one may remain a headscratcher for a little while longer.
Another day, another landmark energy investment from Google. This time, the tech giant has made a deal with the long-duration energy storage startup Form Energy to deploy what Katie wrote “would be the largest battery in the world by energy capacity: an iron-air system capable of delivering 300 megawatts of power at once while storage 30 gigawatt-hours of energy, enabling continuous discharge for 100 hours straight.” The project will power a data center in Minnesota. “For all of 2025, I believe the installed capacity [added to the grid] in the entire U.S. was 57 gigawatt-hours. And in one project, we’re going to install 30 gigawatt-hours,” Form CEO Mateo Jaramillo told Katie. “What it highlights is, once you get to the 100-hour duration, you can really stop thinking about energy to some extent. “