You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
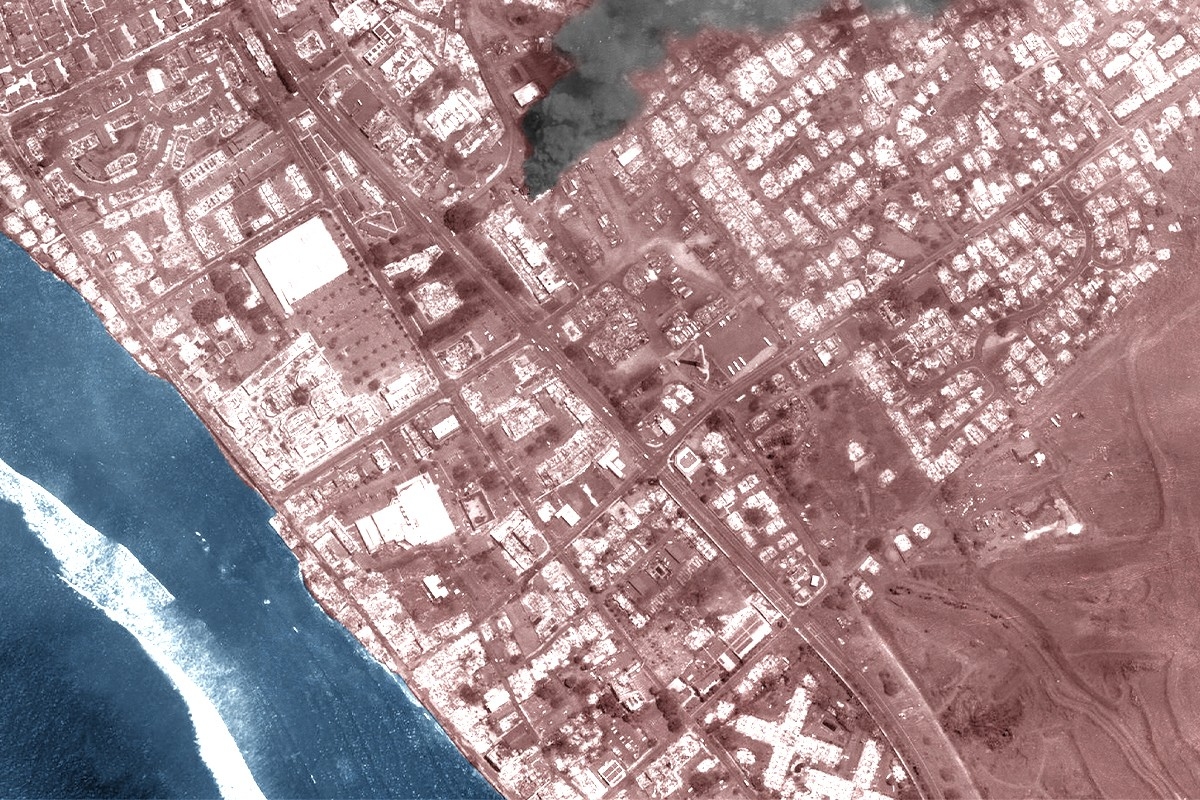

“Unbelievable. This looks like Baghdad or something.”
The shocked voice in the viral flyover video of Lahaina, Hawaii, belongs to helicopter tour pilot Richard Olsten, who attempted on Wednesday to find the words to describe the devastating transformation of the land below. Grass fires that burned on the fringes of the western Maui town early Tuesday, and were initially believed to be contained, have been fanned by powerful winds toward populated areas, fueling a fast-moving conflagration that took both residents and rescue workers by surprise.
Aerial video shows wildfire devastation in Lahaina, Mauiwww.youtube.com
The fires have killed at least 93 people, although authorities caution that the toll could rise as search-and-rescue efforts are ongoing. Here’s what you need to know about the Maui fires.
The cause of the fires is not known, although they appear to have originated as brush fires that did not draw much initial alarm. But high winds that NOAA and the National Weather Service attribute to Hurricane Dora, some 600 miles to the south, knocked out power on the island, grounded firefighting helicopters, and fanned deadly flare-ups that took residents by surprise.
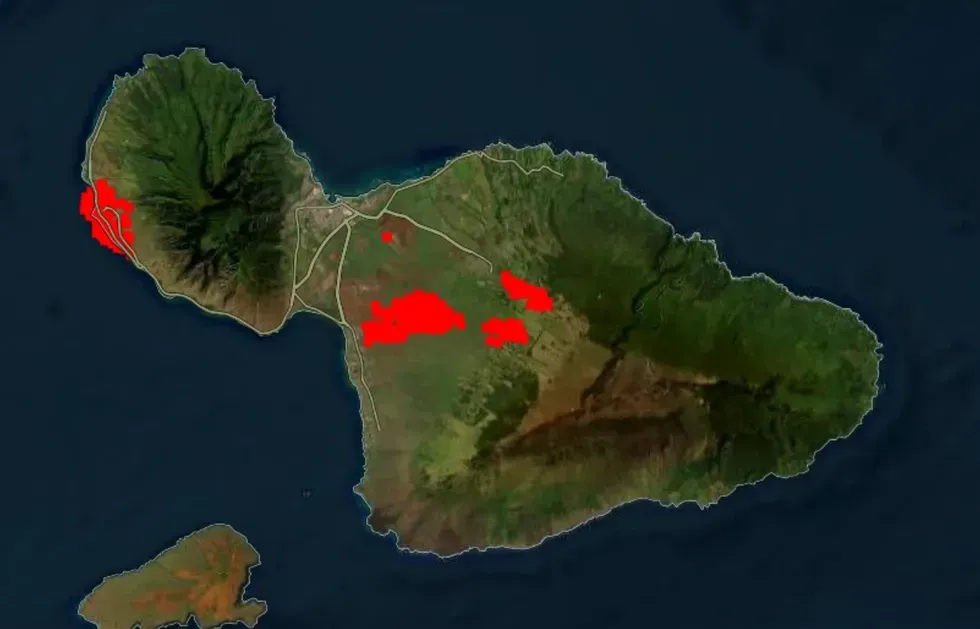
The location of the Maui fires.
NASA/FIRMS
The location of the fires as of August 10 at 12:30 PM ET are above. You can follow the location of the fires using NASA’s Fire Information for Resource Management System (FIRMS) here. There are also a number of small fires burning on Hawaii’s Big Island.
More than 271 structures have been impacted, according to the Maui County website, and “thousands” of acres have burned. More than 11,000 tourists have been evacuated from Maui and some 2,100 residents are reportedly being housed in emergency shelters.
“Local people have lost everything,” Jimmy Tokioka, the director of Hawaii’s Department of Business, Economic Development and Tourism, told the press. “They’ve lost their house. They’ve lost their animals. It’s devastating.”
Lahaina, the former capital of the Kingdom of Hawaii and a place of historic and cultural importance to Native Hawaiians, has been “wiped off the map,” witnesses say. A 150-year-old banyan tree, thought to be the oldest in the state, has been scorched by the fire but appears to still be standing.
With 93 dead, the fires are one of the deadliest natural disasters in Hawaii’s recorded history and one of the deadliest modern U.S. wildfires. Authorities have warned that the death toll could rise.
As of Thursday, helicopters have resumed water drops and at least 100 Maui firefighters are working around the clock to stop the fire.
Horrifying. Survivors said they had little warning before the fire was upon them, with some being so taken by surprise that they had to jump into the ocean to escape the flames.
“While driving through the neighborhood, it looked like a war zone,” one Lahaina resident told USA Today of his escape. “Houses throughout that neighborhood were already on fire. I’m driving through the thickest black smoke, and I don’t know what’s on the other side or what’s in front of me.”
Another evacuee told Maui News she had no time to think through what to pack. “I grabbed some stuff, I put some clothes on, got some dog food. I have a giant tortoise. I couldn’t move him so I opened his gate so he could get out if he needed to,” she said.
“I was the last one off the dock when the firestorm came through the banyan tree and took everything with it,” another survivor recounted to the BBC. “And I just ran out to the beach and I ran south and I just helped everybody I could along the way.”
Hawaii’s brush fires tend to be smaller than the forest fires in the Western United States, but the proliferation of non-native vegetation, which dries out and is particularly fire-prone, has fueled a rise in recent blazes, The Washington Post reports.
There has been a 400% increase in wildfires “over the past several decades” in Hawaii, according to a 2022 report by Hawaii Business Magazine. “From 1904 through the 1980s, [University of Hawaii at Mānoa botanist and fire scientist Clay Trauernicht] estimates that 5,000 acres on average burned each year in Hawaii. In the decades that followed, that number jumped to 20,000 acres burned.”
Though Hawaii is imagined to be lush, wet, and tropical, Maui is experiencing moderate to severe drought, which has dried out the non-native grasses that make particularly good wildfire fuel. And while it is tricky to link Hawaii’s current drought directly to climate change, drought conditions in the Pacific Islands are expected to continue to increase along with warming.
Stronger hurricanes are also more likely due to climate change, and it was the strong winds buffeting Maui that made the fires this week so destructive and fast-moving. “These kinds of climate change-related disasters are really beyond the scope of things that we’re used to dealing with,” University of British Columbia researcher Kelsey Copes-Gerbitz told The Associated Press. “It’s these kind of multiple, interactive challenges that really lead to a disaster.”
The Hawaiʻi Tourism Authority has asked that “visitors who are on non-essential travel … leave Maui, and non-essential travel to Maui is strongly discouraged at this time.” If you have plans to travel to West Maui in the coming weeks, you are “encouraged to consider rescheduling [your] travel plans for a later time.”
This article was last updated on August 13 at 8:32 AM ET.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
On fusion’s big fundraise, nuclear fears, and geothermal’s generations uniting
Current conditions: Severe thunderstorms across the Great Plains are raising the risk late into Friday night of nocturnal tornadoes, which are nearly three times as deadly as daytime twisters • The Red and Mississippi rivers are poised swell as clouds dump up to 4 inches of rain on the region • Strong katabatic winds up to 65 miles per hour are blasting Antarctica with blizzard conditions.

Back in November, I told you that China’s emissions had stayed steady in the third quarter of last year, extending a flat or falling trend that began in March 2024. Earlier this week, the Financial Times reported that the country’s solar boom had balanced out an increase in planet-heating pollution from other sectors of the world’s second-largest economy. So Beijing’s announcement yesterday that it would slightly water down its climate goals for the rest of the decade came with only muted criticism. In its latest five-year plan published Thursday, the People’s Republic pledged to cut carbon emissions per unit of gross domestic product by 17% between 2026 and 2030, down from the 18% set out in the document that covered the 2021 to 2025 period. Lauri Myllyvirta, lead analyst for the Helsinki-based Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air, told Climate Home News the target was “underwhelming.” Li Shuo, director of the China Climate Hub at the Asia Society Policy Institute, told the publication that China’s decarbonization efforts were stymied by the pandemic and slowing economic growth, noting that the new target “indicates a quiet recalibration, effectively acknowledging how difficult the goal has become.”
In the United States, meanwhile, scientists published a first-of-a-kind assessment of the health of American nature and wildlife on their own after the Trump administration pulled its support from the project commissioned by the Biden administration. The 868-page draft went live this week, seeking public comment and scientific review. The findings paint what The New York Times called a “grim” picture: “Freshwater ecosystems across the country are in crisis, ‘overdrawn, polluted, fragmented and invaded.’ Marine and terrestrial ecosystems are degraded, with reduced biodiversity. An estimated 34% of plant species and 40% of animal species are at risk of extinction.”
On Wednesday, the Department of the Interior ended the Trump administration’s first Alaskan oil and gas lease sale without a single bidder for more than a million acres of federal waters in the Cook Inlet. In a statement, the Sierra Club called the auction, which it opposed, “a big fat failure” and a repeat of the last offshore lease sale in Alaska in 2022, which brought in just one bid. At the time, the Biden administration tried to cancel the lease, citing a lack of interest from industry. Senators Lisa Murkowski and Dan Sullivan accused Biden of “blatantly lying to the American people” and presenting a “fantasy” about industry demand as part of a broader attempt to “shun U.S. energy production.” In statements to the television outlet KTUU in Anchorage, both Republicans called this week’s results “disappointing.”
Get Heatmap AM directly in your inbox every morning:
Heatmap’s Jeva Lange had a big scoop yesterday: The embattled Federal Emergency Management Agency suspended all of its training and education programs for emergency managers across the country — except for those “directly supporting the 2026 FIFA World Cup.” Jeva got her hands on an internal communication from the agency’s leadership directing the National Training and Education Division to “cease course delivery operations” for the nearly 300 trainings it provides to local first responders and emergency managers. “In states like California, where all public employees are sworn in as disaster service workers, jurisdictions have been left without the resources to train their employees,” she wrote.
Outgoing Secretary of Homeland Security Kristi Noem, the first cabinet chief fired since Trump returned to office, “all but killed” FEMA by shredding its budgets, as Grist put it. Long delays for FEMA assistance in disaster-struck states such as North Carolina spurred Republican fury at Noem, The New York Times reported. Whether her successor, Oklahoma Senator Markwayne Mullin, represents a significant change from Noem’s worldview remains to be seen.
Sign up to receive Heatmap AM in your inbox every morning:
Amazon, Google, JPMorgan Chase and other corporate giants signed onto a $100 million effort to fund projects that cut climate superpollutants such as methane, black carbon, and refrigerant gases. The campaign, called the Superpollutant Action Initiative, is set to supply financing through 2030. For a taste of what it might mean, Axios reported that “Randy Spock, Google's carbon credits and removals lead, cited potential project areas like cutting landfill methane and stemming the release of refrigerant gases when HVAC systems are replaced.”
The announcement came a day after both Amazon and Google joined the White House’s “ratepayer protection pledge,” which Politico called the “build your own power plant pledge.” Aside from the obvious fact that it’s voluntary, the pact has limits. Namely, a lot of decisions about power plants are dictated by local regulations and regional electricity markets.
BYD just revealed a new battery that InsideEVs said “makes Western EV tech look ancient.” The second generation of its Blade battery can charge from 10% to 70% in just five minutes and 10% to 97% in 10 minutes. The release comes as sales at the world’s largest electric automaker decline amid mounting competition in the Chinese market.
The global asset manager Galvanize has raised $370 million for a new subsidiary focused on helping “undercapitalized” commercial buildings slash energy bills. The Galvanize Real Estate Fund will target buildings “in supply-constrained, high growth U.S. markets that represent attractive opportunities to drive net operating income growth.” The company will then come into the buildings with “decarbonization and resilience interventions — which include a combination of on-site renewable energy generation, energy efficiency retrofits, and electrification — aim to protect against rising costs and reduce building emissions.”
Rob hosts a Heatmap roundtable about Iran, Ukraine, long-duration batteries, seabed mining, and more.
We’re watching a new global energy crisis unfold in the wake of America and Israel’s campaign in Iran — and it could rapidly spiral into other industries and commodities. At the same time, there’s been legitimately promising news on iron-air batteries, suggesting the cheap and long-term energy storage technology might be ready for take-off.
Rob is joined by Heatmap staff writers Matthew Zeitlin and Katie Brigham, as well as Heatmap’s deputy editor Jillian Goodman, to discuss the busy news week. They discuss whether we’re looking at two different (but linked) energy crises, gauge how insulated the U.S. economy actually is, and share which energy news stories have gotten lost in the shuffle.
Shift Key is hosted by Robinson Meyer, the founding executive editor of Heatmap News.
Subscribe to “Shift Key” and find this episode on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, Amazon, or wherever you get your podcasts.
You can also add the show’s RSS feed to your podcast app to follow us directly.
Here is an excerpt from their conversation:
Robinson Meyer: As I’ve been thinking about this story, I hadn’t realized, Matt, the degree to which the two most volatile commodity prices are affected by this, in that this is now both an energy inflation story and a food inflation story because of fertilizer. I think as I’ve been thinking about this domestically, because of how the U.S. plugs into the global economy and because U.S. liquified natural gas export is basically already running at full bore — we’re exporting it basically as much natural gas as we can with the system that we have, which means that there’s not a ton of passthrough that could happen into our domestic natural gas prices — we’re kind of looking at a system — and you should correct me if this is wrong, but as I think through what, politically, the ramifications of the war are, at least as far as energy goes, obviously, this is globally going to be a gas and fertilizer story and energy security story.
Domestically, this is probably far more likely to be an oil price story. You know, gas prices now are like at $3.25 nationally. They could very well be higher by the time we release the episode. Conventional wisdom is that gas prices don’t really matter until they get above $3.50. It’s nice to have them for a president below $3, and it’s bad to have them above $4. And so they were previously, the U.S. average was right below $3. Now it’s like $3.25. It’s gone up $0.25 in just a few days. And so as I think about what are the constraints on the Trump administration’s economic policymaking? What are the constraints on the president’s decision-making insofar as he feels any constraints from the economy? Domestically, it’s far more of an oil story than it is a gas story.
Matthew Zeitlin: Yeah. I mean, domestically, to the extent that the natural gas matters at all, it’s good for the United States. Some of these cargoes will be more expensive that we’re able to sell, which will, you know, improve the terms of trade for the U.S., and will probably make it so, you know, construction workers will have to spend less time at casinos in Lake Charles and have to spend more time finishing up these projects that are supposed to be online this month. Yeah, I mean, gas prices are — gasoline prices, sorry, do feed in, are kind of more twitchy and responsive to the global economy.
You can find a full transcript of the episode here.
Mentioned:
From Heatmap: Oil Is Surging. Clean Energy Stocks Are Down Anyway.
From Heatmap: War With Iran Isn’t Just an Oil Story
From Heatmap: Inside Form Energy’s Big Google Data Center Deal
BlackRock and other infrastructure investors are buying AES for $10.7 billion
The fate of New York’s climate law is in doubt
Luckin Coffee to buy Blue Bottle Coffee
This episode of Shift Key is sponsored by …
Accelerate your clean energy career with Yale’s online certificate programs. Explore the 10-month Financing and Deploying Clean Energy program or the 5-month Clean and Equitable Energy Development program. Use referral code HeatMap26 and get your application in by the priority deadline for $500 off tuition to one of Yale’s online certificate programs in clean energy. Learn more at cbey.yale.edu/online-learning-opportunities.
Music for Shift Key is by Adam Kromelow.
This transcript has been automatically generated.
Subscribe to “Shift Key” and find this episode on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, Amazon, or wherever you get your podcasts.
You can also add the show’s RSS feed to your podcast app to follow us directly.
Robinson Meyer:
[1:26] Hi, I’m Robinson Meyer, and you are listening to Shift Key, Heatmap’s podcast about decarbonization and the shift away from fossil fuels. It is Friday, March 6, and it’s been an enormous week for energy news. At the time we’re recording this, at least 870 people have been killed in the fighting in the Middle East since the United States and Israel attacked Iran on Saturday, setting off Iranian counterattacks across the region. Six American soldiers died in a strike in Kuwait. They were members of the U.S. Army Reserve. In energy, Qatar, the world’s second largest producer of liquified natural gas, has totally shut down its production, which could take weeks to restart. Oil exports are significantly bottlenecked at the Strait of Hormuz. Gasoline prices in the U.S. are on average already up $0.27 per gallon. Our reporters here at Heatmap have been tracking this burgeoning energy crisis, so today we’re going to talk to them about it. Catch up, find out what’s been affected so far and what might still be yet to come. Today’s a special panel episode of Shift Key about the Iranian energy crisis. And I should add the rest of the week in climate news, too. It’s not all bad news this week. We have some good climate tech news for you. Joining me now are Heatmap staff writers, Matthew Zeitlin and Katie Brigham, as well as Heatmap’s deputy editor, Jillian Goodman. Let’s just get into the discussion. Matt, Jillian, Katie, welcome to Shift Key. Let’s start with what is clearly the biggest news of the week.
Robinson Meyer:
[2:48] Iran. And I think that the topic that has pushed every other energy topic to the side and driven, at this point, it’s pushed some conversations aside and it’s pushed other topics that like feel like things we were talking about in 2022 back to the fore. And so let’s just start here. Matt, you’ve been tracking the energy fallout from the Iran war. What have been the biggest like real world energy consequences so far?
Matthew Zeitlin:
Yeah, obviously, the Persian Gulf area is best known for being oil production. You know, you have Saudi Arabia, Iraq, Iran, Qatar, UAE. But I think the biggest story has been the natural gas, liquified natural gas specifically, Qatar produces something like a fifth of the world’s liquified natural gas. It’s the second largest exporter. And when the Strait of Hormuz, which is how all these Gulf countries are able to access global maritime shipping, was effectively closed over the weekend and then on Monday and Tuesday. Tankers don’t want to go through there anymore. Natural gas prices instantly shot up and a lot of countries were kind of rerunning a playbook that they had seen from 2022 when Russia invaded Ukraine. And there were similar kind of shortfalls in natural gas locally and then also prices going up globally. As you look around the global economy, like what’s been the biggest effect of higher natural gas prices so far, given that we’re only what at the time of recording this three or four days into this? Yes, I’d say the most immediate effect has actually not been electricity, although people are definitely expecting higher electricity prices, especially in Europe, which is very dependent on natural gas imports. I’d say the biggest effect has actually been on fertilizer. Lots of fertilizer is synthesized. If you remember from your high school chemistry class or the Haber-Bosch process, and then another process to make urea in the Persian Gulf, in Qatar specifically, and surrounding countries. And natural gas is an energy source, and most crucially, it’s part of the chemical reactions that create synthetic fertilizer. And so a lot of fertilizer synthesis happens in and around the Persian Gulf, and that is all slowing down. South Asia, which is obviously historically and geographically linked to the Persian Gulf, has seen a lot of this kind of fertilizer slowdown happen immediately with plants reducing production. And so when that happens, it’s affecting agricultural yields. It means the input for farmers all over the world will kind of shoot up in price if they’re even able to get it. So it’s kind of a shock to the global food system, probably more immediately than the global energy system.
Jillian Goodman:
[5:29] I think it might be worth even taking a step back and clarify why we’re talking about liquified natural gas in particular versus like natural gas as the more general commodity, because this is the way we ship natural gas around the world. And so we’re talking about natural gas exports and imports. We’re not talking about like the gas that Qataris use and we’re not talking about, importantly, the gas that Americans use either. We’re talking about the gas that like the Japanese and the South Koreans use.
Matthew Zeitlin:
[6:02] Yeah, that’s exactly right. I mean, Qatar has been exporting liquified natural gas since the 1996 or 1997. The U.S. has been doing it since the mid 2010s. This is a huge technological and economic development. Natural gas is plentiful. It’s drilled off in the same place oil is, but traditionally it could only be moved around through pipelines. And that kind of limited its ability to be exported. And it also meant that you had a bunch of different natural gas prices based on where it was. When people realized that you could get a really, really, really cold, put it into a ship, sail the ship, heat it up again, called regasification, you kind of create a global natural gas market. And so this meant that countries, especially in Asia, which don’t always have the same domestic fossil fuel capacity, could start having a more gas-fired economy in terms of electricity and industrial processes. Whereas before, it had been kind of more limited in the United States, North America, Europe, too.
Robinson Meyer:
As I’ve been thinking about this story, I hadn’t realized, Matt, the degree to which the two most volatile commodity prices are affected by this, in that this is now both an energy inflation story and a food inflation story because of fertilizer. I think as I’ve been thinking about this domestically, because of how the U.S. plugs into the global economy. And because U.S. liquified natural gas export is basically already running at full bore, we’re exporting it basically as much natural gas as we can with the system that we have, which means that there’s not a ton of pass through that could happen into our domestic natural gas prices. We’re kind of looking at a system, and you should correct me if this is wrong, but like as I think through what politically the ramifications of the war are, at least as far as energy goes, obviously. This is globally going to be like a gas and fertilizer story and energy security story. Domestically, this is probably far more likely to be an oil price story. You know, gas prices now are like at $3.25 nationally. They could very well be higher by the time we release the episode. Conventional wisdom is that gas prices don’t really matter until they get above $3.50. It’s nice to have them for a president below $3, and it’s bad to have them above $4. And so they were previously, the U.S. average was right below $3. Now it’s like $3.25. It’s gone up $0.25 in just a few days. And so as I think about what are the constraints on the Trump administration’s economic policymaking? What are the constraints on the president’s decision-making insofar as he feels any constraints from the economy? Like domestically, it’s far more of an oil story than it is a gas story.
Matthew Zeitlin:
Yeah. I mean, domestically, to the extent that the natural gas matters at all, it’s actually, it’s good for the United States. I mean, just like the, some of these cargoes will be more expensive that we’re able to sell, which will, you know, improve the terms of trade for the U S and we’ll probably make it so, you know, construction workers will have to spend less time at casinos in Lake Charles and have to spend more time finishing up these projects that are supposed to be online this month. Yeah, I mean, gas prices are, gasoline prices, sorry, do feed in, are kind of more twitchy and responsive to the global economy. Now the U.S. is the world’s largest oil exporter as well.
Jillian Goodman:
[9:25] What’s so interesting to me too, and this is something you wrote about this week, Matthew, is that, you know, I think people in clean energy, especially I think the knee-jerk response is to kind of say, oh, well, this will be great for renewables, like high gas prices. Great. More people buying EVs. And yet we’ve seen that has not been the way the market has responded, which very much reflects just the complexity of global supply chains. But like Tesla was down, you know, more than the market as of Monday morning, the first market open day after the attacks commenced, for instance.
Matthew Zeitlin:
[9:58] Yeah, it’s really more in the developing world where you see these kind of crash electrification efforts. I was talking to Kingsville Bond, kind of a big energy thinker at Ember. And he was pointing, I think, to Nepal and Ethiopia as countries that have really aggressively electrified their transportation so they don’t get on the wrong side of these kind of oil gasoline price shocks. And the U.S., depending on how you look at it, is either blessed or cursed by, abundant fossil fuel resources. And so you’re never going to have that moment where you wake up one day and it’s like. We need to immediately get off of oil so that we can make sure cars work all the time in a way that a poorer country that’s more dependent on the global market might think.
Robinson Meyer:
Or even in the way that China thinks. I mean, I think this is the struggle here is that China has made a set of decisions around its energy security that have led it to a very rapid electrification pathway, basically because it has secure supply of coal and the sun and wind, and doesn’t have secure supply of oil and that’s pushed it to adopt EVs. I think the challenge for American, you know, decarbonization advocates, this is something I think about all the time, is like, if you were to adopt a similar mindset in the U.S. to security of supply is really what matters, we should focus on that. It’s not clear to me that you wind up making the same technology decisions that China has made. And there could be very good reasons for national competitiveness, for economic development, for manufacturing, for the U.S. To ultimately pursue an electrification pathway that’s like similar to China’s electrification of its light vehicle fleet. But it’s like you don’t have the same constraints.
Matthew Zeitlin
Yeah, it works both ways, too. The U.S. being now an energy superpower in the way it was in, say, 20 years ago, I don’t think it’s a coincidence that the U.S., especially with Donald Trump as president, is so much more aggressive around Iran, especially, than the Bush administration was. Because in 2003, 2004, 2005, like anytime up to 2008. Risking some kind of huge shock to the global energy system and oil especially would be like a huge problem politically because the U.S. was still a very large oil importer. The price of oil is still set globally, so we’re still, you know, vulnerable to price shock, but it’s not existential in the same way that it may have been 20 years ago. And so I think, ironically, as the U.S. energy situation has kind of gotten more stable and more secure, The global energy situation may have gotten less stable and less secure because it increases the freedom of action of a sometimes volatile state in the Western Hemisphere.
Robinson Meyer:
[12:47] It also means that you wind up with these bizarre situations where the U.S. Has a long-term security interest in protecting and being the military hegemon in the Middle East, partially because of the region’s importance to global energy supplies. But the largest users of those global energy supplies are like China and East Asian countries. And specifically, there’s a chance that we see, even potentially before this podcast comes out, the image of American naval ships ferrying tankers to the Strait of Hormuz when those tankers will now go entirely to service Chinese oil demand, which has been the country buying almost all of Iran’s oil up until the current moment. I think there’s something else, too, about how different things are from the 2000s that in some ways I feel like the politics had never quite caught up to, which is that there were enormous anti-OPEC politics in the 2000s. And they were quite bipartisan. And they were hooked into U.S.-Israel politics because the long-term rivalries between the Arab states and Israel played into American resentment of OPEC’s control of the oil markets. And the rise of America as an oil producer has in some ways already reshaped some of these relationships around the U.S.. But I sometimes feel like American politics hasn’t caught up to the ways that.
This should change how we view the Middle East.
Matthew Zeitlin:
Can I say one more thing here that was kind of funny about, you know, so those 2000 energy.
Politics, one thing it gave us was kind of this massive subsidy scheme for biofuels, because this was seen as homegrown energy resource, especially in kind of politically influential rural states like Iowa. And then yesterday, yesterday, amidst, you know, many tweets about kind of the DHS situation and stuff that senators talk about. Chuck Grassley, a long tenured senator from Iowa, said, a key to President Trump’s affordability agenda, biofuels, E15. It’s a regulatory scheme that they get fed into refineries. Year-round nationwide E15 and lower consumer costs and shore up our fuel supply amid unrest in Iran. We need it now. This is basically idea you require refineries over all year to have a certain amount of ethanol, biofuel in them. And so this is like pure uncut energy crisis economics policy. You could see this in the 70s, you would see this in 2000s. And, you know, biofuels, they’re obviously a huge industry, but they’re not like the backbone of America energy independence anymore. We kind of just have enough fuel now, but because the policy was set during a different time, you have this vestigial interest in things like biofuels.
Robinson Meyer:
Oh, and the subsidy itself created a kind of parasitic industry. I mean, I remember looking at this after the war in Ukraine began where. All of American energy politics after the 1970s is basically about developing alternatives to Middle Eastern hydrocarbons. And Congress makes a number of bets. And the politics of all of this works because the bets are kind of regionally distributed and don’t break in a clear way on a partisan basis. And one of those bets is biofuels. But another set of the bets is wind energy. And another bet is solar. And another bet is hydraulic fracturing and advanced extraction techniques from shale. And part of what has happened, and in some ways it happened very quickly from like 2008 to 2015, is that a number of those bets actually worked out. And what we used to call alternative energy, like solar or wind or renewables, and at the same time with alternative oil and gas extraction, became real energy resources that could operate and meet demand at the scale of the full economy. And that divergence of, I would say, wind, solar, fracking, and batteries from biofuels, from other forms of experimental energy technology, that scrambled energy politics in a way that I feel like Congress has struggled to come to a new bipartisan playbook because now that wind and solar are real.
And now that fracking is such a big deal in the U.S. economy, you can’t craft the same that you could in, say, the 2005 Energy Act.
Jillian Goodman:
[17:20] Well, I was thinking about this this morning because the other big trade story that we’ve covered since the start of the Trump administration is tariffs. And that it was so easy to point to like pretty specific effects for clean energy. Like, OK, we get our rare earths from China and if tariffs go up and we really need a lot of copper. And so you could kind of draw out these very specific sort of chains of events. The supply chain disruptions from this, especially regarding clean energy, are extremely diffuse about just like the global economy is a little bit scrambled, like all inputs are getting more expensive. And so I think that the way we will see this filter out at the company level, at the microeconomic level, is going to be a lot more subtle and take a lot longer.
Robinson Meyer:
[18:09] If this war ends in a week or even in two weeks, it’s very possible that we look back on this as a minor economic event and not one with lasting changes. Now, some of what’s already happened is going to be hard to reverse on, say, week-long timeframes. So it seems like Qatar is going to fully shut down its LNG production. That takes like a week to spin down. It’s going to take two weeks to spin back up. That basically could mean that Qatar is like a month behind over the next six to seven months. And that’s a problem because the summer is when the Northeast Asian countries, when Western Europe, when countries in the Northern hemisphere that rely on LNG broadly, like stock up on LNG and buy it at off season rates. And so we could see this event in European LNG stocks in a year, even if this event kind of dissipates in the next few days.
Robinson Meyer:
[19:10] If it doesn’t dissipate, then we’re in energy crisis territory. And Democrats have already reframed, I think, a lot of their climate policy in terms of affordability rather than decarbonization per se. One point that Leah Stokes always makes is that you tend to get big climate policies historically when there’s an energy crisis. And I think if this continues, it opens the window a little bit to maybe more ambitious, decarbonization policymaking on the back of an energy crisis and affordability concerns that maybe we’ve thought we would see from Democrats in, say, the 2026 or 2028 cycle. I also am required to note here that the president in 2024, President Trump, while campaigning, promised to cut Americans’ electricity bills in half and their energy costs in half. And he said it would take him six to 12 months. We’re now fully past the deadline. It didn’t happen. And he’s completely failed at it. It was bizarre and he was never going to be able to do it, but he didn’t do it.
Robinson Meyer:
[21:47] To totally pivot here from war and destruction and the breakdown of the international order to some good news, you recently reported on a huge deal between the iron air battery company Form and Google. Can you tell us about this deal?
Katie Brigham:
[22:03] Yeah, totally. So last week it was announced that Form Energy would deploy what would be the largest battery in the world by energy capacity for a new Google data center in Minnesota. This iron air battery would be capable of delivering 300 megawatts of power continuously while storing 30 gigawatt hours of energy. That means it’s capable of continuous discharge for 100 hours straight. That’s about four days. And just to put this in perspective, by comparison, the entire U.S. Grid added just 57 gigawatt hours of storage over all of 2025, meaning like this single form battery is over half the size of all the energy storage capacity that was added nationwide last year. So it’s huge.
Robinson Meyer:
Which is also crazy because last year was seen as a very good year for battery installation. Like 57 gigawatts was a lot of batteries to add to the U.S. I think we set a new record last year. It was not like we kind of had a middling year with batteries last year, but this one installation is basically going to come close to 50% of our installed capacity, our new installed capacity from last year. I remember when Form first announced it was a Wall Street Journal story. I feel like it was in 2021 or 2022. And they were very excited about their technology.
Robinson Meyer:
[23:17] Crucially, as we’ve been alluding to, they use this novel battery chemistry that isn’t lithium ion. It’s a rust battery, basically. If you can interject to even explain what’s happening here, but it like turns, it rusts iron and then de-rusts iron as a way of discharging energy.
Katie Brigham:
At a high level, when it’s discharging, the battery oxidizes iron, which basically means rusts iron. And this process of oxidation releases electrons that then are able to flow through a circuit to provide electricity. And the inverse of this process just converts that iron rust back into metallic iron. So at a high level, that’s how it works. Obviously, like iron is cheap. All of the elements that go into making this are extremely cheap, way cheaper than lithium ion batteries. And that’s kind of one of the main promises is not only can it, you know, discharge energy, presumably economically for way longer than lithium ion batteries can, but it can do it using these elements that are very abundantly available.
Robinson Meyer:
I remember when they first announced this technology. And at the time, they didn’t have manufacturing for it. And they said the technology worked, but there was no proof of it. At this point, they have a factory set up in West Virginia. And they are now selling the biggest battery in the country to Google like it. It seems like. In a way that was not clear two years ago, the Form technology seems to work, or at least Google thinks it seems to work.
Katie Brigham:
Totally. Google and the kind of third partner in this deal, Xcel Energy, which is it’s really like a Google data center being developed with Xcel Energy. And Xcel Energy is the entity that has like a longstanding relationship with Form. And so, yeah, at this point, both Google and Xcel Energy have toured the Form factory in West Virginia. And when I asked the, you know, form CEO last week, what kind of made this level of scale up possible? He just said, it’s because the company has been basically heads down for the last 18 months working on scaling up its manufacturing operations. He said something that I thought was kind of poignant, which is like, you can’t really say your chemistry works until you’ve scaled it. And so now that they, you know, have convinced themselves, convinced Google, convinced Xcel that they have the manufacturing capability at scale locked in, that’s when they, you know, in some sense can finally say like, okay, this does work. And even though they haven’t done a deployment like near this size, the facility was able to demonstrate that it has the capability to do this at scale such that like Xcel and Google were all in on announcing this magnitudes larger battery.
Robinson Meyer:
Elon Musk, complicated figure, but something that I think about that he said all the time is that the product is the factory. Like the factory is the product itself and the ability to scale the technology that works in the manufactured setting is actually what. The test of the company is, not whether the technology works in some kind of demonstrative capacity, but whether it works when you’ve scaled manufacturing of it. And then it’s actually that manufacturing process that is the product you’re selling, even if you’re ultimately selling batteries. I mean, there was another big thing about this deal that I thought was interesting, which was that the data center, because it has this massive storage capacity, is going to run on largely renewable electricity, on entirely renewable electricity. As we talked about with Peter Freed a few weeks ago is like not the case for a lot of data centers, even if they’re building huge batteries at the moment. How does Form compare to other long duration energy storage technologies that
Robinson Meyer:
[26:40] are out there at the moment? Are they the best demonstrated technology? Are they the technology that scaled the most at the moment?
Katie Brigham:
[26:50] So there are other companies that are even targeting this same market segment as Form, the 100 plus hour duration. I reported on a company called Noon Energy a while ago, which recently completed a demonstration of its own fuel cell system. And Form has done internal demonstrations that it hasn’t really been public about. So there are other companies that are out there talking about their long duration pilots and demonstration plans more than Form has. And there are those pilots and some are grid connected already. And so Forum has kind of been lower key than some of these other long-duration storage companies making announcements. But the announcement they made live this week is by far, like, blows every other announcement out of the water just in terms of its scale. So, yeah, Forum has raised $1.2 billion to date. So it’s by far the best-funded startup in this space.
Jillian Goodman:
[27:34] Yeah, I was just going to ask, is this just, like, a first-mover advantage? It sounds like it’s also a funding advantage. How was Forum able to land a deal this size?
Katie Brigham:
[27:43] It is partially first-mover advantage. I mean, they were the first to publicly come out and say that they, you know, could do this 100 plus hour battery storage. Most of the other long duration storage companies in this space have been later to enter than them. They were really the first ones when they made this announcement in, you know, 2021, I think it was. It wasn’t like they initially came out with a ton of scientific evidence and like a lot of third party studies to back it up. So there was still some skepticism, but that did soon follow. And so, you know, the technical validation is very much there at this point. And I think being the first to raise like a really significant sum of capital. And I think they’re farther along now they’ve demonstrated with their manufacturing scale up than probably anyone else at this stage. I think that’s what’s allowed them to make this deal with Google. And they’ve definitely been on the radar, I think, of a lot of these hyperscalers for a long time. This was just the first publicly announced deal that came together.
Robinson Meyer:
What’s the biggest non-form news in climate or energy tech this week, Katie?
Katie Brigham:
[28:41] Yeah, I’ve been following the deep sea mining debate pretty closely. The International Seabed Authority, which is the sort of organization that monitors and sets rules for the open ocean, which has no national jurisdiction, is meeting this week to finalize a plan and establish rules that would hopefully set the boundaries at which private companies would be permitted to collect these, what they’re called like nodules, which are rich in minerals from the ocean floor. So they’re hopefully finalizing the plans this week. The hope is that a draft of these rules could be completed by this year.
Robinson Meyer:
[29:11] But like a lot of that work is happening in this convening right now. I think there’s a lot of nervousness around it from all sides, but it pits like the critical minerals like bowls against like a lot of people that just have grave concern over what this is going to do to the ocean ecosystem and what the risk is of private companies just sort of being unleashed to go do this themselves in an arid area of the world where there’s no national jurisdiction.
Robinson Meyer:
[29:35] And simultaneously, the U.S. is preparing its own competing scheme for this, right? Or the U.S. is preparing to issue permits about this.
Katie Brigham:
The U.S. wants to issue permits. The Trump administration is very enthusiastic about the potential of deep sea mining. And the leading company in the space called The Metals Company is extremely bullish on this, too. They are trying to partner. They have already acquired a partner in an island nation that can be a partner to them in mining these metallic nodules off the floor and off the seabed. So they’re working in tandem with the administration in many ways to get this going as soon as possible, which I think a lot of people are, from an outside perspective, quite worried about because they haven’t necessarily given people great confidence in their ability to do this responsibly.
Robinson Meyer:
Because of the Trump administration, yes. Stepping back, so because of Iran, it’s been funny. There’s been a number of news stories outside of energy this week that would have been massive, massive stories, such as France potentially extending its nuclear umbrella over all of Western Europe that really didn’t get a lot of attention because the U.S. and Israel are conducting an open-ended war against Iran. I just wanted to go around before we close and ask each of you for one story this week that stuck out that you think didn’t get the attention it deserves because the campaign in Iran has understandably led global headlines at this point for several days?
Jillian Goodman:
[30:52] Can I go first? Because I’m afraid Matthew has the same story as I do.
Robinson Meyer:
[30:56] Jillian will go first.
Jillian Goodman:
[30:59] For me, speaking of big deals, it is BlackRock, well, a subsidiary of BlackRock, buying the utility AES. The deal also includes a Swedish private equity called EQT, as well as CalPERS, the California pension fund. And this was a $33 billion deal. It’s expected to close next year. And it shows the extent to which America’s largest asset manager is banking on the expansion of data center. Power and really thinks that this is going to drive value for shareholders over the next years.
Robinson Meyer:
[31:36] And not only that, but banking on the returns from the utility business, which even if you think electricity demand is going to go up, is not necessarily a sure thing. And I remember Warren Buffett in his penultimate investor letter in 2024 was like, people are going to keep using electricity. I’m not sure that the utility industry is going to be a great business going forward. But evidently, Calpers and BlackRock disagree. That’s so interesting. Matt, did Jillian just steal your story? And if not, what is your biggest story of the week that should have gotten attention but didn’t?
Matthew Zeitlin:
[32:09] Julian made a great choice, but it was not my story. Maybe it should have been. My biggest story this week is one that’s close to home. It’s tussling over New York’s landmark climate law. Kathy Hochul and the New York State government have been preparing these estimates of the costs of fully implementing the law, which includes a very aggressive decarbonization, renewable energy pathway by 2030 and later. Kathy Hochul seems to be preparing the ground to kind of soften, delay, not implement, not go as hard as maybe the law’s biggest boosters would want her to, essentially by trying to portray it as contrary to kind of the affordability narrative that so many, especially Democratic politicians, are pushing right now. And Hochul, of course, is also running for re-election this year. I mean, I think it’s interesting because it just shows like how different the times we are in right now is. This law was passed at a time when, for one, it was signed by Andrew Cuomo, which is in 2019, just seems so long ago. And it was at a time when there was just a lot more optimism about how quickly renewable energy and how quickly and cheaply renewable energy could be deployed, especially in the Northeast, with offshore wind being a huge part of it. Obviously, that has not happened in the same way that the law’s proponents have wanted it to. And who knows Kathy Hochul has done these kind of fake outs before you know she canceled congestion pricing to help Long Island Democrats win and then she just brought it back but yeah I mean I think we’re going to see a lot of this a lot of Democratic states pass very aggressive have been passing very aggressive climate laws and have very aggressive climate targets you know they’re usually decadal so in 2030 a lot of this stuff is kicking in and like there’s just you see this in Europe a lot you’ve seen in Washington you’ve seen in other places as climate laws, that are effective, that would actually work if implemented to reduce emissions, become binding, the chance that they will be delayed or watered down skyrockets. It’s like an asymptotic situation. And I think we’re seeing something like that happening in New York.
Robinson Meyer:
And I don’t think that’s only going to happen in New York. I think this is maybe one of the most interesting aspects of the Mamdani campaign in that in New York, Local Law 97, which requires aggressive decarbonization from the existing building fleet, is going to start really kicking in 2028 during the current mayor’s time in office.
Robinson Meyer:
[34:39] And Mamdani, who had been a fairly aggressive advocate of climate policy in the State House, not only didn’t really run on climate policy, but didn’t try to polarize it at all either. And I think the question of how he now manages.
Robinson Meyer:
[34:55] The Local Law 97 implementation while also meeting his affordability goals is like one of the biggest questions facing his administration going forward. And he says to be clear that he’s going to enforce the law as written. We’ll also maybe look for ways to help companies meet the law’s standards. And so there’s an entire set of companies too that made a set of commitments in the early 2020s that are all going to hit between 2028 and 2030. And how those companies approach those commitments in a world where it turns out, for instance, that there are far more binding constraints on renewable deployment than it seemed, in a world where there is significant electricity load growth in a way that wasn’t maybe projected in the same way in the early 20-teens, and in a way where I think also there’s just been more recognition of the physical constraints on decarbonization than maybe there was in 2020, and an understanding of how many of those physical constraints are political as well. That is maybe one of the biggest stories of the next few years before we go though. Katie what’s your big story that didn’t get attention and should?
Katie Brigham:
Sure, yeah so Jillian actually did take mine. I’m no utilities reporter, but I did think that that was really interesting as it comes on the heels of a lot of other big financial institution acquisitions of utility companies as well which again like Jillian said is just interesting in terms of the bet that they’re taking on load growth continuing but anyway. Instead, I think there’s, and again, I don’t know if this is like the hugest news, but there’s some interesting like things happening in the green hydrogen space, which is obviously like doing terribly overall, but there’s been some small rays of sunshine. There’s a 220-megawatt project in Utah, green hydrogen project. It’s by far the largest in the U.S. and it’s now ready to come online. As of last week, like was reported in our AM newsletter, all 40 of the electrolyzers at the facility are now installed, are fully operational. So I think it will be really interesting to monitor that and how the financials of that facility end up working out in an environment that has become far less favorable for green hydrogen as incentives go away and consumers are worried about price. And then as was also reported another day on our AM newsletter, Spain is also moving forward with a green hydrogen project that’s way bigger than this one in the U.S. It’s 2 gigawatts. It’s called the Andalusian Green Hydrogen Valley Project, and it’s worth $1.2 billion. And so even though this is like supposedly a scaled down version of what this project is going to be, again, it’s still two gigawatts. Total value of the project is $1.2 billion. And so I think just monitoring both of these projects will be interesting. Europe is often seen as like a more viable market for this technology, but I think it’s struggling overall here and abroad. So some rays of hope potentially for a, you know.
Matthew Zeitlin:
Some green shoots, if you will.
Robinson Meyer:
Green shoots for the technology that I think has performed worst overall during the Trump administration. Can I have one?
Jillian Goodman:
[37:49] Yes.
Robinson Meyer:
[37:50] Great. Okay, great. The story that I think deserved a lot of attention this week and may still get it, we’re recording pretty soon to when it was announced, is that Luckin Coffee, the Chinese coffee chain. Did anyone see this?
Jillian Goodman:
No.
Matthew Zeitlin:
They bought Blue Bottle. No. Luckin Coffee has bought Blue Bottle.
Jillian Goodman:
What? That’s wild.
Robinson Meyer:
And I think that is so interesting. And let me say why it’s interesting, because even though this is a story of two coffee companies, I think it’s relevant to things we talk about here on Schiffsky and a kind of broader question about the integration of the Chinese and American economies, which is that Luckin Coffee is very famous for selling very cheap coffee. And for producing lattes and frappuccinos and any number of kind of iced, sweet, milky drinks and selling them for far below what Starbucks would sell them for. We’re talking coffees that in U.S. dollar terms are $1 or $2 or $3. Blue Bottle, meanwhile, is on the total other end of the spectrum, right? It’s hard to get anything coffee flavored at Blue Bottle for less than like $6 or $7. And Blue Bottle, to be clear, is this frou-frou chain that exists primarily, I think, in California.
Jillian Goodman:
[38:57] Yeah, it was venture-funded, if I recall correctly.
Robinson Meyer:
[39:00] Yes, exactly. It was a venture-funded coffee chain that kind of came out of the Bay Area. Now you can find it in Washington, D.C., in New York City, and it’s in both New York and D.C.’s big train stations. It’s very expensive. It’s like $7, $8, $9, $10 per coffee. These are two classic companies of their type, right? You have Luckin Coffee, which sells very cheap goods to mass consumers. And then you have Blue Bottle Coffee, which has these, through brand differentiation, commands incredible profit margins with its largely American audience. And the question historically has been like, if, say, some Chinese electronics brands or Chinese.
Robinson Meyer:
[39:46] Consumer brands were to expand in the United States or in Canada. We were talking about this back when Prime Minister Carney opened up the Canadian auto market to Chinese EVs. If we see Chinese companies expand in North America, are they going to use the North American market to undercut existing producers? Or are they going to use it to harvest profit from the incredibly wealthy North American consumer? Right. And so here you have Luckin Coffee, purveyor of the $2 coffee and Blue Bottle, purveyor of the $9 coffee. And Luckin’s going to absorb Blue Bottle. And I’m so curious to see what they do to Blue Bottle because in some ways it’s a guide to what the U.S.-China economic integration story could look like going forward and how as Chinese firms and Chinese brands continue to enter the United States and sell themselves as Chinese brands, how they accommodate themselves to the American consumer base.
Jillian Goodman:
[40:39] Well, I think that comparison is especially interesting because we have a contributor on EVs named Andrew Moseman who’s written about various stories about the ways that Chinese EVs could be integrated into the U.S. Market. And one point that he has made is that there is no way an American version of the cheapest Chinese EVs, as cool as they are, as zippy as they are, could be as cheap in the U.S. Because of American safety and manufacturing requirements. And so the idea that they would not try to undercut American manufacturers and instead try to extract value from American consumers kind of squares that circle.
Robinson Meyer:
[41:20] Yeah, totally. It gets at this kind of challenge for American companies in meeting the competitiveness demands of Chinese companies, which is that the Chinese consumer, part of why the Chinese companies are so good at making low-cost products, is the Chinese consumer is not as wealthy as the American consumer. And they will buy a $9,000 car. They will buy a $15,000 car. And there isn’t the same competition from the existing used vehicle fleet that exists here in the U.S. when consumers are making the decisions they’re making, or they might have different consumption preferences. Anyway, this is all to say, such an interesting story. And we’re going to keep covering it here on Shift Key. I want to thank Matt Zeitlin, Jillian Goodman, and Katie Brigham for joining us in this special panel episode of Shift Key. Thank you, Matt.
Matthew Zeitlin:
Thanks for having me. It’s a lot of fun.
Robinson Meyer:
Thanks so much for joining us, Katie.
Katie Brigham:
Thanks for having me.
Robinson Meyer:
And Jillian, it’s so good to have you on the other side of the digital recording studio. We’ll be back next Wednesday with a new episode of Shift Key. Until then, Shift Key is a production of Heatmap News. Our editors are Jillian Goodman, our very own, and Nico Lauricella. Multimedia editing and audio engineering is by Jacob Lambert and by Nick Woodbury. Our music is by Adam Kromelow. Thank you so much for listening and see you next week.