You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
On greenhouse gas regulations, coal power, and contaminated drinking water

Current conditions: An electricity transmission line failure triggered a massive blackout in Chile • Six tropical storms are currently swirling in the Southern Hemisphere • The Santa Ana winds are returning to Southern California this week.
Environmental Protection Agency Administrator Lee Zeldin has reportedly been advising the Trump administration to repeal a landmark scientific finding that explicitly identified greenhouse gases as a public health threat. The 2009 “endangerment finding” gave the EPA the authority to regulate these gases. President Trump ordered the EPA to review the finding, but the agency has not publicly released any recommendations yet. According to The Washington Post, Zeldin has “privately urged the White House” to strike it down.
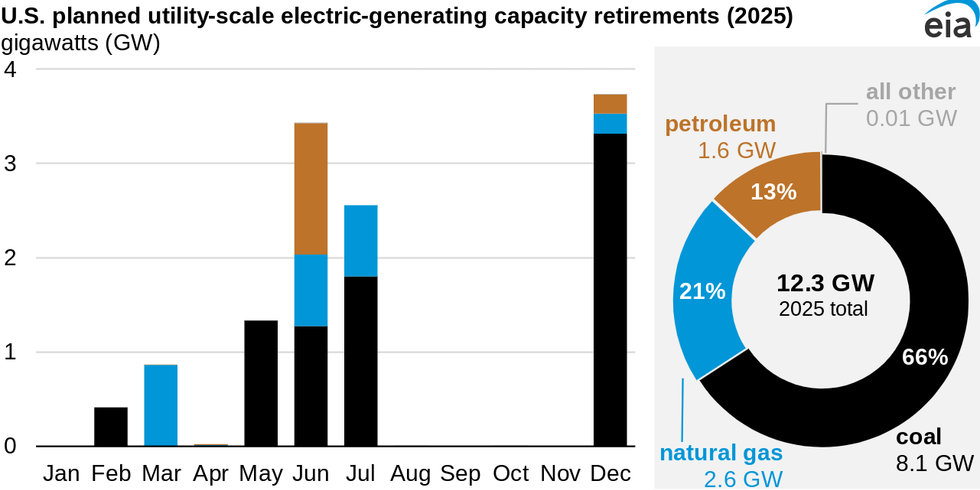
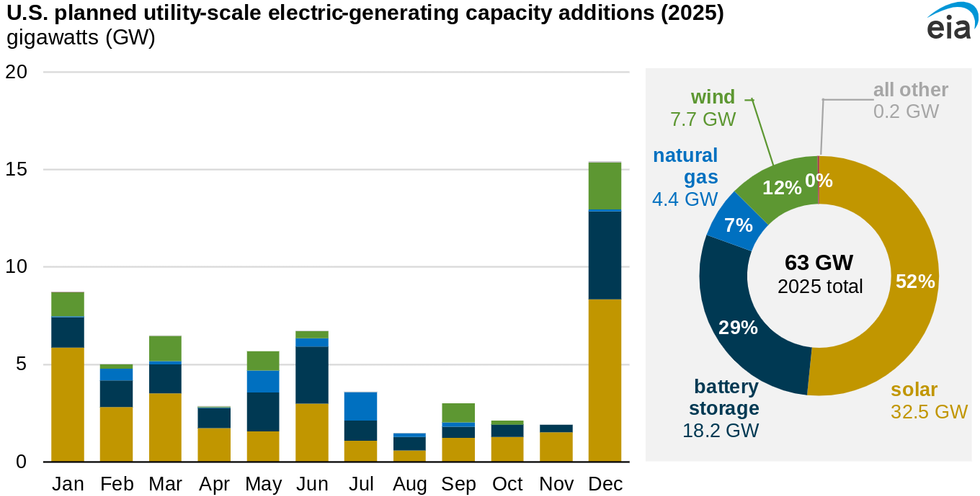
Power generators in the U.S. plan to retire 8.1 gigawatts of coal-fired capacity this year, according to the Energy Information Administration. That’s more than double the 4 GW retired last year but less than the 9.8 GW that have been taken offline each year over the last decade. Planned retirements across all sources for 2025 total about 12.3 GW, and coal power retirements account for the largest share at 66%, followed by natural gas at 21%. At the same time, the EIA expects 63 GW of new utility-scale power capacity to come online this year, 81% of which will be solar and battery storage.
The U.S. and Ukraine have reportedly reached a deal that would see Ukraine share some of the revenue from its state-owned natural resources – including oil, gas, and critical minerals – with the United States. Ukraine has large deposits of critical minerals and rare earth materials, some of which are essential in clean technologies including electric vehicles. President Trump previously said he wanted access to some of those materials. The terms of the new deal remain unclear, but a draft seen by some outlets suggests Ukraine would put 50% of future mineral proceeds into a newly established joint fund, up to $500 billion. Some of the money would be reinvested into the war-battered country, and “the United States would provide a long-term financial commitment to the development of a ‘stable and economically prosperous Ukraine,’” according to Retuers. However, there do not seem to be any clear security guarantees for Ukraine in the deal. The Financial Times also noted that it “leaves crucial questions such as the size of the U.S. stake in the fund and the terms of ‘joint ownership’ deals to be thrashed out in follow-up agreements.” Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky reportedly plans to meet with Trump in Washington on Friday.
The nonprofit Environmental Working Group has published its newly updated tap water database, showing that millions of Americans are drinking water that contains “forever chemicals” (or PFAS) and other contaminants. EWG synthesized reports from 50,000 individual water systems across the country. In total, 563 utilities reported unsafe levels of forever chemicals. Almost all community water systems contained detectable levels of contaminants of some kind – from PFAS to heavy metals to radioactive substances. As Heatmap’s Jeva Lange reports, the Environmental Protection Agency is required to report drinking water data, but it’s never released a comprehensive database, and information can be hard to come by. “EWG is filling this need for people to have a national clearinghouse where they can easily access their drinking water data,” Tasha Stoiber, a senior scientist with EWG, told Lange.
Get Heatmap AM directly in your inbox every morning:
The UK needs to bring its emissions down by 87% compared to 1990 levels by 2040 if it is to remain on track for net zero by 2050, according to a new report from the Climate Change Committee, which is an independent climate adviser to the government. Sixty percent of those 2040 reductions will come from electrification – decarbonizing the grid, switching to EVs, and swapping out fossil fuel home systems with heat pumps, etc. The report noted that the UK has already cut its greenhouse gas emissions in half since 1990 by “expanding renewable power and phasing out coal in the electricity sector.” Going forward, surface transport alone will account for nearly 30% of emissions cuts, with three-quarters of cars and vans on the road in the UK expected to be electric by 2040.
A recent study found that in spring and summer, trees and other vegetation in Central Los Angeles can absorb up to 60% of the carbon dioxide that gets emitted during the daytime.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Rob takes Jesse through our battery of questions.
Every year, Heatmap asks dozens of climate scientists, officials, and business leaders the same set of questions. It’s an act of temperature-taking we call our Insiders Survey — and our 2026 edition is live now.
In this week’s Shift Key episode, Rob puts Jesse through the survey wringer. What is the most exciting climate tech company? Are data centers slowing down decarbonization? And will a country attempt the global deployment of solar radiation management within the next decade? It’s a fun one! Shift Key is hosted by Robinson Meyer, the founding executive editor of Heatmap, and Jesse Jenkins, a professor of energy systems engineering at Princeton University.
Subscribe to “Shift Key” and find this episode on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, Amazon, or wherever you get your podcasts.
You can also add the show’s RSS feed to your podcast app to follow us directly.
Here is an excerpt from our conversation:
Robinson Meyer: Next question — you have to pick one, and then you’ll get a free response section. Do you think AI and data centers energy needs are significantly slowing down decarbonization, yes or no?
Jesse Jenkins: Significantly. Yeah, I guess significantly would … yes, I think so. I think in general, the challenge we have with decarbonization is we have to add new, clean supplies of energy faster than demand growth. And so, in order to make progress on existing emissions, you have to exceed the demand growth, meet all of that growth with clean resources, and then start to drive down emissions.
If you look at what we’ve talked about — are China’s emissions peaking, or global emissions peaking? I mean, that really is a game. It’s a race between how fast we can add clean supply and how fast demand for energy’s growing. And so in the power sector in particular, an area where we’ve made the most progress in recent years in cutting emissions, now having a large, and rapid growth in electricity demand for a whole new sector of the economy — and one that doesn’t directly contribute to decarbonization, like, say, in contrast to electric vehicles or electrifying heating —certainly makes things harder. It just makes that you have to run that race even faster.
I would say in the U.S. context in particular, in a combination of the Trump policy environment, we are not keeping pace, right? We are not going to be able to both meet the large demand growth and eat into the substantial remaining emissions that we have from coal and gas in our power sector. And in particular, I think we’re going to see a lot more coal generation over the next decade than we would’ve otherwise without both AI and without the repeal of the Biden-era EPA regulations, which were going to really drive the entire coal fleet into a moment of truth, right? Are they gonna retrofit for carbon capture? Are they going to retire? Was basically their option, by 2035.
And so without that, we still have on the order of 150 gigawatts of coal-fired power plants in the United States, and many of those were on the way out, and I think they’re getting a second lease on life because of the fact that demand for energy and particularly capacity are growing so rapidly that a lot of them are now saying, Hey, you know what, we can actually make quite a bit of money if we stick around for another 5, 10, 15 years. So yeah, I’d say that’s significantly harder.
That isn’t an indictment to say we shouldn’t do AI. It’s happening. It’s valuable, and we need to meet as much, if not all of that growth with clean energy. But then we still have to try to go faster, and that’s the key.
Mentioned:
This year’s Heatmap Insiders Survey
Last year’s Heatmap Insiders Survey
The best PDF Jesse read this year: Flexible Data Centers: A Faster, More Affordable Path to Power
The best PDF Rob read this year: George Marshall’s Guide to Merleau-Ponty's Phenomenology of Perception
This episode of Shift Key is sponsored by …
Heatmap Pro brings all of our research, reporting, and insights down to the local level. The software platform tracks all local opposition to clean energy and data centers, forecasts community sentiment, and guides data-driven engagement campaigns. Book a demo today to see the premier intelligence platform for project permitting and community engagement.
Music for Shift Key is by Adam Kromelow.
They still want to decarbonize, but they’re over the jargon.
Where does the fight to decarbonize the global economy go from here? The past 12 months, after all, have been bleak. Donald Trump has pulled the United States out of the Paris Agreement (again) and is trying to leave a precursor United Nations climate treaty, as well. He ripped out half the Inflation Reduction Act, sidetracked the Environmental Protection Administration, and rechristened the Energy Department’s in-house bank in the name of “energy dominance.” Even nonpartisan weather research — like that conducted by the National Center for Atmospheric Research — is getting shut down by Trump’s ideologues. And in the days before we went to press, Trump invaded Venezuela with the explicit goal (he claims) of taking its oil.
Abroad, the picture hardly seems rosier. China’s new climate pledge struck many observers as underwhelming. Mark Carney, who once led the effort to decarbonize global finance, won Canada’s premiership after promising to lift parts of that country’s carbon tax — then struck a “grand bargain” with fossiliferous Alberta. Even Europe seems to dither between its climate goals, its economic security, and the need for faster growth.
Now would be a good time, we thought, for an industry-wide check-in. So we called up 55 of the most discerning and often disputatious voices in climate and clean energy — the scientists, researchers, innovators, and reformers who are already shaping our climate future. Some of them led the Biden administration’s climate policy from within the White House; others are harsh or heterodox critics of mainstream environmentalism. And a few more are on the front lines right now, tasked with responding to Trump’s policies from the halls of Congress — or the ivory minarets of academia.
We asked them all the same questions, including: Which key decarbonization technology is not ready for primetime? Who in the Trump administration has been the worst for decarbonization? And how hot is the planet set to get in 2100, really? (Among other queries.) Their answers — as summarized and tabulated by my colleagues — are available in these pages.
You can see whether insiders think data centers are slowing down decarbonization and what folks have learned (or, at least, say they’ve learned) from the repeal of clean energy tax credits in the Inflation Reduction Act.
But from many different respondents, a mood emerged: a kind of exhaustion with “climate” as the right frame through which to understand the fractious mixture of electrification, pollution reduction, clean energy development, and other goals that people who care about climate change actually pursue. When we asked what piece of climate jargon people would most like to ban, we expected most answers to dwell on the various colors of hydrogen (green, blue, orange, chartreuse), perhaps, or the alphabet soup of acronyms around carbon removal (CDR, DAC, CCS, CCUS, MRV). Instead, we got:
“‘Climate.’ Literally the word climate, I would just get rid of it completely,” one venture capitalist told us. “I would love to see people not use 'climate change' as a predominant way to talk to people about a global challenge like this,” seconded a former Washington official. “And who knows what a ‘greenhouse gas emission’ is in the real world?” A lobbyist agreed: “Climate change, unfortunately, has become too politicized … I’d rather talk about decarbonization than climate change.”
Not everyone was as willing to shift to decarbonization, but most welcomed some form of specificity. “I’ve always tried to reframe climate change to be more personal and to recognize it is literally the biggest health challenge of our lives,” the former official said. The VC said we should “get back to the basics of, are you in the energy business? Are you in the agriculture business? Are you in transportation, logistics, manufacturing?”
“You're in a business,” they added, “there is no climate business.”
Not everyone hated “climate” quite as much — but others mentioned a phrase including the word. One think tanker wanted to nix “climate emergency.” Another scholar said: “I think the ‘climate justice’ term — not the idea — but I think the term got spread so widely that it became kind of difficult to understand what it was even referring to.” And one climate scientist didn’t have a problem with climate change, per se, but did say that people should pare back how they discuss it and back off “the notion that climate change will result in human extinction, or the sudden and imminent end to human civilization.”
There were other points of agreement. Four people wanted to ban “net zero” or “carbon neutrality.” One scientist said activists should back off fossil gas — “I know we’re always trying to try convince people of something, but, like, the entire world calls it ’natural gas’” — and another scientist said that they wished people would stop “micromanaging” language: “People continually changing jargon to try and find the magic words that make something different than it is — that annoys me.”
Two more academics added they wish to banish discussion of “overshoot”: “It’s not clear if it's referring to temperatures or emissions — I just don't think it's a helpful frame for thinking about the problem.”
“Unit economics,” “greenwashing,” and — yes — the whole spectrum of hydrogen colors came in for a lashing. But perhaps the most distinctive ban suggestion came from Todd Stern, the former chief U.S. climate diplomat, who negotiated the Kyoto Protocol and the Paris Agreement.
“I hate it when people say ’are you going to COP?’” he told me, referring to the United Nations’ annual climate summit, officially known as the Conference of the Parties. His issue wasn’t calling it “COP,” he clarified. It was dropping the definite article.
“The way I see it, no one has the right to suddenly become such intimate pals with ‘COP.’ You go to the ball game or the conference or what have you. And you go to ‘the COP,’” he said. “I am clearly losing this battle, but no one will ever hear me drop the ‘the.’”
Now, since I talked to Stern, the United States has moved to drop the COP entirely — with or without the “the” — because Trump took us out of the climate treaty under whose aegis the COP is held. But precision still counts, even in unfriendly times. And throughout the rest of this package, you’ll find insiders trying to find a path forward in thoughtful, insightful, and precise ways.
You’ll also find them remaining surprisingly upbeat — and even more optimistic, in some ways, than they were last year. Twelve months ago, 30% of our insider panel thought China would peak its emissions in the 2020s; this year, a plurality said the peak would come this decade. Roughly the same share of respondents this year as last year thought the U.S. would hit net zero in the 2060s. Trump might be setting back American climate action in the near term. But some of the most important long-term trends remain unchanged.
OUR PANEL INCLUDED… Gavin Schmidt, director of the NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies | Ken Caldeira, senior scientist emeritus at the Carnegie Institution for Science and visiting scholar at Stanford University | Kate Marvel, research physicist at the NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies | Holly Jean Buck, associate professor of environment and sustainability at the University at Buffalo | Kim Cobb, climate scientist and director of the Institute at Brown for Environment and Society | Jennifer Wilcox, chemical engineering professor at the University of Pennsylvania and former U.S. Assistant Secretary for Fossil Energy and Carbon Management | Michael Greenstone, economist and director of the Energy Policy Institute at the University of Chicago | Solomon Hsiang, professor of global environmental policy at Stanford University | Chris Bataille, global fellow at Columbia University’s Center on Global Energy Policy | Danny Cullenward, senior fellow at the Kleinman Center for Energy Policy at the University of Pennsylvania | J. Mijin Cha, environmental studies professor at UC Santa Cruz and fellow at Cornell University’s Climate Jobs Institute | Lynne Kiesling, director of the Institute for Regulatory Law and Economics at Northwestern University | Daniel Swain, climate scientist at the University of California Agriculture and Natural Resources | Emily Grubert, sustainable energy policy professor at the University of Notre Dame | Jon Norman, president of Hydrostor | Chris Creed, managing partner at Galvanize Climate Solutions | Amy Heart, senior vice president of public policy at Sunrun | Kate Brandt, chief sustainability officer at Google | Sophie Purdom, managing partner at Planeteer Capital and co-founder of CTVC | Lara Pierpoint, managing director at Trellis Climate | Andrew Beebe, managing director at Obvious Ventures | Gabriel Kra, managing director and co-founder of Prelude Ventures | Joe Goodman, managing partner and co-founder of VoLo Earth Ventures | Erika Reinhardt, executive director and co-founder of Spark Climate Solutions | Dawn Lippert, founder and CEO of Elemental Impact and general partner at Earthshot Ventures | Rajesh Swaminathan, partner at Khosla Ventures | Rob Davies, CEO of Sublime Systems | John Arnold, philanthropist and co-founder of Arnold Ventures | Gabe Kleinman, operating partner at Emerson Collective | Amy Duffuor, co-founder and general partner at Azolla Ventures | Amy Francetic, managing general partner and founder of Buoyant Ventures | Tom Chi, founding partner at At One Ventures | Francis O’Sullivan, managing director at S2G Investments | Cooper Rinzler, partner at Breakthrough Energy Ventures | Gina McCarthy, former administrator of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency | Neil Chatterjee, former commissioner of the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission | Representative Scott Peters, member of the U.S. House of Representatives | Todd Stern, former U.S. special envoy for climate change | Representative Sean Casten, member of the U.S. House of Representatives | Representative Mike Levin, member of the U.S. House of Representatives | Zeke Hausfather, climate research lead at Stripe and research scientist at Berkeley Earth | Shuchi Talati, founder and executive director of the Alliance for Just Deliberation on Solar Geoengineering | Nat Bullard, co-founder of Halcyon | Bill McKibben, environmentalist and founder of 350.org | Ilaria Mazzocco, senior fellow at the Center for Strategic and International Studies | Leah Stokes, professor of environmental politics at UC Santa Barbara | Noah Kaufman, senior research scholar at Columbia University’s Center on Global Energy Policy | Arvind Ravikumar, energy systems professor at the University of Texas at Austin | Jessica Green, political scientist at the University of Toronto | Jonas Nahm, energy policy professor at Johns Hopkins SAIS | Armond Cohen, executive director of the Clean Air Task Force | Costa Samaras, director of the Scott Institute for Energy Innovation at Carnegie Mellon University | John Larsen, partner at Rhodium Group | Alex Trembath, executive director of the Breakthrough Institute | Alex Flint, executive director of the Alliance for Market Solutions
The Heatmap Insiders Survey of 55 invited expert respondents was conducted by Heatmap News reporters during November and December 2025. Responses were collected via phone interviews. All participants were given the opportunity to record responses anonymously. Not all respondents answered all questions.
Plus, which is the best hyperscaler on climate — and which is the worst?
The biggest story in energy right now is data centers.
After decades of slow load growth, forecasters are almost competing with each other to predict the most eye-popping figure for how much new electricity demand data centers will add to the grid. And with the existing electricity system with its backbone of natural gas, more data centers could mean higher emissions.
Hyperscalers with sustainability goals are already reporting higher emissions, and technology companies are telling investors that they plan to invest hundreds of billions, if not trillions of dollars, into new data centers, increasingly at gigawatt scale.
And yet when we asked our Heatmap survey participants “Do you think AI and data centers’ energy needs are significantly slowing down decarbonization?” only about 34% said they would, compared to 66% who said they wouldn’t.
There were some intriguing differences between different types of respondents. Among our “innovator” respondents — venture capitalists, founders, and executives working at climate tech startups — the overwhelming majority said that AI and data centers are not slowing down decarbonization. “I think it’s the inverse — I think we want to launch the next generation of technologies when there’s demand growth and opportunity to sell into a slightly higher priced, non-commoditized market,” Joe Goodman co-founder and managing partner at VoLo Earth Ventures, told us.
Not everyone in Silicon Valley is so optimistic, however. “I think in a different political environment, it may have been a true accelerant,” one VC told us. “But in this political environment, it’s a true albatross because it’s creating so many more emissions. It’s creating so much stress on the grid. We’re not deploying the kinds of solutions that would be effective."
Scientists were least in agreement on the question. While only 47% of scientists thought the growth of data centers would significantly slow down decarbonization, most of the pessimistic camp was in the social sciences. In total, over 62% of the physical scientists we surveyed thought data centers weren’t slowing down decarbonization, compared to a third of social scientists.
Michael Greenstone, a University of Chicago economist, told us he didn’t see data centers and artificial intelligence as any different from any other use of energy. “I also think air conditioning and lighting, computing, and 57,000 other uses of electricity are slowing down decarbonization,” he said. The real answer is the world is not trying to minimize climate change.”
Mijin Cha, an assistant professor of environment studies at the University of California Santa Cruz, was even more gloomy, telling us, “Not only do I think it’s slowing down decarbonization, I think it is permanently extending the life of fossil fuels, especially as it is now unmitigated growth.”
Some took issue with the premise of the question, expressing skepticism of the entire AI industry. “I’m actually of the opinion that most of the AI and data center plans are a massive bubble,” a scientist told us. “And so, are there plans that would be disruptive to emissions? Yes. Are they actually doing anything to emissions yet? Not obvious.”
We also asked respondents to name the “best” and “worst” hyperscalers, large technology companies pursuing the data center buildout. Many of these companies have some kind of renewables or sustainability goal, but there are meaningful differences among them. Google and Microsoft look to match their emissions with non-carbon-power generation in the same geographic area and at the same time. The approach used by Meta and Amazon, on the other hand, is to develop renewable projects that have the biggest “bang for the buck” on global emissions by siting them in areas with high emissions that the renewable generation can be said to displace.
Among our respondents, the 24/7 “time and place” approach is the clear winner.
Google was the “best” pick for 19 respondents, including six who said “Google and Microsoft.” By contrast, Amazon and Meta had just three votes combined.
As for the “worst,” there was no clear consensus, although two respondents from the social sciences picked “everyone besides Microsoft and Google” and “everyone but Google and Microsoft.” Another one told us, “The best is a tie between Microsoft and Google. Everyone else is in the bottom category.”
A third social scientist summed it up even more pungently. “Google is the best, Meta is the worst. Evil corporation” — though with more expletives than that.
The Heatmap Insiders Survey of 55 invited expert respondents was conducted by Heatmap News reporters during November and December 2025. Responses were collected via phone interviews. All participants were given the opportunity to record responses anonymously. Not all respondents answered all questions.