You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
Paradise, California, is snatching up high-risk properties to create a defensive perimeter and prevent the town from burning again.

The 2018 Camp Fire was the deadliest wildfire in California’s history, wiping out 90% of the structures in the mountain town of Paradise and killing at least 85 people in a matter of hours. Investigations afterward found that Paradise’s town planners had ignored warnings of the fire risk to its residents and forgone common-sense preparations that would have saved lives. In the years since, the Camp Fire has consequently become a cautionary tale for similar communities in high-risk wildfire areas — places like Chinese Camp, a small historic landmark in the Sierra Nevada foothills that dramatically burned to the ground last week as part of the nearly 14,000-acre TCU September Lightning Complex.
More recently, Paradise has also become a model for how a town can rebuild wisely after a wildfire. At least some of that is due to the work of Dan Efseaff, the director of the Paradise Recreation and Park District, who has launched a program to identify and acquire some of the highest-risk, hardest-to-access properties in the Camp Fire burn scar. Though he has a limited total operating budget of around $5.5 million and relies heavily on the charity of local property owners (he’s currently in the process of applying for a $15 million grant with a $5 million match for the program) Efseaff has nevertheless managed to build the beginning of a defensible buffer of managed parkland around Paradise that could potentially buy the town time in the case of a future wildfire.
In order to better understand how communities can build back smarter after — or, ideally, before — a catastrophic fire, I spoke with Efseaff about his work in Paradise and how other communities might be able to replicate it. Our conversation has been lightly edited and condensed for clarity.
Do you live in Paradise? Were you there during the Camp Fire?
I actually live in Chico. We’ve lived here since the mid-‘90s, but I have a long connection to Paradise; I’ve worked for the district since 2017. I’m also a sea kayak instructor and during the Camp Fire, I was in South Carolina for a training. I was away from the phone until I got back at the end of the day and saw it blowing up with everything.
I have triplet daughters who were attending Butte College at the time, and they needed to be evacuated. There was a lot of uncertainty that day. But it gave me some perspective, because I couldn’t get back for two days. It gave me a chance to think, “Okay, what’s our response going to be?” Looking two days out, it was like: That would have been payroll, let’s get people together, and then let’s figure out what we’re going to do two weeks and two months from now.
It also got my mind thinking about what we would have done going backwards. If you’d had two weeks to prepare, you would have gotten your go-bag together, you’d have come up with your evacuation route — that type of thing. But when you run the movie backwards on what you would have done differently if you had two years or two decades, it would include prepping the landscape, making some safer community defensible space. That’s what got me started.
Was it your idea to buy up the high-risk properties in the burn scar?
I would say I adapted it. Everyone wants to say it was their idea, but I’ll tell you where it came from: Pre-fire, the thinking was that it would make sense for the town to have a perimeter trail from a recreation standpoint. But I was also trying to pitch it as a good idea from a fuel standpoint, so that if there was a wildfire, you could respond to it. Certainly, the idea took on a whole other dimension after the Camp Fire.
I’m a restoration ecologist, so I’ve done a lot of river floodplain work. There are a lot of analogies there. The trend has been to give nature a little bit more room: You’re not going to stop a flood, but you can minimize damage to human infrastructure. Putting levees too close to the river makes them more prone to failing and puts people at risk — but if you can set the levee back a little bit, it gives the flood waters room to go through. That’s why I thought we need a little bit of a buffer in Paradise and some protection around the community. We need a transition between an area that is going to burn, and that we can let burn, but not in a way that is catastrophic.
How hard has it been to find willing sellers? Do most people in the area want to rebuild — or need to because of their mortgages?
Ironically, the biggest challenge for us is finding adequate funding. A lot of the property we have so far has been donated to us. It’s probably upwards of — oh, let’s see, at least half a dozen properties have been donated, probably close to 200 acres at this point.
We are applying for some federal grants right now, and we’ll see how that goes. What’s evolved quite a bit on this in recent years, though, is that — because we’ve done some modeling — instead of thinking of the buffer as areas that are managed uniformly around the community, we’re much more strategic. These fire events are wind-driven, and there are only a couple of directions where the wind blows sufficiently long enough and powerful enough for the other conditions to fall into play. That’s not to say other events couldn’t happen, but we’re going after the most likely events that would cause catastrophic fires, and that would be from the Diablo winds, or north winds, that come through our area. That was what happened in the Camp Fire scenario, and another one our models caught what sure looked a lot like the [2024] Park Fire.
One thing that I want to make clear is that some people think, “Oh, this is a fire break. It’s devoid of vegetation.” No, what we’re talking about is a well-managed habitat. These are shaded fuel breaks. You maintain the big trees, you get rid of the ladder fuels, and you get rid of the dead wood that’s on the ground. We have good examples with our partners, like the Butte Fire Safe Council, on how this works, and it looks like it helped protect the community of Cohasset during the Park Fire. They did some work on some strips there, and the fire essentially dropped to the ground before it came to Paradise Lake. You didn’t have an aerial tanker dropping retardant, you didn’t have a $2-million-per-day fire crew out there doing work. It was modest work done early and in the right place that actually changed the behavior of the fire.
Tell me a little more about the modeling you’ve been doing.
We looked at fire pathways with a group called XyloPlan out of the Bay Area. The concept is that you simulate a series of ignitions with certain wind conditions, terrain, and vegetation. The model looked very much like a Camp Fire scenario; it followed the same pathway, going towards the community in a little gulch that channeled high winds. You need to interrupt that pathway — and that doesn’t necessarily mean creating an area devoid of vegetation, but if you have these areas where the fire behavior changes and drops down to the ground, then it slows the travel. I found this hard to believe, but in the modeling results, in a scenario like the Camp Fire, it could buy you up to eight hours. With modern California firefighting, you could empty out the community in a systematic way in that time. You could have a vigorous fire response. You could have aircraft potentially ready. It’s a game-changing situation, rather than the 30 minutes Paradise had when the Camp Fire started.
How does this work when you’re dealing with private property owners, though? How do you convince them to move or donate their land?
We’re a Park and Recreation District so we don’t have regulatory authority. We are just trying to run with a good idea with the properties that we have so far — those from willing donors mostly, but there have been a couple of sales. If we’re unable to get federal funding or state support, though, I ultimately think this idea will still have to be here — whether it’s five, 10, 15, or 50 years from now. We have to manage this area in a comprehensive way.
Private property rights are very important, and we don’t want to impinge on that. And yet, what a person does on their property has a huge impact on the 30,000 people who may be downwind of them. It’s an unusual situation: In a hurricane, if you have a hurricane-rated roof and your neighbor doesn’t, and theirs blows off, you feel sorry for your neighbor but it’s probably not going to harm your property much. In a wildfire, what your neighbor has done with the wood, or how they treat vegetation, has a significant impact on your home and whether your family is going to survive. It’s a fundamentally different kind of event than some of the other disasters we look at.
Do you have any advice for community leaders who might want to consider creating buffer zones or something similar to what you’re doing in Paradise?
Start today. You have to think about these things with some urgency, but they’re not something people think about until it happens. Paradise, for many decades, did not have a single escaped wildfire make it into the community. Then, overnight, the community is essentially wiped out. But in so many places, these events are foreseeable; we’re just not wired to think about them or prepare for them.
Buffers around communities make a lot of sense, even from a road network standpoint. Even from a trash pickup standpoint. You don’t think about this, but if your community is really strung out, making it a little more thoughtfully laid out also makes it more economically viable to provide services to people. Some things we look for now are long roads that don’t have any connections — that were one-way in and no way out. I don’t think [the traffic jams and deaths in] Paradise would have happened with what we know now, but I kind of think [authorities] did know better beforehand. It just wasn’t economically viable at the time; they didn’t think it was a big deal, but they built the roads anyway. We can be doing a lot of things smarter.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
This week is light on the funding, heavy on the deals.
This week’s Funding Friday is light on the funding but heavy on the deals. In the past few days, electric carmaker Rivian and virtual power plant platform EnergyHub teamed up to integrate EV charging into EnergyHub’s distributed energy management platform; the power company AES signed 20-year power purchase agreements with Google to bring a Texas data center online; and microgrid company Scale acquired Reload, a startup that helps get data centers — and the energy infrastructure they require — up and running as quickly as possible. Even with venture funding taking a backseat this week, there’s never a dull moment.
Ahead of the Rivian R2’s launch later this year, the EV-maker has partnered with EnergyHub, a company that aggregates distributed energy resources into virtual power plants, to give drivers the opportunity to participate in utility-managed charging programs. These programs coordinate the timing and rate of EV charging to match local grid conditions, enabling drivers to charge when prices are low and clean energy is abundant while avoiding periods of peak demand that would stress the distribution grid.
As Seth Frader-Thompson, EnergyHub’s president, said in a statement, “Every new EV on the road is a win for drivers and the environment, and by managing charging effectively, we ensure this growth remains a benefit for the grid as well.”
The partnership will fold Rivian into EnergyHub’s VPP ecosystem, giving the more than 150 utilities on its platform the ability to control when and how participating Rivian drivers charge. This managed approach helps alleviate grid stress, thus deferring the need for costly upgrades to grid infrastructure such as substations or transformers. Extending the lifespan of existing grid assets means lower electricity costs for ratepayers and more capacity to interconnect new large loads — such as data centers.
Google seems to be leaning hard into the “bring-your-own-power” model of data center development as it looks to gain an edge in the AI race.
The latest evidence came on Tuesday, when the power company and utility operator AES announced a partnership with the hyperscaler to provide on-site power for a new data center in Texas. signing 20-year power purchase agreements. AES will develop, own, and operate the generation assets, as well as all necessary electricity infrastructure, having already secured the land and interconnection agreements to bring this new power online. The data center is set to begin operations in 2027.
As of yet, neither company has disclosed the exact type of energy infrastructure that AES will be building, although Amanda Peterson Corio, Google’s head of data center energy, said in a press release that it will be “clean.”
“In partnership with AES, we are bringing new clean generation online directly alongside the data center to minimize local grid impact and protect energy affordability,” she said.
This announcement came the same day the hyperscaler touted a separate agreement with the utility Xcel Energy to power another data center in Minnesota with 1.6 gigawatts of solar and wind generation and 300 megawatts of long-duration energy storage from the iron-air battery startup Form Energy.
The microgrid developer Scale has acquired Reload, a “powered land” startup founded in 2024, for an undisclosed sum. What is “powered land”? Essentially, it’s land that Reload has secured and prepared for large data centers customers, obtaining permits and planning for onsite energy infrastructure such that sites can be energized immediately. This approach helps developers circumvent the years-long utility interconnection queue and builds on Scale’s growing focus on off-grid data center projects, as the company aims to deliver gigawatts of power for hyperscalers in the coming years powered by a diverse mix of sources, from solar and battery storage to natural gas and fuel cells.
Early last year, the Swedish infrastructure investor EQT acquired Scale. The goal, EQT said, was to enable the company “to own and operate billions of dollars in distributed generation assets.” At the time of the acquisition, Scale had 2.5 gigawatts of projects in its pipeline. In its latest press release the company announced it has secured a multi-hundred-megawatt contract with a leading hyperscaler, though it did not name names.
As Jan Vesely, a partner at EQT said in a statement, “By bringing together Reload’s campus development capabilities, Scale’s proven islanded power operating platform, and EQT’s deep expertise across energy, digital infrastructure and technology, we are supporting a more integrated approach to delivering power for next-generation digital infrastructure today.”
Not to say there’s been no funding news to speak of!
As my colleague Alexander C. Kaufman reported in an exclusive on Thursday, fusion company Shine Technologies raised $240 million in a Series E round, the majority of which came from biotech billionaire Patrick Soon-Shiong. Unlike most of its peers, Shine isn’t gunning to build electricity-generating reactors anytime soon. Instead, its initial focus is producing valuable medical isotopes — currently made at high cost via fission — which it can sell to customers such as hospitals, healthcare organizations, or biopharmaceutical companies. The next step, Shine says, is to scale into recycling radioactive waste from spent fission fuel.
“The basic premise of our business is fusion is expensive today, so we’re starting by selling it to the highest-paying customers first,” the company’s CEO, Greg Piefer told Kaufman, calling electricity customers the “lowest-paying customer of significance for fusion today.”
On the solar siege, New York’s climate law, and radioactive data center
Current conditions: A rain storm set to dump 2 inches of rain across Alabama, Tennessee, Georgia, and the Carolinas will quench drought-parched woodlands, tempering mounting wildfire risk • The soil on New Zealand’s North Island is facing what the national forecast called a “significant moisture deficit” after a prolonged drought • Temperatures in Odessa, Texas, are as much as 20 degrees Fahrenheit hotter than average.
For all its willingness to share in the hype around as-yet-unbuilt small modular reactors and microreactors, the Trump administration has long endorsed what I like to call reactor realism. By that, I mean it embraces the need to keep building more of the same kind of large-scale pressurized water reactors we know how to construct and operate while supporting the development and deployment of new technologies. In his flurry of executive orders on nuclear power last May, President Donald Trump directed the Department of Energy to “prioritize work with the nuclear energy industry to facilitate” 5 gigawatts of power uprates to existing reactors “and have 10 new large reactors with complete designs under construction by 2030.” The record $26 billion loan the agency’s in-house lender — the Loan Programs Office, recently renamed the Office of Energy Dominance Financing — gave to Southern Company this week to cover uprates will fulfill the first part of the order. Now the second part is getting real. In a scoop on Thursday, Heatmap’s Robinson Meyer reported that the Energy Department has started taking meetings with utilities and developers of what he said “would almost certainly be AP1000s, a third-generation reactor produced by Westinghouse capable of producing up to 1.1 gigawatts of electricity per unit.”
Reactor realism includes keeping existing plants running, so notch this as yet more progress: Diablo Canyon, the last nuclear station left in California, just cleared the final state permitting hurdle to staying open until 2030, and possibly longer. The Central Coast Water Board voted unanimously on Thursday to give the state’s last nuclear plant a discharge permit and water quality certification. In a post on LinkedIn, Paris Ortiz-Wines, a pro-nuclear campaigner who helped pass a 2022 law that averted the planned 2025 closure of Diablo Canyon, said “70% of public comments were in full support — from Central Valley agricultural associations, the local Chamber of Commerce, Dignity Health, the IBEW union, district supervisors, marine meteorologists, and local pro-nuclear organizations.” Starting in 2021, she said, she attended every hearing on the bill that saved the plant. “Back then, I knew every single pro-nuclear voice testifying,” she wrote. “Now? I’m meeting new ones every hearing.”
It was the best of times, it was the worst of times. It was a year of record solar deployments, it was a year of canceled solar megaprojects, choked-off permits, and desperate industry pleas to Congress for help. But the solar industry’s political clouds may be parting. The Department of the Interior is reviewing at least 20 commercial-scale projects that E&E News reported had “languished in the permitting pipeline” since Trump returned to office. “That includes a package of six utility-scale projects given the green light Friday by Interior Secretary Doug Burgum to resume active reviews, such as the massive Esmeralda Energy Center in Nevada,” the newswire reported, citing three anonymous career officials at the agency.
Heatmap’s Jael Holzman broke the news that the project, also known as Esmeralda 7, had been canceled in October. At the time, NextEra, one of the project’s developers, told her that it was “committed to pursuing our project’s comprehensive environmental analysis by working closely with the Bureau of Land Management.” That persistence has apparently paid off. In a post on X linking to the article, Morgan Lyons, the senior spokesperson at the Solar Energy Industries Association, called the change “quite a tone shift” with the eyes emoji. GOP voters overwhelmingly support solar power, a recent poll commissioned by the panel manufacturer First Solar found. The MAGA coalition has some increasingly prominent fans. As I have covered in the newsletter, Katie Miller, the right-wing influencer and wife of Trump consigliere Stephen Miller, has become a vocal proponent of competing with China on solar and batteries.
Get Heatmap AM directly in your inbox every morning:
MP Materials operates the only active rare earths mine in the United States at California’s Mountain Pass. Now the company, of which the federal government became the largest shareholder in a landmark deal Trump brokered earlier this year, is planning a move downstream in the rare earths pipeline. As part of its partnership with the Department of Defense, MP Materials plans to invest more than $1 billion into a manufacturing campus in Northlake, Texas, dedicated to making the rare earth magnets needed for modern military hardware and electric vehicles. Dubbed 10X, the campus is expected to come online in 2028, according to The Wall Street Journal.
Sign up to receive Heatmap AM in your inbox every morning:
New York’s rural-urban divide already maps onto energy politics as tensions mount between the places with enough land to build solar and wind farms and the metropolis with rising demand for power from those panels and turbines. Keeping the state’s landmark climate law in place and requiring New York to generate the vast majority of its power from renewables by 2040 may only widen the split. That’s the obvious takeaway from data from the New York State Energy Research and Development Authority. In a memo sent Thursday to Governor Kathy Hochul on the “likely costs of” complying with the law as it stands, NYSERDA warned that the statute will increase the cost of heating oil and natural gas. Upstate households that depend on fossil fuels could face hikes “in excess of $4,000 a year,” while New York City residents would see annual costs spike by $2,300. “Only a portion of these costs could be offset by current policy design,” read the memo, a copy of which City & State reporter Rebecca C. Lewis posted on X.
Last fall, this publication’s energy intelligence unit Heatmap Pro commissioned a nationwide survey asking thousands of American voters: “Would you support or oppose a data center being built near where you live?” Net support came out to +2%, with 44% in support and 42% opposed. Earlier this month, the pollster Embold Research ran the exact same question by another 2,091 registered voters across the country. The shift in the results, which I wrote about here, is staggering. This time just 28% said they would support or strongly support a data center that houses “servers that power the internet, apps, and artificial intelligence” in their neighborhood, while 52% said they would oppose or strongly oppose it. That’s a net support of -24% — a 26-point drop in just a few months.
Among the more interesting results was the fact that the biggest partisan gap was between rural and urban Republicans, with the latter showing greater support than any other faction. When I asked Emmet Penney at the right-leaning Foundation for American Innovation to make sense of that for me, he said data centers stoke a “fear of bigness” in a way that compares to past public attitudes on nuclear power.
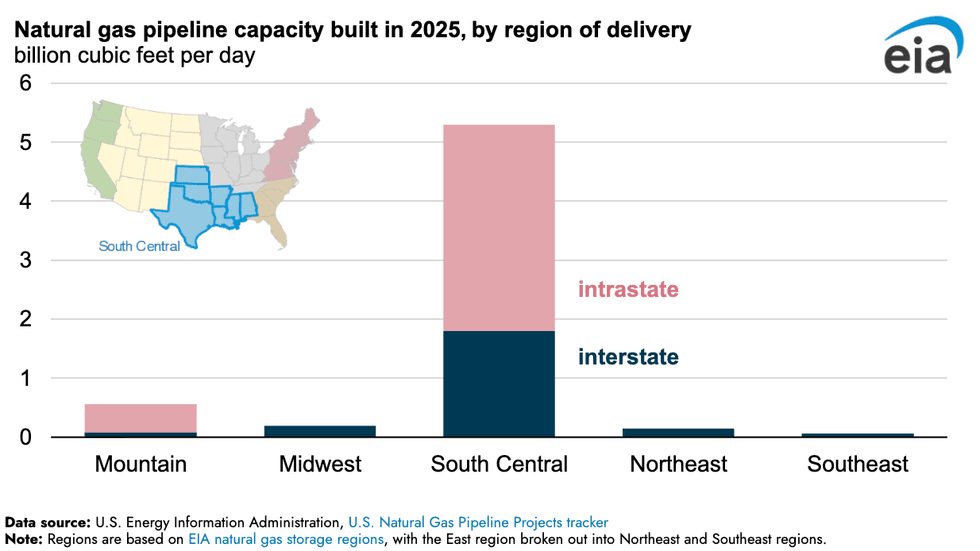
Gas pipeline construction absolutely boomed last year in one specific region of the U.S. Spanning Texas, Oklahoma, Kansas, Arkansas, Louisiana, Mississippi, and Alabama, the so-called South Central bloc saw a dramatic spike in intrastate natural gas pipelines, more than all other regions combined, per new Energy Information Administration data. It’s no mystery as to why. The buildout of liquified natural gas export terminals along the Gulf coast needs conduits to carry fuel from the fracking fields as far west as the Texas Permian.
Rob sits down with Jane Flegal, an expert on all things emissions policy, to dissect the new electricity price agenda.
As electricity affordability has risen in the public consciousness, so too has it gone up the priority list for climate groups — although many of their proposals are merely repackaged talking points from past political cycles. But are there risks of talking about affordability so much, and could it distract us from the real issues with the power system?
Rob is joined by Jane Flegal, a senior fellow at the Searchlight Institute and the States Forum. Flegal was the former senior director for industrial emissions at the White House Office of Domestic Climate Policy, and she has worked on climate policy at Stripe. She was recently executive director of the Blue Horizons Foundation.
Shift Key is hosted by Robinson Meyer, the founding executive editor of Heatmap News.
Subscribe to “Shift Key” and find this episode on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, Amazon, or wherever you get your podcasts.
You can also add the show’s RSS feed to your podcast app to follow us directly.
Here is an excerpt from their conversation:
Robinson Meyer: What’s interesting is the scarcity model is driven by the fact that ultimately rate payers that is utility customers are where the buck stops, and so state regulators don’t want utilities to overbuild for a given moment because ultimately it is utility customers — it’s people who pay their power bills — who will bear the burden of a utility overbuilding. In some ways, the entire restructured electricity market system, the entire shift to electricity markets in the 90s and aughts, was because of this belief that utilities were overbuilding.
And what’s been funny is that, what, we started restructuring markets around the year 2000. For about five or six or seven years. Wall Street was willing to finance new electricity. I mean, I hear two stories here — basically it’s another place where I hear two stories, and I think where there’s a lot of disagreement about the path forward on electricity policy, in that I’ve heard a story that, basically, electricity restructuring starts in the late 90s you know year 2000, and for five years, Wall Street is willing to finance new power investment based entirely on price risk based entirely on the idea that market prices for electricity will go up. Then three things happen: The Great Recession, number one, wipes out investment, wipes out some future demand.
Number two, fracking. Power prices tumble, and a bunch of plays that people had invested in, including then advanced nuclear, are totally out of the money suddenly. Number three, we get electricity demand growth plateaus, right? So for 15 years, electricity demand plateaus. We don’t need to finance investments into the power grid anymore. This whole question of, can you do it on the back of price risk? goes away because electricity demand is basically flat, and different kinds of generation are competing over shares and gas is so cheap that it’s just whittling away.
Jane Flegal: But this is why that paradigm needs to change yet again. Like ,we need to pivot to like a growth model where, and I’m not, again —
Meyer: I think what’s interesting, though, is that Texas is the other counterexample here. Because Texas has had robust load growth for years, and a lot of investment in power production in Texas is financed off price risk, is financed off the assumption that prices will go up. Now, it’s also financed off the back of the fact that in Texas, there are a lot of rules and it’s a very clear structure around finding firm offtake for your powers. You can find a customer who’s going to buy 50% of your power, and that means that you feel confident in your investment. And then the other 50% of your generation capacity feeds into ERCOT. But in some ways, the transition that feels disruptive right now is not only a transition like market structure, but also like the assumptions of market participants about what electricity prices will be in the future.
Flegal: Yeah, and we may need some like backstop. I hear the concerns about the risks of laying early capital risks basically on rate payers in the frame of growth rather than scarcity. But I guess my argument is just there’s ways to deal with that. Like we could come up with creative ways to think about dealing with that. And I’m not seeing enough ideation in that space, which — I would like, again, a call for papers, I guess — that I would really like to get a better handle on.
The other thing that we haven’t talked about, but that I do think, you know, the States Forum, where I’m now a senior fellow, I wrote a piece for them on electricity affordability several months ago now. But one of the things that doesn’t get that much attention is just like getting BS off of bills, basically. So there’s like the rate question, but then there’s the like, what’s in a bill? And like, what, what should or should not be in a bill? And in truth, you know, we’ve got a lot of social programs basically that are being funded by the rate base and not the tax base. And I think there are just like open questions about this — whether it’s, you know, wildfire in California, which I think everyone recognizes is a big challenge, or it’s efficiency or electrification or renewable mandates in blue states. There are a bunch of these things and it’s sort of like there are so few things you can do in the very near term to constrain rate increases for the reasons we’ve discussed.
You can find a full transcript of the episode here.
Mentioned:
Cheap and Abundant Electricity Is Good, by Jane Flegal
From Heatmap: Will Virtual Power Plants Ever Really Be a Thing?
Previously on Shift Key: How California Broke Its Electricity Bills and How Texas Could Destroy Its Electricity Market
This episode of Shift Key is sponsored by …
Accelerate your clean energy career with Yale’s online certificate programs. Explore the 10-month Financing and Deploying Clean Energy program or the 5-month Clean and Equitable Energy Development program. Use referral code HeatMap26 and get your application in by the priority deadline for $500 off tuition to one of Yale’s online certificate programs in clean energy. Learn more at cbey.yale.edu/online-learning-opportunities.
Music for Shift Key is by Adam Kromelow.