You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
With the ongoing disaster approaching its second week, here’s where things stand.
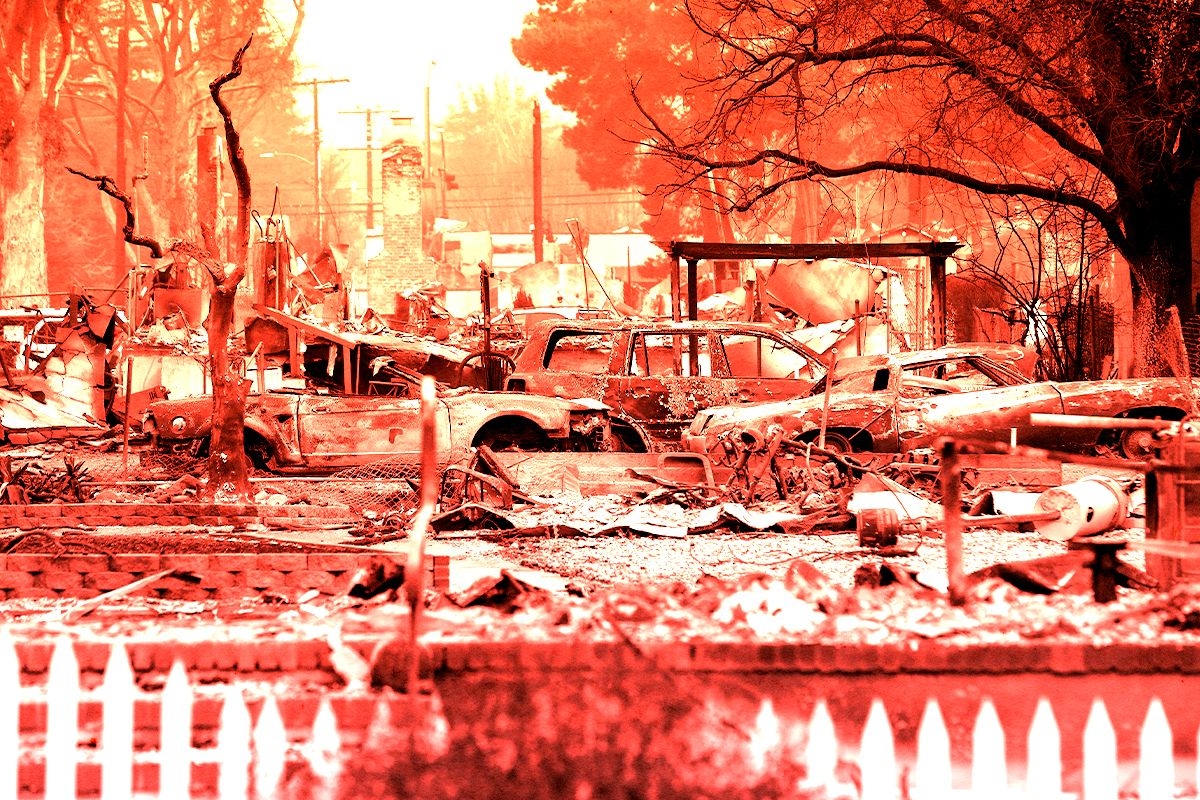

A week ago, forecasters in Southern California warned residents of Los Angeles that conditions would be dry, windy, and conducive to wildfires. How bad things have gotten, though, has taken everyone by surprise. As of Monday morning, almost 40,000 acres of Los Angeles County have burned in six separate fires, the biggest of which, Palisades and Eaton, have yet to be fully contained. The latest red flag warning, indicating fire weather, won’t expire until Wednesday.
Many have questions about how the second-biggest city in the country is facing such unbelievable devastation (some of these questions, perhaps, being more politically motivated than others). Below, we’ve tried to collect as many answers as possible — including a bit of good news about what lies ahead.
A second Santa Ana wind event is due to set in Monday afternoon. “We’re expecting moderate Santa Ana winds over the next few days, generally in the 20 to 30 [mile per hour] range, gusting to 50, across the mountains and through the canyons,” Eric Drewitz, a meteorologist with the Forest Service, told me on Sunday. Drewitz noted that the winds will be less severe than last week’s, when the fires flared up, but he also anticipates they’ll be “more easterly,” which could blow the fires into new areas. A new red flag warning has been issued through Wednesday, signaling increased fire potential due to low humidity and high winds for several days yet.
If firefighters can prevent new flare-ups and hold back the fires through that wind event, they might be in good shape. By Friday of this week, “it looks like we could have some moderate onshore flow,” Drewitz said, when wet ocean air blows inland, which would help “build back the marine layer” and increase the relative humidity in the region, decreasing the chances of more fires. Information about the Santa Anas at that time is still uncertain — the models have been changing, and the wind is tricky to predict the strength of so far out — but an increase in humidity will at least offer some relief for the battered Ventura and Orange Counties.
The Palisades Fire, the biggest in L.A., ripped through the hilly and affluent area between Santa Monica and Malibu, including the Pacific Palisades neighborhood, the second-most expensive zip code in Los Angeles and home to many celebrities. Structures in Big Rock, a neighborhood in Malibu, have also burned. The fire has also encroached on the I-405 and the Getty Villa, and destroyed at least two homes in Mandeville Canyon, a neighborhood of multimillion-dollar homes. Students at nearby University of California, Los Angeles, were told on Friday to prepare for a possible evacuation.
The Eaton Fire, the second biggest blaze in the area, has killed 16 people in Altadena, a neighborhood near Pasadena, according to the Los Angeles Times, making it one of the deadliest fires in the modern history of California.
The 1,000-acre Kenneth fire is 100% contained but still burning near Calabasas and the gated community of Hidden Hills. The Hurst Fire has burned nearly 800 acres and is 89% contained and is still burning near Sylmar, the northernmost neighborhood in L.A. Though there are no evacuation notices for either the Kenneth or the Hurst fires, residents in the L.A. area should monitor the current conditions as the situation continues to be fluid and develop.
The 43-acre Sunset Fire, which triggered evacuations last week in Hollywood and Hollywood Hills, burned no homes and is 100% contained.
The Lidia Fire, which ignited in a remote area south of Acton, California, on Wednesday afternoon, burned 350 acres of brush and is 100% contained.
It can take years to determine the cause of a fire, and investigations typically don’t begin until after the fire is under control and the area is safe to reenter, Edward Nordskog, a retired fire investigator from the Los Angeles Sheriff’s Department, told Heatmap’s Emily Pontecorvo. He also noted, however, that urban fires are typically easier to pinpoint the cause of than wildland fires due to the availability of witnesses and surveillance footage.
The vast majority of wildfires, 85%, are caused by humans. So far, investigators have ruled out lightning — another common fire-starter — because there were no electrical storms in the area when the fires started. In the case of the Palisades Fire, there were no power lines in the area of the ignition, though investigators are now looking into an electrical transmission tower in Eaton Canyon as the possible cause of the deadly fire in Altadena. There have been rumors that arsonists started the fires, but investigators say that scenario is also pretty unlikely due to the spread of the fires and how remote the ignition areas are.
Officially, 24 people have died, but that tally is likely to rise. California Governor Gavin Newsom said Sunday that he expects “a lot more” deaths will be added to the total in the coming days as search efforts continue.
Incoming President Donald Trump slammed the response to the L.A. fires in a Truth Social post on Sunday morning: “This is one of the worst catastrophes in the history of our Country,” he wrote. “They just can’t put out the fires. What’s wrong with them?”
Though there is much blame going around — not all of it founded in reality — the challenges facing firefighters are immense. Last week, because of strong Santa Ana winds, fire crews could not drop suppressants like water or chemical retardant on the initial blazes. (In strong winds, water and retardant will blow away before they reach the flames on the ground.)
Fighting a fire in an urban or suburban area is also different from fighting one in a remote, wild area. In a true wildfire, crews don’t use much water; firefighters typically contain the blazes by creating breaks — areas cleared of vegetation that starve a fire of fuel and keep it from spreading. In an urban or suburban event, however, firefighters can’t simply hack through a neighborhood, and typically have to use water to fight structure fires. Their priority also shifts from stopping the fire to evacuating and saving people, which means putting out the fire itself has to wait.
What’s more, the L.A. area faced dangerous fire weather going into last week — with wind gusts up to 100 miles per hour and dry air — and the persistence of the Santa Ana winds during firefighting operations through the weekend made it extremely difficult for emergency managers to gain a foothold.
Trump and others have criticized Los Angeles for being unprepared for the fires, given reports that some fire hydrants ran dry or had low pressure during operations in Pacific Palisades. According to the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power, about 20% of hydrants were affected, mostly at higher elevations.
The problem isn’t a lack of preparation, however. It’s that the L.A. wildfires are so large and widespread, the county’s preparations were quickly overwhelmed. “We’re fighting a wildfire with urban water systems, and that is really challenging,” Los Angeles Department of Water and Power CEO Janisse Quiñones said in a news conference last week. When houses burn down, water mains can break open. Civilians also put a strain on the system when they use hoses or sprinkler systems to try to protect their homes.
On Sunday, Judy Chu, the Democratic lawmaker representing Altadena, confirmed that fire officials had told her there was enough water to continue the battle in the days ahead. “I believe that we're in a good place right now,” she told reporters. Newsom, meanwhile, has responded to criticism over the water failure by ordering an investigation into the weak or dry hydrants.
So-called “super soaker” planes have had no problem with water access; they’re scooping directly from the ocean.
Yes. Although aerial support was grounded in the early stages of the wildfires due to severe Santa Ana winds, flights resumed during lulls in the storms last week.
There is a misconception, though, that water and retardant drops “put out” fires; they don’t. Instead, aerial support suppresses a fire so crews can get in close and use traditional methods, like cutting a fire break or spraying water. “All that up in the air, all that’s doing is allowing the firefighters [on the ground] a chance to get in,” Bobbie Scopa, a veteran firefighter and author of the memoir Both Sides of the Fire Line, told me last week.
With winds expected to pick up early this week, aerial firefighting operations may be grounded again. “If you have erratic, unpredictable winds to where you’ve got a gust spread of like 20 to 30 knots,” i.e. 23 to 35 miles per hour, “that becomes dangerous,” Dan Reese, a veteran firefighter and the founder and president of the International Wildfire Consulting Group, told me on Friday.
Because of the direction of the Santa Ana winds, wildfire smoke should mostly blow out to sea. But as winds shift, unhealthy air can blow into populated areas, affecting the health of residents.
Wildfire smoke is unhealthy, period, but urban and suburban smoke like that from the L.A. fires can be particularly detrimental. It’s not just trees and brush immolating in an urban fire, it’s also cars, and batteries, and gas tanks, and plastics, and insulation, and other nasty, chemical-filled things catching fire and sending fumes into the air. PM2.5, the inhalable particulates from wildfire smoke, contributes to thousands of excess deaths annually in the U.S.
You can read Heatmap’s guide to staying safe during extreme smoke events here.
“The bad news is, I’m not seeing any rain chances,” Drewitz, the Forest Service meteorologist, told me on Sunday. Though the marine layer will bring wetter air to the Los Angeles area on Friday, his models showed it’ll be unlikely to form precipitation.
Though some forecasters have signaled potential rain at the end of next week, the general consensus is that the odds for that are low, and that any rain there may be will be too light or short-lived to contribute meaningfully to extinguishing the fires.
The chaparral shrublands around Los Angeles are supposed to burn every 30 to 130 years. “There are high concentrations of terpenes — very flammable oils — in that vegetation; it’s made to burn,” Scopa, the veteran firefighter, told me.
What isn’t normal, though, is the amount of rain Los Angeles got ahead of this past spring — 52.46 inches in the preceding two years, the wettest period in the city’s history since the late 1800s — which was followed by a blisteringly hot summer and a delayed start to this year’s rainy season. Since October, parts of Southern California have received just 10% of their normal rainfall
This “weather whiplash” is caused by a warmer atmosphere, which means that plants will grow explosively due to the influx of rain and then dry out when the drought returns, leaving lots of dry fuels ready and waiting for a spark. “This is really, I would argue, a signature of climate change that is going to be experienced almost everywhere people actually live on Earth,” Daniel Swain, a climate scientist at the University of California, Los Angeles, who authored a new study on the pattern, told The Washington Post.
We know less about how climate change may affect the Santa Anas, though experts have some theories.
At least 12,000 structures have burned so far in the fires, which is already exacerbating the strain on the Los Angeles housing market — one of the country’s tightest even before the fires — as thousands of displaced people look for new places to live. “Dozens and dozens of people are going after the same properties,” one real estate agent told the Los Angeles Times. The city has reminded businesses that price gouging — including raising rental prices more than 10% — during an emergency is against the law.
Los Angeles had a shortage of about 370,000 homes before the fires, and between 2021 and 2023, the county added fewer than 30,000 new units per year. Recovery grants and federal aid can lag, and it often takes more than two years for even the first Housing and Urban Development Disaster Recovery Grants’ expenditures to go out.
My colleague Matthew Zeitlin wrote for Heatmap that the economic impact of the Los Angeles fire is already much higher than that of other fires, such as the 2018 Camp fire, partly because of the value of the Pacific Palisades real estate.
The wildfires may “deal a devastating blow to [California’s] fragile home insurance market,” Heatmap’s Matthew Zeitlin wrote last week. In recent years, home insurers have left California or declined to write new policies, at least partially due to the increased risk of wildfires in the state.
Depending on the extent of the damage from the fires, the coffers of California’s FAIR Plan — which insures homeowners who can’t get insurance otherwise, including many in Pacific Palisades and Altadena — could empty, causing it to seek money from insurers, according to the state’s regulations. As Zeitlin writes, “This would mean that Californians who were able to buy private insurance — because they don’t live in a region of the state that insurers have abandoned — could be on the hook for massive wildfire losses.”
First and foremost, sign up for all relevant emergency alerts. Make sure to turn on the sound on your phone and keep it near you in case of a change in conditions. Pack a “go bag” with essentials and consider filling your gas tank now so that you can evacuate at a moment’s notice if needed. Read our guide on what to do if you get a pre-evacuation or an evacuation notice ahead of time so that you’re not scrambling for information if you get an alert.
The free Watch Duty app has become a go-to resource for people affected by the fires, including friends and family of Angelenos who may themselves be thousands of miles away. The app provides information on fire perimeters, evacuation notices, and power outages. Its employees pull information directly from emergency responders’ radio broadcasts and sometimes beat official sources to disseminating it. If you need an endorsement: Emergency responders rely on the app, too.
There are many scams in the wake of disasters as crooks look to take advantage of desperate people — and those who want to help them. To play it safe, you can use a hub like the one established by GoFundMe, which is actively vetting campaigns related to the L.A. fires. If you’re looking to volunteer your time, make a donation of clothing or food, or if you’re able to foster animals the fire has displaced, you can use this handy database from the Mutual Aid Network L.A. There are also many national organizations, such as the Red Cross, that you can connect with if you want to help.
The City of Los Angeles and the Los Angeles Fire Department have asked that do-gooders not bring donations directly to fire stations or shelters; such actions can interfere with emergency operations. Their website provides more information about how you can help — productively — on their website.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
The maker of the Prius is finally embracing batteries — just as the rest of the industry retreats.
Selling an electric version of a widely known car model is no guarantee of success. Just look at the Ford F-150 Lightning, a great electric truck that, thanks to its high sticker price, soon will be no more. But the Toyota Highlander EV, announced Tuesday as a new vehicle for the 2027 model year, certainly has a chance to succeed given America’s love for cavernous SUVs.
Highlander is Toyota’s flagship titan, a three-row SUV with loads of room for seven people. It doesn’t sell in quite the staggering numbers of the two-row RAV4, which became the third-best-selling vehicle of any kind in America last year. Still, the Highlander is so popular as a big family ride that Toyota recently introduced an even bigger version, the Grand Highlander. Now, at last, comes the battery-powered version. (It’s just called Highlander and not “Highlander EV,” by the way. The Highlander nameplate will be electric-only, while gas and hybrid SUVs will fly the Grand Highlander flag.)
The American-made electric Highlander comes with a max range of 287 miles in its less expensive form and 320 in its more expensive form. The SUV comes with the NACS port to charge at Tesla Superchargers and vehicle-to-load capability that lets the driver use their battery power for applications like backing up the home’s power supply. Six seats come standard, but the upgraded Highlander comes with the option to go to seven. The interior is appropriately high-tech.
Toyota will begin to build this EV later this year at a factory in Kentucky and start sales late in the year. We don’t know the price yet, but industry experts expect Highlander to start around $55,000 — in the same ballpark as big three-row SUVs like the Kia EV9 and Hyundai Ioniq 9 — and go up from there.
The most important point of the electric Highlander’s arrival, however, is that it signals a sea change for the world’s largest automaker. Toyota was decidedly not all in on the first wave (or two) of modern electric cars. The Japanese giant was content to make money hand over first while the rest of the industry struggled, losing billions trying to catch up to Tesla and deal with an unpredictable market for electrics.
A change was long overdue. This year, Toyota was slated to introduce better EVs to replace the lackluster bZ4x, which had been its sole battery-only model. That included an electrified version of the C-HR small crossover. Now comes the electrified Highlander, marking a much bigger step into the EV market at a time when other automakers are reining in their battery-powered ambitions. (Fellow Japanese brand Subaru, which sold a version of bZ4x rebadged as the Solterra, seems likely to do the same with the electric Highlander and sell a Subaru-labeled version of essentially the same vehicle.)
The Highlander EV matters to a lot of people simply because it’s a Toyota, and they buy Toyotas. This pattern was clear with the success of the Honda Prelude. Under the skin that car was built on General Motors’ electric vehicle platform, but plenty of people bought it because they were simply waiting for their brand, Honda, to put out an EV. Toyota sells more cars than anyone in the world. Its act of putting out a big family EV might signal to some of its customers that, yeah, it’s time to go electric.
Highlander’s hefty size matters, too. The five-seater, two-row crossover took over as America’s default family car in the past few decades. There are good EVs in this space, most notably the Tesla Model Y that has led the world in sales for a long time. By contrast, the lineup of true three-row SUVs that can seat six, seven, or even eight adults has been comparatively lacking. Tesla will cram two seats in the back of the Model Y to make room for seven people, but this is not a true third row. The excellent Rivian R1S is big, but expensive. Otherwise, the Ioniq 9 and EV9 are left to populate the category.
And if nothing else, the electrified Highlander is a symbolic victory. After releasing an era-defining auto with the Prius hybrid, Toyota arguably had been the biggest heel-dragger about EVs among the major automakers. It waited while others acted; its leadership issued skeptical statements about battery power. Highlander’s arrival is a statement that those days are done. Weirdly, the game plan feels like an announcement from the go-go electrification days of the Biden administration — a huge automaker going out of its way to build an important EV in America.
If it succeeds, this could be the start of something big. Why not fully electrify the RAV4, whose gas-powered version sells in the hundreds of thousands in America every year?
Third Way’s latest memo argues that climate politics must accept a harsh reality: natural gas isn’t going away anytime soon.
It wasn’t that long ago that Democratic politicians would brag about growing oil and natural gas production. In 2014, President Obama boasted to Northwestern University students that “our 100-year supply of natural gas is a big factor in drawing jobs back to our shores;” two years earlier, Montana Governor Brian Schweitzer devoted a portion of his speech at the Democratic National Convention to explaining that “manufacturing jobs are coming back — not just because we’re producing a record amount of natural gas that’s lowering electricity prices, but because we have the best-trained, hardest-working labor force in the history of the world.”
Third Way, the long tenured center-left group, would like to go back to those days.
Affordability, energy prices, and fossil fuel production are all linked and can be balanced with greenhouse gas-abatement, its policy analysts and public opinion experts have argued in a series of memos since the 2024 presidential election. Its latest report, shared exclusively with Heatmap, goes further, encouraging Democrats to get behind exports of liquified natural gas.
For many progressive Democrats and climate activists, LNG is the ultimate bogeyman. It sits at the Venn diagram overlap of high greenhouse gas emissions, the risk of wasteful investment and “stranded” assets, and inflationary effects from siphoning off American gas that could be used by domestic households and businesses.
These activists won a decisive victory in the Biden years when the president put a pause on approvals for new LNG export terminal approvals — a move that was quickly reversed by the Trump White House, which now regularly talks about increases in U.S. LNG export capacity.
“I think people are starting to finally come to terms with the reality that oil and gas — and especially natural gas— really aren’t going anywhere,” John Hebert, a senior policy advisor at Third Way, told me. To pick just one data point: The International Energy Agency’s latest World Energy Outlook included a “current policies scenario,” which is more conservative about policy and technological change, for the first time since 2019. That saw the LNG market almost doubling by 2050.
“The world is going to keep needing natural gas at least until 2050, and likely well beyond that,” Hebert said. “The focus, in our view, should be much more on how we reduce emissions from the oil and gas value chain and less on actually trying to phase out these fuels entirely.”
The memo calls for a variety of technocratic fixes to America’s LNG policy, largely to meet demand for “cleaner” LNG — i.e. LNG produced with less methane leakage — from American allies in Europe and East Asia. That “will require significant efforts beyond just voluntary industry engagement,” according to the Third Way memo.
These efforts include federal programs to track methane emissions, which the Trump administration has sought to defund (or simply not fund); setting emissions standards with Europe, Japan, and South Korea; and more funding for methane tracking and mitigation programs.
But the memo goes beyond just a few policy suggestions. Third Way sees it as part of an effort to reorient how the Democratic Party approaches fossil fuel policy while still supporting new clean energy projects and technology. (Third Way is also an active supporter of nuclear power and renewables.)
“We don’t want to see Democrats continuing to slow down oil and gas infrastructure and reinforce this narrative that Democrats are just a party of red tape when these projects inevitably go forward anyway, just several years delayed,” Hebert told me. “That’s what we saw during the Biden administration. We saw that pause of approvals of new LNG export terminals and we didn’t really get anything for it.”
Whether the Democratic Party has any interest in going along remains to be seen.
When center-left commentator Matthew Yglesias wrote a New York Times op-ed calling for Democrats to work productively with the domestic oil and gas industry, influential Democratic officeholders such as Illinois Representative Sean Casten harshly rebuked him.
Concern over high electricity prices has made some Democrats a little less focused on pursuing the largest possible reductions in emissions and more focused on price stability, however. New York Governor Kathy Hochul, for instance, embraced an oft-rejected natural gas pipeline in her state (possibly as part of a deal with the Trump administration to keep the Empire Wind 1 project up and running), for which she was rewarded with the Times headline, “New York Was a Leader on Climate Issues. Under Hochul, Things Changed.”
Pennsylvania Governor Josh Shapiro (also a Democrat) was willing to cut a deal with Republicans in the Pennsylvania state legislature to get out of the Northeast’s carbon emissions cap and trade program, which opponents on the right argued could threaten energy production and raise prices in a state rich with fossil fuels. He also made a point of working with the White House to pressure the region’s electricity market, PJM Interconnection, to come up with a new auction mechanism to bring new data centers and generation online without raising prices for consumers.
Ruben Gallego, a Democratic Senator from Arizona (who’s also doing totally normal Senate things like having town halls in the Philadelphia suburbs), put out an energy policy proposal that called for “ensur[ing] affordable gasoline by encouraging consistent supply chains and providing funding for pipeline fortification.”
Several influential Congressional Democrats have also expressed openness to permitting reform bills that would protect oil and gas — as well as wind and solar — projects from presidential cancellation or extended litigation.
As Democrats gear up for the midterms and then the presidential election, Third Way is encouraging them to be realistic about what voters care about when it comes to energy, jobs, and climate change.
“If you look at how the Biden administration approached it, they leaned so heavily into the climate message,” Hebert said. “And a lot of voters, even if they care about climate, it’s just not top of mind for them.”
Current conditions: A foot of snow piled up on Hawaii's mountaintops • Fresh snow in parts of the Northeast’s highlands, from the New York Adirondacks to Vermont’s Green Mountains, could top 10 inches • The seismic swarm that rattled Iceland with more than 600 relatively low-level earthquakes over the course of two days has finally subsided.
Say what you will about President Donald Trump’s cuts to electric vehicles, renewables, and carbon capture, the administration has given the nuclear industry red-carpet treatment. The Department of Energy refashioned its in-house lender into a financing hub for novel nuclear projects. After saving the Biden-era nuclear funding from the One Big Beautiful Bill Act’s cleaver, the agency distributed hundreds of millions of dollars to specific small modular reactors and rolled out testing programs to speed up deployment of cutting-edge microreactors. The Department of Commerce brokered a deal with the Japanese government to provide the Westinghouse Electric Company with $80 billion to fund construction of up to 10 large-scale AP1000 reactors. But still, in private, I’m hearing from industry sources that utilities and developers want more financial protection against bankruptcy if something goes wrong. My sources tell me the Trump administration is resistant to providing companies with a blanket bailout if nuclear construction goes awry. But legislation in the Senate could step in to provide billions of dollars in federal backing for over-budget nuclear reactors. Senator Jim Risch, an Idaho Republican, previously introduced the Accelerating Reliable Capacity Act in 2024 to backstop nuclear developers still reeling from the bankruptcies associated with the last AP1000 buildout. This time, as E&E News noted, “he has a prominent Democrat as a partner.” Senator Ruben Gallego, an Arizona Democrat who stood out in 2024 by focusing his campaign’s energy platform on atomic energy and just recently put out an energy strategy document, co-sponsored the bill, which authorizes up to $3.6 billion to help offset cost overruns at three or more next-generation nuclear projects.
Nuclear generation set a new global record in 2025, the International Energy Agency said in its latest electricity outlook published last Friday. That’s largely thanks to Japan restarting reactors idled after Fukushima, France ramping up generation at its fleet, and China and India opening new plants. By 2030, however, China will account for 40% of the global increase in nuclear generation. You can see the difference in the growth rate already. Nuclear power worldwide is on track to grow by an average of 2.8% per year, more than double the 1.3% pace of the previous four years. China’s nuclear capacity, by contrast, will grow by an average of 6% per year through the end of the decade.
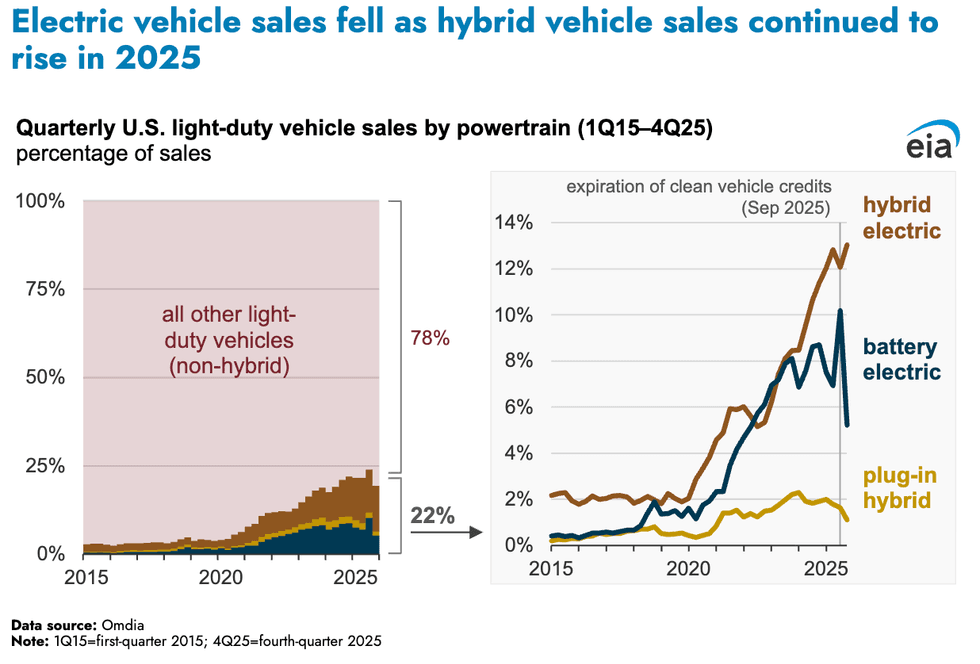
Roughly 22% of light-duty vehicles sold last year in the U.S. were hybrid and battery electric, up from 20% in 2024. While sales of battery-powered vehicles have fallen, demand for hybrids has only increased, according to estimates from the research firm Omdia that the U.S. Energy Information Administration highlighted in a new analysis. Electric vehicles accounted for just 2% of all registered light-duty vehicles on U.S. roads in 2024, the most recent year for which annual data is available. Sales for 2025 will show a spike, especially around September when Americans rushed to cash in on electric vehicle tax credits before Trump’s phaseout took effect.
The Department of Transportation, meanwhile, proposed boosting the domestic content requirements for federally funded electric vehicle charging stations from 55% to 100%. The Biden administration had waived some “Buy American” requirements for the $5 billion federal program to fund the infrastructure buildout. The proposal would set steep hurdles for projects, likely slowing the rollout of chargers. The agency, Reuters reported, said it believes it must “protect Americans from foreign-made EV charger components that use technology with cybersecurity vulnerabilities.”
Sign up to receive Heatmap AM in your inbox every morning:
Equinor is scaling back its near-term investments in carbon capture and sequestration projects as prices go up and customer demand stagnates. Despite its reputation as what the Carbon Herald called “one of the global standard-bearers for carbon capture and storage,” the Norwegian energy giant said the commercial conditions needed to justify more large-scale investments in carbon pipelines and wells were not yet there. CEO Anders Opedal said during the company’s latest earnings call that, because CCS markets were growing more slowly than previously thought, Equinor would hold off on committing more capital to new projects.
CCS had something of a moment last fall when Google agreed to finance construction of a gas plant equipped with carbon capture technology, as Heatmap’s Matthew Zeitlin wrote. But Trump’s plan to go for the climate killshot, repealing the legal underpinning of all federal regulations on planet-heating emissions, would really dampen demand for CCS in the U.S.
The new U.S.-India trade deal that will lower tariffs on Indian goods to 18% from 25% is set to bolster the country’s booming solar manufacturing industry. The pact represents what Prashant Mathur, chief executive of the solar manufacturer Saatvik Green Energy, described to PV-Tech as a “strategic turning point.” Cutting tariffs by seven percentage points “materially improves cost competitiveness, making U.S. projects more profitable and creating new demand for high-efficiency, Made-in-India products.” Gyanesh Chaudhary, the managing director of Vikram Solar, called the deal a “structural inflection point.” But the trade agreement won’t fix all the problems for Indian solar exporters. New restrictions known as Section 232 tariffs, which raise prices on imports that threaten national security by undercutting domestic manufacturers, are expected to come into effect on India’s exports of polysilicon. A separate antidumping and countervailing duty investigation into whether India is unfairly flooding the U.S. market with cheap crystalline silicon solar cells called for a duty of 123.04%, though nothing has yet been imposed.
The Trump administration, meanwhile, is setting the stage for more coal in the U.S. On Wednesday, according to Bloomberg, Trump plans to sign an executive order directing the military to buy more power from coal-fired plants in a bid to prop up the sector.
Despite Trump’s best attempts to stop it, Orsted is finishing its offshore wind farms in New England and, after that, is expected to save its money for new projects overseas. In its native Europe, the energy giant is preparing for a big multinational buildout in the North Sea. Now the Danish developer is charging ahead in a new market. Australia does not have any operating offshore wind farms. But Orsted just submitted an application for an environmental review of a 2.8 gigawatt project proposed off the coast of Gippsland, Victoria. Together with a second site Orsted started lining up in 2024, the area could host a combined 4.8 gigawatts of turbine capacity, according to Renewables Now.
Yet another fusion energy startup has officially entered the race. Inertia Enterprises, a fusion startup aimed at mimicking the technology that managed for the first time in history to generate more energy than it took to start the reaction, has raised $450 million in a Series A round. The venture firm Bessemer Venture Partners led the round, with backing from Google Ventures, Modern Capital, and Threshold Ventures. “Inertia is building on decades of science and billions of dollars invested to reach the ignition milestone that proved the science,” Jeff Lawson, the co-founder and chief executive of Inertia, said in a statement.